Chemistry 30: Organic Chemistry * An Introduction
... another. In linked questions, the answer from one question is used to complete the next question. If you answer the first question incorrectly but use that answer correctly to answer the second question, you will still receive full marks for the second question The examination is 2.5 hours in length ...
... another. In linked questions, the answer from one question is used to complete the next question. If you answer the first question incorrectly but use that answer correctly to answer the second question, you will still receive full marks for the second question The examination is 2.5 hours in length ...
Year End Practice Diploma2010_11
... another. In linked questions, the answer from one question is used to complete the next question. If you answer the first question incorrectly but use that answer correctly to answer the second question, you will still receive full marks for the second question The examination is 2.5 hours in length ...
... another. In linked questions, the answer from one question is used to complete the next question. If you answer the first question incorrectly but use that answer correctly to answer the second question, you will still receive full marks for the second question The examination is 2.5 hours in length ...
Revista Portuguesa Química - Sociedade Portuguesa de Química
... the complex to a pyridinone (wherein a nitrogen replaces the ring O) the water solubility decreases. BMOV can be prepared on a large scale (up to 0.5 kg) simply by combining vanadyl sulphate with maltol at roughly neutral pH, to give a 95% yield, quite pure (14). Some properties of interest include ...
... the complex to a pyridinone (wherein a nitrogen replaces the ring O) the water solubility decreases. BMOV can be prepared on a large scale (up to 0.5 kg) simply by combining vanadyl sulphate with maltol at roughly neutral pH, to give a 95% yield, quite pure (14). Some properties of interest include ...
Chapter 11 - Department of Chemistry and Physics
... Because the -OH group is quite polar, the properties of alcohols depend upon the number of -OH groups per molecule and the size of the organic group. The boiling points of alcohols increase with increasing molecular weight. The solubility of alcohols in water decrease with increasing molecular ...
... Because the -OH group is quite polar, the properties of alcohols depend upon the number of -OH groups per molecule and the size of the organic group. The boiling points of alcohols increase with increasing molecular weight. The solubility of alcohols in water decrease with increasing molecular ...
247th American Chemical Society National Meeting and Exposition
... destroyed within two weeks. This process was tracked by X-ray diffraction (XRD) which showed a new structure had been formed, as well as infrared (IR) showing the formation of protonated carboxylic acid groups and 13 C magic angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which showed the pres ...
... destroyed within two weeks. This process was tracked by X-ray diffraction (XRD) which showed a new structure had been formed, as well as infrared (IR) showing the formation of protonated carboxylic acid groups and 13 C magic angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which showed the pres ...
Pi-Acid handout - U of L Class Index
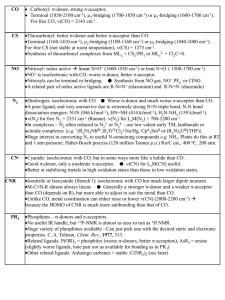
... Unlike CO, metal coordination can either raise or lower n(CN) (2000-2200 cm-1) because the HOMO of CNR is much more antibonding than that of CO. ...
... Unlike CO, metal coordination can either raise or lower n(CN) (2000-2200 cm-1) because the HOMO of CNR is much more antibonding than that of CO. ...
C7 Revision Notes 2015
... •The best-known are hydrocarbons, which are made of only carbon and hydrogen. •There are several subclasses of hydrocarbons, the simplest being the "alkanes", which are straight or branch-chained molecules, all joined with single C-C bonds. •The simplest alkane is methane (CH4), followed by ethane ( ...
... •The best-known are hydrocarbons, which are made of only carbon and hydrogen. •There are several subclasses of hydrocarbons, the simplest being the "alkanes", which are straight or branch-chained molecules, all joined with single C-C bonds. •The simplest alkane is methane (CH4), followed by ethane ( ...
Solubility of Organic Compounds
... diethyl ether, dichloromethane, chloroform, petroleum ether, hexanes etc.) but not in polar solvents like water. However, some organic molecules are more polar and therefore soluble in water. This denotes a rather high ratio of polar group(s) to the non-polar hydrocarbon chain, i.e., a low molecular ...
... diethyl ether, dichloromethane, chloroform, petroleum ether, hexanes etc.) but not in polar solvents like water. However, some organic molecules are more polar and therefore soluble in water. This denotes a rather high ratio of polar group(s) to the non-polar hydrocarbon chain, i.e., a low molecular ...
Copper(II) bromide as efficient catalyst for silyl
... of the transformation compared to TIPS and TBDPS ethers, the latter being by far the slowest to interconvert (entry 5 vs 4 vs 1–3). The reaction rates were thus mostly dependent on the size of the substituents at the core Si atom. Interestingly, they approximately followed the rate order of acid-cat ...
... of the transformation compared to TIPS and TBDPS ethers, the latter being by far the slowest to interconvert (entry 5 vs 4 vs 1–3). The reaction rates were thus mostly dependent on the size of the substituents at the core Si atom. Interestingly, they approximately followed the rate order of acid-cat ...
Phenol
... For o-nitrophenol, the –NO2 and –OH groups are closed to each other and they form intramolecular hydrogen bonding (within a single molecule). Therefore o-nitrophenol does not have the low volatility of an associated liquid, cannot form hydrogen bonding with water, therefore it have lower solubility ...
... For o-nitrophenol, the –NO2 and –OH groups are closed to each other and they form intramolecular hydrogen bonding (within a single molecule). Therefore o-nitrophenol does not have the low volatility of an associated liquid, cannot form hydrogen bonding with water, therefore it have lower solubility ...
π bonded ligands
... Most of the neutral ligands we have studied (apart from carbenes) have been stable in the free state. Cyclobutadienes on the other hand are highyl reactive when not complexed to a late transition metal. The free molecule, with four π electrons, is antiaromatic and rectangular, but the ligand is squa ...
... Most of the neutral ligands we have studied (apart from carbenes) have been stable in the free state. Cyclobutadienes on the other hand are highyl reactive when not complexed to a late transition metal. The free molecule, with four π electrons, is antiaromatic and rectangular, but the ligand is squa ...
Chapter - FIU Faculty Websites
... • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please note that hemiacetals can be hydrolyzed back to aldehydes or ketones in acidic and basic solutions while acetals can ...
... • In acetal synthesis, since water is formed as a by-product, the equilibrium can be driven to the right by removing H2O as it is formed using distillation or other techniques. Please note that hemiacetals can be hydrolyzed back to aldehydes or ketones in acidic and basic solutions while acetals can ...
Lecture8
... Direct nucleophilic addition to an unsaturated ligand (e.g. CO, alkene, allyl, benzene) Because they are electron rich, molecules such as CO, alkenes, polyenes and arenes generally do not react with nucleophiles in the absence of a metal. • Once attached to a metal, these ligands give up some of th ...
... Direct nucleophilic addition to an unsaturated ligand (e.g. CO, alkene, allyl, benzene) Because they are electron rich, molecules such as CO, alkenes, polyenes and arenes generally do not react with nucleophiles in the absence of a metal. • Once attached to a metal, these ligands give up some of th ...
Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Reading: Wade
... Compare the boiling points of n-pentane (36°C) vs. n-octane (127°C), and CCl4 (77°C) vs. CHCl3 (62°C). Hydrogen Bonds are particularly strong dipole-dipole attractions due to a highly polarized O–H or N–H bond (only when H is bonded to an electronegative element). The partial positive charge on H in ...
... Compare the boiling points of n-pentane (36°C) vs. n-octane (127°C), and CCl4 (77°C) vs. CHCl3 (62°C). Hydrogen Bonds are particularly strong dipole-dipole attractions due to a highly polarized O–H or N–H bond (only when H is bonded to an electronegative element). The partial positive charge on H in ...
Lecture 2
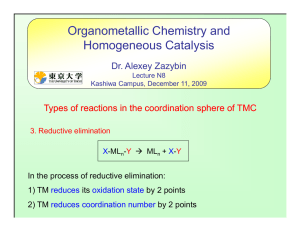
... Higher oxidation states of elements to the right of transition metals have more soft character. There are electrons outside the d shell which interfere with pi bonding. In higher oxidation states they are removed. For transition metals: high oxidation states and position to the left of periodic tabl ...
... Higher oxidation states of elements to the right of transition metals have more soft character. There are electrons outside the d shell which interfere with pi bonding. In higher oxidation states they are removed. For transition metals: high oxidation states and position to the left of periodic tabl ...
Lab 3. Chemical Reactions
... rolled into pellets, or pounded into sheets and foil). It conducts heat and electricity but is not magnetic. It has a high melting point (it takes a lot of energy to make it turn from a solid to a liquid) and it is not soluble (doesn’t dissolve) in water. These characteristics are physical propertie ...
... rolled into pellets, or pounded into sheets and foil). It conducts heat and electricity but is not magnetic. It has a high melting point (it takes a lot of energy to make it turn from a solid to a liquid) and it is not soluble (doesn’t dissolve) in water. These characteristics are physical propertie ...
Hydrothermal Reactions of Pyruvic Acid
... The principal objective of this study was to determine the chemical and physical properties of the end products of reactions that do not proceed spontaneously at ordinary temperatures and pressures, but can be driven by high-pressure/high-temperature regimes in CO2-rich hydrothermal environments. Th ...
... The principal objective of this study was to determine the chemical and physical properties of the end products of reactions that do not proceed spontaneously at ordinary temperatures and pressures, but can be driven by high-pressure/high-temperature regimes in CO2-rich hydrothermal environments. Th ...
Reactions of 2, 6-cycloheptadienone and 2, 7
... The LiClO4 served only as a source of HC104 and could be replaced by any inorganic perchlorate which would dissolve sufficiently in H z S O ~to liberate the required perchloric acid. Alternatively 70% HClO4 could be added directly to 967' HzSOd. If a large amount of perchloric acid was used, it was ...
... The LiClO4 served only as a source of HC104 and could be replaced by any inorganic perchlorate which would dissolve sufficiently in H z S O ~to liberate the required perchloric acid. Alternatively 70% HClO4 could be added directly to 967' HzSOd. If a large amount of perchloric acid was used, it was ...
Chapter 10 Introduction to Organic Chemistry: Alkanes
... Functional groups are • a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable, similar way. • composed of an atom or group of atoms. • groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the ...
... Functional groups are • a characteristic feature of organic molecules that behave in a predictable, similar way. • composed of an atom or group of atoms. • groups that replace a hydrogen atom in the ...
The separation, purification and identification of the components of a
... (D) A sample should be packed tightly into a capillary m.p. tube. ...
... (D) A sample should be packed tightly into a capillary m.p. tube. ...
Worksheet Key
... 36. For each system described below, indicate in which direction the equilibrium will shift when each stress is added or removed. Also explain how the system will react to alleviate the stress. a) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g): more H2 is added to this reaction at equilibrium. Reaction will shift to ...
... 36. For each system described below, indicate in which direction the equilibrium will shift when each stress is added or removed. Also explain how the system will react to alleviate the stress. a) N2 (g) + 3 H2 (g) 2 NH3 (g): more H2 is added to this reaction at equilibrium. Reaction will shift to ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.