Use the following answers for questions 10
... 35. The addition of an oxidizing agent such as chlorine water to a clear solution of an unknown compound results in the appearance of a brown color. When this solution is shaken with the organic solvent, methylene dichloride, the organic solvent layer turns purple. The unknown compound probably cont ...
... 35. The addition of an oxidizing agent such as chlorine water to a clear solution of an unknown compound results in the appearance of a brown color. When this solution is shaken with the organic solvent, methylene dichloride, the organic solvent layer turns purple. The unknown compound probably cont ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... • They are often drawn to look like alkenes, but they behave much differently than alkenes. • They have an alternating pattern of double and single bonds within a ring. • Benzene is an example ...
... • They are often drawn to look like alkenes, but they behave much differently than alkenes. • They have an alternating pattern of double and single bonds within a ring. • Benzene is an example ...
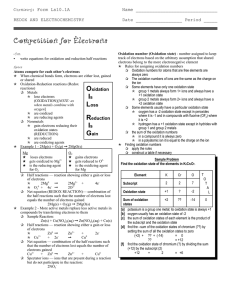
Competition for Electrons
... q Net equation — combination of the half reactions such that the number of electrons lost equals the number of electrons gained Cu2+ + Zn0 ! Zn2+ ...
... q Net equation — combination of the half reactions such that the number of electrons lost equals the number of electrons gained Cu2+ + Zn0 ! Zn2+ ...
Lecture 3 Polar and non-polar covalent bonds
... The three major types of bonding found in most compounds are ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. • An ionic bond is the transfer of electrons. • A covalent bond is the sharing of electrons. • A polar covalent bond is between atoms of different electronegativity. • A nonpolar covalent ...
... The three major types of bonding found in most compounds are ionic, polar covalent, and nonpolar covalent bonds. • An ionic bond is the transfer of electrons. • A covalent bond is the sharing of electrons. • A polar covalent bond is between atoms of different electronegativity. • A nonpolar covalent ...
one of the tasks (coordination chemistry)
... principle when the examples have been presented to them but their understanding is challenged more deeply if they are required to identify examples of a principle from a range of possibilities. In such a case, one also needs to be able to identify non-examples and to recognise why they are non-examp ...
... principle when the examples have been presented to them but their understanding is challenged more deeply if they are required to identify examples of a principle from a range of possibilities. In such a case, one also needs to be able to identify non-examples and to recognise why they are non-examp ...
Reaction Stoichiometry
... production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, dyes, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine. C6H6(l) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl(l) + HCl(g) When 36.8 g benzene react with an excess of Cl2, the actual yield of chlorobenzene is 38. ...
... production of many important chemicals, such as aspirin, dyes, and disinfectants. One industrial method of preparing chlorobenzene is to react benzene, C6H6, with chlorine. C6H6(l) + Cl2(g) → C6H5Cl(l) + HCl(g) When 36.8 g benzene react with an excess of Cl2, the actual yield of chlorobenzene is 38. ...
Coordination Compounds
... 2. Structural isomerism: same chemical formula but possess different types of bonds , differ in the extent of ionization, position of ligands, etc. These are further classified as follows: (i) Linkage isomerism: It arises in the coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligands. An ambidentate l ...
... 2. Structural isomerism: same chemical formula but possess different types of bonds , differ in the extent of ionization, position of ligands, etc. These are further classified as follows: (i) Linkage isomerism: It arises in the coordination compounds containing ambidentate ligands. An ambidentate l ...
Problem 14. MAGNESIUM DETERMINATION
... Problem 1. ON THE BORDERS OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM.................................................................................................. 3 Problem 2. SCHRÖDINGER CAT AND CHEMISTRY .............................................................................................................. ...
... Problem 1. ON THE BORDERS OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM.................................................................................................. 3 Problem 2. SCHRÖDINGER CAT AND CHEMISTRY .............................................................................................................. ...
Alkanes
... Alkanes don’t react with acids, bases, or most other common laboratory reagents. Their only major reactions are with oxygen and with halogens. Combustion: Reaction of alkanes with oxygen. Carbon dioxide and water are produced in this combustion reaction. Halogenation reaction: Replacement of a hydro ...
... Alkanes don’t react with acids, bases, or most other common laboratory reagents. Their only major reactions are with oxygen and with halogens. Combustion: Reaction of alkanes with oxygen. Carbon dioxide and water are produced in this combustion reaction. Halogenation reaction: Replacement of a hydro ...
Alcohols
... • Anisole is a pleasant-smelling aromatic ether used in perfumery • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a cyclic ether that is often used as a solvent • Thiols and sulfides are found in various biomolecules ...
... • Anisole is a pleasant-smelling aromatic ether used in perfumery • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a cyclic ether that is often used as a solvent • Thiols and sulfides are found in various biomolecules ...
Development of Multi-Component Reactions using Catalytically Generated Allyl Metal Reagents
... metal catalysis is a powerful combination of synthetic efficiency and highly selective transformations. Since the catalytically generated intermediates (such as organometallic compounds) need not to be isolated, but react with other components present in the reaction mixture, cumbersome purification ...
... metal catalysis is a powerful combination of synthetic efficiency and highly selective transformations. Since the catalytically generated intermediates (such as organometallic compounds) need not to be isolated, but react with other components present in the reaction mixture, cumbersome purification ...
Carboxylic Acids
... room temperature. The liquids have sharp pungent odours and all have high boiling points. Smaller molecules, less than 10 carbons, are completely miscible in water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with the water. The highly polar carboxylic acids dimerise in the liquid phase and in nonaqueous ...
... room temperature. The liquids have sharp pungent odours and all have high boiling points. Smaller molecules, less than 10 carbons, are completely miscible in water due to the formation of hydrogen bonds with the water. The highly polar carboxylic acids dimerise in the liquid phase and in nonaqueous ...
Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
... years. Ethers are significant solvents and synthetic important supplements for the production of fragrances, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and dyestuffs [1,2]. The Williamson reaction is the best technique for the synthesis of symmetrical and unsymmetrical ethers. The Williamson reaction generally inv ...
Polyethylene
... Resists alcohols, acids, bases, esters, and aldehydes Specific Gravity: 0.94 to 0.97 Melting point 130 to 135 deg C Carbon chains can are 10,000 to 100,000 carbon ...
... Resists alcohols, acids, bases, esters, and aldehydes Specific Gravity: 0.94 to 0.97 Melting point 130 to 135 deg C Carbon chains can are 10,000 to 100,000 carbon ...
CHEM 242 Organic Chemistry II-Bender
... There are no excused absences. Labs will be graded by quiz or a brief summary of the lab. Practice in running organic reaction mechanisms is the main goal of the laboratory exercises. Lab reports are due at the beginning of the next lab class. You are expected to have pre-lab information completed p ...
... There are no excused absences. Labs will be graded by quiz or a brief summary of the lab. Practice in running organic reaction mechanisms is the main goal of the laboratory exercises. Lab reports are due at the beginning of the next lab class. You are expected to have pre-lab information completed p ...
Methylcyclohexane + bromine and heat = 1-bromo-1
... with the alcohol and get the product shown. Then separate the trans isomers. There are other ways to make this product, but given the starting materials, this is pretty much the only way. The borane/THF step is important if you want the stereo-correct product; -2 points for using a different method. ...
... with the alcohol and get the product shown. Then separate the trans isomers. There are other ways to make this product, but given the starting materials, this is pretty much the only way. The borane/THF step is important if you want the stereo-correct product; -2 points for using a different method. ...
STUDY GUIDE
... multiple bonds, and they are more reactive than alkanes. They may participate in addition reactions, including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration. A naming scheme has been established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to name the organic comp ...
... multiple bonds, and they are more reactive than alkanes. They may participate in addition reactions, including hydrogenation, halogenation, hydrohalogenation, and hydration. A naming scheme has been established by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) to name the organic comp ...
Overview in PDF format
... species in the reaction of zirconocene complex with MAO regardless of the leaving ligands. The same result, but with different active species, was obtained in the reaction of zirconocene with [Me2HNPh]+[B(C6F5)4]-/TIBA: leaving ligands did not significantly affect the structure of the active species ...
... species in the reaction of zirconocene complex with MAO regardless of the leaving ligands. The same result, but with different active species, was obtained in the reaction of zirconocene with [Me2HNPh]+[B(C6F5)4]-/TIBA: leaving ligands did not significantly affect the structure of the active species ...
Biodiesel Production and Fuel Quality_JVG
... solubility of glycerol in the esters, this separation generally occurs quickly and may be accomplished with either a settling tank or a centrifuge. The excess methanol tends to act as a solubilizer and can slow the separation. However, this excess methanol is usually not removed from the reaction st ...
... solubility of glycerol in the esters, this separation generally occurs quickly and may be accomplished with either a settling tank or a centrifuge. The excess methanol tends to act as a solubilizer and can slow the separation. However, this excess methanol is usually not removed from the reaction st ...
Prelab Assignment: The lodination of Acetone
... the reaction will give you information about the order of the reaction with respect to H+. Repeat the experiment with this mixture to establish the time of reaction to within 15 seconds, again making sure that the temperature is within about a degree of that observed previously. From the rate you de ...
... the reaction will give you information about the order of the reaction with respect to H+. Repeat the experiment with this mixture to establish the time of reaction to within 15 seconds, again making sure that the temperature is within about a degree of that observed previously. From the rate you de ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.