Exames anteriores a 1994
... occur in the cells. Note: PtCl2(NH3)2 hydrolyses to Pt(NH3)2(H2O)22+ and 2 Cl-. In cells the Cl- concentration is low, in blood it is fairly high. After hydrolysis in the tumour cell a reactive platinum ion is formed to which two NH3 groups are still bound, which were found in the urine of patients ...
... occur in the cells. Note: PtCl2(NH3)2 hydrolyses to Pt(NH3)2(H2O)22+ and 2 Cl-. In cells the Cl- concentration is low, in blood it is fairly high. After hydrolysis in the tumour cell a reactive platinum ion is formed to which two NH3 groups are still bound, which were found in the urine of patients ...
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
... on the mechanism are currently under investigation [16]. All data points to a sequence of aminometallation followed by a second alkyl-nitrogen bond formation. No radical intermediates are involved in the overall process as selective deuteration at the terminal position of the alkene leads to diaster ...
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones – Nucleophilic Addition
... C4. The Aldol Addition The two-step process (aldol addition plus dehydration) is called an aldol condensation. It is possible to carry out an aldol reaction between two different carbonyl compounds. Such reactions are called crossed or mixed aldol reactions. It requires that only one of the reactant ...
... C4. The Aldol Addition The two-step process (aldol addition plus dehydration) is called an aldol condensation. It is possible to carry out an aldol reaction between two different carbonyl compounds. Such reactions are called crossed or mixed aldol reactions. It requires that only one of the reactant ...
International Indian School Dammam
... (i) Electronic configuration (ii) Variability in oxidation state (b) Account for the following: (i) Transition elements possess high enthalpy of atomization. (ii) Lower oxides of transition elements are basic while higher oxides are acidic. (iii) Sodium dichromate is preferred to potassium dichromat ...
... (i) Electronic configuration (ii) Variability in oxidation state (b) Account for the following: (i) Transition elements possess high enthalpy of atomization. (ii) Lower oxides of transition elements are basic while higher oxides are acidic. (iii) Sodium dichromate is preferred to potassium dichromat ...
Carboxylic Acids and Esters
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain the carboxyl group (COOH). The carboxyl group is always on a terminal carbon atom. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, since only a small fraction of acid molecules ionize when dissolved in water. They give up the hydrogen on the car ...
... CARBOXYLIC ACIDS Carboxylic acids are organic compounds that contain the carboxyl group (COOH). The carboxyl group is always on a terminal carbon atom. Carboxylic acids are weak acids, since only a small fraction of acid molecules ionize when dissolved in water. They give up the hydrogen on the car ...
IN VITRO Research Article S. NITHIYA *, N. KARTHIK
... Department of Chemistry, Periyar University, Salem, India, 2Department of Chemistry, Rajalakshmi Engineering College , Chennai, India. 3Department of Chemistry, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, India. Email: [email protected] ...
... Department of Chemistry, Periyar University, Salem, India, 2Department of Chemistry, Rajalakshmi Engineering College , Chennai, India. 3Department of Chemistry, Annamalai University, Annamalai Nagar, India. Email: [email protected] ...
INFRARED SPECTROSCOPY PURDUE UNIVERSITY
... The emphasis in this experiment is on the methods of organic qualitative analysis. Nevertheless, a brief discussion of the properties and molecular structures of the substances to be tested should prove useful. Organic compounds are often defined as those substances containing carbon; most contain h ...
... The emphasis in this experiment is on the methods of organic qualitative analysis. Nevertheless, a brief discussion of the properties and molecular structures of the substances to be tested should prove useful. Organic compounds are often defined as those substances containing carbon; most contain h ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
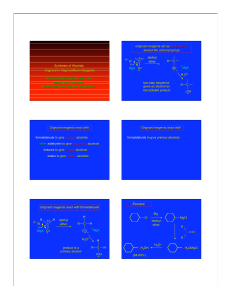
... Factors affecting the geometry of a coordination compound 1) Prediction can be difficult 2) VSEPR usually is a good first approximation; don’t count the d-electrons 3) Maximize the number of bonds (more bonds = more stable) 4) Occupancy of the d-orbitals (Chapter 10) 5) Steric interference by large ...
... Factors affecting the geometry of a coordination compound 1) Prediction can be difficult 2) VSEPR usually is a good first approximation; don’t count the d-electrons 3) Maximize the number of bonds (more bonds = more stable) 4) Occupancy of the d-orbitals (Chapter 10) 5) Steric interference by large ...
CHEMISTRY OF CARBOHYDRATES
... glycosidic bond So there are no free carbonyl groups Such sugars are called non-reducing sugars They do NOT reduce Benedict’s reagent ...
... glycosidic bond So there are no free carbonyl groups Such sugars are called non-reducing sugars They do NOT reduce Benedict’s reagent ...
The Shale Gas Revolution: A Methane-to
... technolog is needed to utilize tili e all components of shale gas for organic chemical production? EES — 15 ...
... technolog is needed to utilize tili e all components of shale gas for organic chemical production? EES — 15 ...
CHEMISTRY OF CARBOHYDRATES
... glycosidic bond So there are no free carbonyl groups Such sugars are called non-reducing sugars They do NOT reduce Benedict’s reagent ...
... glycosidic bond So there are no free carbonyl groups Such sugars are called non-reducing sugars They do NOT reduce Benedict’s reagent ...
Assessment Statements-Chem HL Topics 1-20
... Exceptions to the principle for copper and chromium should be known. You should be familiar with orbital box diagrams and the use of up/down arrows to show spinning electrons. ...
... Exceptions to the principle for copper and chromium should be known. You should be familiar with orbital box diagrams and the use of up/down arrows to show spinning electrons. ...
Synthesis and characterization of inorganic complexes
... e.g. Ti(IV), V(V) (high valent); hard metal ions (binds to hard ligands) Late TM : low metal oxidation state, e.g. Pt(II), Au(I) (low valent); soft metal ions (binds to soft ligands) 93-92 نیم سال اول ...
... e.g. Ti(IV), V(V) (high valent); hard metal ions (binds to hard ligands) Late TM : low metal oxidation state, e.g. Pt(II), Au(I) (low valent); soft metal ions (binds to soft ligands) 93-92 نیم سال اول ...
enespp - Knockhardy
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
... This Powerpoint show is one of several produced to help students understand selected topics at AS and A2 level Chemistry. It is based on the requirements of the AQA and OCR specifications but is suitable for other examination boards. Individual students may use the material at home for revision purp ...
Topic 10.4 Organic Chemistry Alcohols
... The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they -- have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water -- dissolve in water to some degree -- are more polar than hydrocarbons but less polar than water ...
... The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they -- have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water -- dissolve in water to some degree -- are more polar than hydrocarbons but less polar than water ...
Derivatization of polar compounds for GC - Sigma
... •Reaction mechanism: nucleophilic attack on the silicon atom in the silylating reagent •For completion of the reaction, the basicity of the leaving group on the silyating reagent (X), must be greater than the group to be replaced on the sample •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: ...
... •Reaction mechanism: nucleophilic attack on the silicon atom in the silylating reagent •For completion of the reaction, the basicity of the leaving group on the silyating reagent (X), must be greater than the group to be replaced on the sample •Ease of silylation generally follows this trend: ...
Basic Organic Chemistry Laboratory Course
... precipitate which is insoluble in nitric acid confirms the presence of halogen. If this test is positive, the halogens present are identified according to the following tests. Place a second sample of the ...
... precipitate which is insoluble in nitric acid confirms the presence of halogen. If this test is positive, the halogens present are identified according to the following tests. Place a second sample of the ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.