Unit-I_Coordination_Chemistry_part_2_full
... The coordination compounds differ largely from double salts. As the double salts tend to retain their identity even in solution, the properties of complexes are entirely different from those of the constituents. A ligand that is capable of forming one coordinate covalent bond to the nuclear atom is ...
... The coordination compounds differ largely from double salts. As the double salts tend to retain their identity even in solution, the properties of complexes are entirely different from those of the constituents. A ligand that is capable of forming one coordinate covalent bond to the nuclear atom is ...
alcohols - GC12chem
... with the OH group attached is attached to two other C atoms CH3CH2CHOHCH3 Tertiary alcohol: the C atom with the OH group attached is attached to three other C atoms CH3CH2C(CH3)OHCH3 12 Chemistry 2.5 organic chemistry CR 07 ...
... with the OH group attached is attached to two other C atoms CH3CH2CHOHCH3 Tertiary alcohol: the C atom with the OH group attached is attached to three other C atoms CH3CH2C(CH3)OHCH3 12 Chemistry 2.5 organic chemistry CR 07 ...
Organic Compounds
... Models are often used by chemists to visualize molecular structures. Structural differences between functional groups provide reasons for differences in chemical reactivity. In preparation for this laboratory exercise, review the sections in your text book pertaining to molecular structure of compou ...
... Models are often used by chemists to visualize molecular structures. Structural differences between functional groups provide reasons for differences in chemical reactivity. In preparation for this laboratory exercise, review the sections in your text book pertaining to molecular structure of compou ...
Acidity of Alcohols
... • Yeast is killed by ethanol concentrations in excess of about 15%, and that limits the purity of the ethanol that can be produced. The ethanol is separated from the mixture by fractional distillation to give 96% pure ethanol. • For theoretical reasons, it is impossible to remove the last 4% of wate ...
... • Yeast is killed by ethanol concentrations in excess of about 15%, and that limits the purity of the ethanol that can be produced. The ethanol is separated from the mixture by fractional distillation to give 96% pure ethanol. • For theoretical reasons, it is impossible to remove the last 4% of wate ...
Some chemistry of the Periodic Table Electronic configuration and
... them to explain why zinc and scandium are often regarded as not being transition metals. Oxidation states In ionic compounds the oxidation number is equal to the charge on the ion in a compound. For example, in iron(II) chloride, Fe2+(Cl-)2, iron is in oxidation state +2 and in iron(III) chloride, F ...
... them to explain why zinc and scandium are often regarded as not being transition metals. Oxidation states In ionic compounds the oxidation number is equal to the charge on the ion in a compound. For example, in iron(II) chloride, Fe2+(Cl-)2, iron is in oxidation state +2 and in iron(III) chloride, F ...
Chapter 19 C-H Bond Activation with Neutral Platinum Methyl
... Four coordinate platinum methyl complexes 13-19 were prepared by a similar salt metathesis route from PtMeCl(SMe2)2 10 or via protonolysis of a methyl group in [PtMe2(µ-SR2)]2 (11, R = Me; 12, R= Et) by the N-H bond of the neutral ligand (Eqs. 4-9). With the exception of the bulky 2,6diisopropylphen ...
... Four coordinate platinum methyl complexes 13-19 were prepared by a similar salt metathesis route from PtMeCl(SMe2)2 10 or via protonolysis of a methyl group in [PtMe2(µ-SR2)]2 (11, R = Me; 12, R= Et) by the N-H bond of the neutral ligand (Eqs. 4-9). With the exception of the bulky 2,6diisopropylphen ...
Mixed ligand transition metal(II) complexes of Knoevenagel
... mol)/ HEOA ( 1. 17 g, 0.005 mol)/HPO B( 1405 g. 0.005 Illol)] was stirred with th e eth anolic .;;oluti on (5 mL ) of copper ch loride (0.670 g, 0.005 M) fo r ca. 5 h. To th e above mixture, an ethanolic soluti on (5 mL) of 1,2-dialllinobenzene ( 1.08 g, 0.0 I mol) was added . and the stirring was c ...
... mol)/ HEOA ( 1. 17 g, 0.005 mol)/HPO B( 1405 g. 0.005 Illol)] was stirred with th e eth anolic .;;oluti on (5 mL ) of copper ch loride (0.670 g, 0.005 M) fo r ca. 5 h. To th e above mixture, an ethanolic soluti on (5 mL) of 1,2-dialllinobenzene ( 1.08 g, 0.0 I mol) was added . and the stirring was c ...
Lecture 2
... Most convenient to use a local coordinate system on each ligand with y pointing in towards the metal. py to be used for s bonding. z being perpendicular to the molecular plane. pz to be used for p bonding perpendicular to the plane, p^. x lying in the molecular plane. px to be used for p bonding in ...
... Most convenient to use a local coordinate system on each ligand with y pointing in towards the metal. py to be used for s bonding. z being perpendicular to the molecular plane. pz to be used for p bonding perpendicular to the plane, p^. x lying in the molecular plane. px to be used for p bonding in ...
Buffers Made Easy
... • Acid-base reactions may change NH3 into NH4+ (or vice versa) which will alter its ability to act as a ligand. • Visually, a precipitate may go back into solution as a complex ion is formed. For example, Cu2+ + a little NH4OH will form the light blue precipitate, Cu(OH)2. With excess ammonia, the c ...
... • Acid-base reactions may change NH3 into NH4+ (or vice versa) which will alter its ability to act as a ligand. • Visually, a precipitate may go back into solution as a complex ion is formed. For example, Cu2+ + a little NH4OH will form the light blue precipitate, Cu(OH)2. With excess ammonia, the c ...
1. For all complexes listed below, determine a) metal oxidation state
... PF3 and P(OCH3)3 have similar cone angles (100‐105). PF3 is more electron withdrawing due to the greater electronegativity of the F atom which lowers the PF ‐accepting orbital. This reduces ‐back donation to the trans CO ligand resulting in a larger CO bond order and a higher frequency v(C ...
... PF3 and P(OCH3)3 have similar cone angles (100‐105). PF3 is more electron withdrawing due to the greater electronegativity of the F atom which lowers the PF ‐accepting orbital. This reduces ‐back donation to the trans CO ligand resulting in a larger CO bond order and a higher frequency v(C ...
Chapter 13, sections 13.5 - Properties of Aldehydes and Ketones
... • The polar carbonyl group provides dipole-dipole interactions. ...
... • The polar carbonyl group provides dipole-dipole interactions. ...
- Wiley Online Library
... The ORCID identification number for an author of this article can be found under http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201606701. ...
... The ORCID identification number for an author of this article can be found under http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/anie.201606701. ...
Oxidative addition of methane and benzene C–H bonds
... this step could be achieved with irradiation. For H–CH3 oxidative addition a sigma Rh complex (3) is directly obtained, while for H–C6H5 oxidative addition a more stable g2-arene Rh complex (3 0 ) is first formed and then the corresponding sigma Rh complex (4 0 ) is obtained via the transition state ...
... this step could be achieved with irradiation. For H–CH3 oxidative addition a sigma Rh complex (3) is directly obtained, while for H–C6H5 oxidative addition a more stable g2-arene Rh complex (3 0 ) is first formed and then the corresponding sigma Rh complex (4 0 ) is obtained via the transition state ...
Document
... The reaction vessel cools. Heat is absorbed. Energy is added to the system. q is positive. In an exothermic reaction: The reaction vessel warms. Heat is evolved. Energy is subtracted from the system. q is negative. ...
... The reaction vessel cools. Heat is absorbed. Energy is added to the system. q is positive. In an exothermic reaction: The reaction vessel warms. Heat is evolved. Energy is subtracted from the system. q is negative. ...
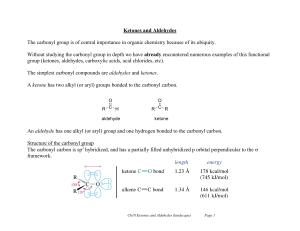
Ketones and Aldehydes
... Hydration of alkynes can either be achieved with Markovnikov (acid and mercury (II) catalyzed reaction) or anti-Markovnikov (hydroboration-oxidation) regiochemistry. ...
... Hydration of alkynes can either be achieved with Markovnikov (acid and mercury (II) catalyzed reaction) or anti-Markovnikov (hydroboration-oxidation) regiochemistry. ...
Organic Synthesis II
... Mechanisms for many oxidation reactions (even well-known ones) are significantly more complex than drawn throughout this course (and in many cases are not known or understood). Some are based on factual mechanistic data; some should be treated more as a mnemonic than explanation. ...
... Mechanisms for many oxidation reactions (even well-known ones) are significantly more complex than drawn throughout this course (and in many cases are not known or understood). Some are based on factual mechanistic data; some should be treated more as a mnemonic than explanation. ...
Experiment #8 – properties of Alcohols and Phenols
... This test is used to distinguish among primary, secondary, and tertiary watersoluble alcohols. Lucas reagent is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride. Zinc chloride is a Lewis acid, which when added to hydrochloric acid makes it even more acidic. Water soluble tertiary alcoho ...
... This test is used to distinguish among primary, secondary, and tertiary watersoluble alcohols. Lucas reagent is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride. Zinc chloride is a Lewis acid, which when added to hydrochloric acid makes it even more acidic. Water soluble tertiary alcoho ...
Chelating agents are ligands for metals that bind via
... Virtually all biochemicals exhibit the ability to dissolve certain metal cations. Thus, proteins, polysaccharides, and polynucleic acids are excellent polydentate ligands for many metal ions. Organic compounds such as the amino acidsglutamic acid and histidine, organic diacids such as malate, and po ...
... Virtually all biochemicals exhibit the ability to dissolve certain metal cations. Thus, proteins, polysaccharides, and polynucleic acids are excellent polydentate ligands for many metal ions. Organic compounds such as the amino acidsglutamic acid and histidine, organic diacids such as malate, and po ...
Chapter 18 Ketones and Aldehydes
... • Good solvent for alcohols. • Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from O-H or N-H. • Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in water. ...
... • Good solvent for alcohols. • Lone pair of electrons on oxygen of carbonyl can accept a hydrogen bond from O-H or N-H. • Acetone and acetaldehyde are miscible in water. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.