* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carboxylic acid
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
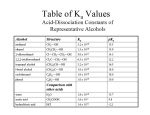
Carboxylic acid Introduction • Carboxylic acids are compounds containing O the carboxyl group, RCOOH C OH • A carboxyl group contains a carbonyl group, C=O, present in aldehydes and ketones. And a hydroxyl group, -OH present in alcohols. However the two groups influence and change the properties of each other. Nomenclature of carboxylic acids • Carboxylic acids are named by replacing the – e of the coressponding alkane by –oic followed by the acid. For example, O O H C OH methanoic acid H3C C OH ethanoic acid H3C CH3 CH3 O C H C H C OH 2,3-dimethylbutanoic acid Name the following (a) (c) O H2 C H3C (b) H2C Cl C CH3 O C H C OH H3C (d) OH H3C OH O C H C CH3 O C H C OH OH Physical Properties of Carboxylic Acids • Carboxylic acids are very polar due to both the carbonyl group and the hydroxyl group • Carboxylic acids can H-bond with each other, and in fact exist primarily of dimers (two molecules held together by H-bonding) • Because of the above properties, carboxylic acids have high boiling points (higher than corresponding alcohols) • Those with less than 5 carbons are soluble in water - those with more than 5 C’s can be soluble when ionized O C + - H O O H + O H O O O O Na carboxylic acids are more soluble in water than are alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, and ketones of comparable molecular weight Preparation of COOH 1. Oxidation of primary alcohol • When primary alcohol is heated under reflux with a solution of potassium manganate (VII) or sodium dichromate (VI), the carboxylic acid is formed. O R H2 C OH KMnO4 reflux R C OH + H2O O H3C H2 C OH KMnO4 reflux H3C C OH + H2O 2. Oxidation of aldehyde • The reagents and conditions are the same as those for the oxidation of primary alcohols given above. O R C O H KMnO4 reflux R O H3C C C OH O H KMnO4 reflux H3C C OH 3. Hydrolysis of nitriles • When a nitrile is heated under reflux with dilute H2SO4, it is hydrolysed to the carboxylic acid. O R C N + 2 H2O + H+ dilute H2SO4 R C OH + NH4+ O H3C C N ethanenitrile + 2 H2O + H+ dilute H2SO4 H3C C OH ethanoic acid + NH4+ 4. Hydrolysis of ester • When an ester is heated with an aqueos alkali, sodium hydroxide, the alcohol is liberated and the acid is left as the sodium salt. O O H3C C O + NaOH R' heat H3C C O- Na+ + R' OH • The acid can be obtained by distilling the sodium salt with an acid. O O dilute H2SO4 + H3C C - + O Na sodium ethanoate H+ heat H3C C ethanoic acid OH + Na+ 5. Oxidation of alkyl benzene • When an alkyl benzene is heated under reflux with a solution of potassium manganate (VII) acidified with dilute H2SO4 , benzoic acid is formed. CH3 KMnO4 heat COOH Exercise 1. Write equation for the following reactions. (a) Ethanol is heated with acidified KMnO4 (b) Ethanal is heated with acidied KMnO4 (c) Propylbenzene is refluxed with acidified KMnO4 (d) Ethanenitrile is heated with dilute HCl Chemical reactions 1. React with bases or alkalis to form salts R COOH + NaOH R COO- Na+ + H2O 2. React with PCl5 or SOCl2 at room temperature to form acyl chlorides R COOH + PCl5 R COCl + POCl3 + HCl R COOH + SOCl2 R COCl + SO2 + HCl Acid Chlorides from RCOOH Reaction with Thionyl Chloride Reaction with Phosphorus Trichloride Reaction with Phosphorus Pentachloride RCOOH 3 RCOOH RCOOH SOCl 2 PCl 3 PCl 5 R C Cl + SO 2 + HCl O 3R C Cl + H 3PO 3 O R C O Cl + POCl 3 + HCl 3. React with alcohols in the presence of concentrated H2SO4 to form esters. COOH + R' R OH R COOR' + H2O 4. Reduction – React with LiAlH4 to form primary alcohols R COOH + 4 [H] LiAlH4 RCH2OH + H2O 5. React with electropositive metals to form salts and H2 gas. O R COOH + K R C O- K+ + 1/2 H2 6. Ammonium salts of carboxylic acids undergo dehydration to form amides. O O R C O- NH4+ R C amides NH2 + H2O THANK YOU..