Lecture 15
... • Cells (plants and animals) rely on O2 for life processes – Water an electron acceptor in plants – Animal cells generate water from the reduction of O2 by H+ ...
... • Cells (plants and animals) rely on O2 for life processes – Water an electron acceptor in plants – Animal cells generate water from the reduction of O2 by H+ ...
Nomenclature of Organic Compounds
... b. Two substituents, cite them alphabetically and give the number 1 position to the first substituent. c. Three or more substituents, the substituent given the number 1 is the one that results in a second substituent getting as low a number as possible. ...
... b. Two substituents, cite them alphabetically and give the number 1 position to the first substituent. c. Three or more substituents, the substituent given the number 1 is the one that results in a second substituent getting as low a number as possible. ...
Session 9 – Organic Chemistry
... The properties of the alkenes The alkenes are more reactive because they are unsaturated. As with the alkanes, compounds that have four or less carbon atoms are gases at room temperature, while those with five or more carbon atoms are liquids. Alkenes can undergo addition reactions because they are ...
... The properties of the alkenes The alkenes are more reactive because they are unsaturated. As with the alkanes, compounds that have four or less carbon atoms are gases at room temperature, while those with five or more carbon atoms are liquids. Alkenes can undergo addition reactions because they are ...
Chapter 4
... • Carbon with its ______ covalent bonds is the basic building block in molecular architecture. • The great diversity of organic molecules with their special properties emerge from the unique arrangement of the carbon skeleton and the functional groups attached to the skeleton. ...
... • Carbon with its ______ covalent bonds is the basic building block in molecular architecture. • The great diversity of organic molecules with their special properties emerge from the unique arrangement of the carbon skeleton and the functional groups attached to the skeleton. ...
CH 3
... both on the same side of a double bond (cis) or on opposite sides (trans). Notice that the bonded neighbors of each atom are the same in both cases, but nevertheless the arrangements of the atoms in space are different. ...
... both on the same side of a double bond (cis) or on opposite sides (trans). Notice that the bonded neighbors of each atom are the same in both cases, but nevertheless the arrangements of the atoms in space are different. ...
Chapter #21 Notes
... 2. Add the names of the alkyl groups. Put in alpha order. 3. Leave appropriate spaces in the name. ...
... 2. Add the names of the alkyl groups. Put in alpha order. 3. Leave appropriate spaces in the name. ...
Chapter 4: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life (pp. 57-59, TABLE 4.1) Functional groups are specific chemically reactive groups of atoms within organic molecules that give the overall molecule distinctive chemical properties. The hydroxyl group (--OH), found in alcohols, has a pol ...
... Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life (pp. 57-59, TABLE 4.1) Functional groups are specific chemically reactive groups of atoms within organic molecules that give the overall molecule distinctive chemical properties. The hydroxyl group (--OH), found in alcohols, has a pol ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... Because they don’t have a hydrogen on the COH carbon, phenols become quinones ...
... Because they don’t have a hydrogen on the COH carbon, phenols become quinones ...
1.4 Alcohols, Ethers and Thiols Answers
... chain. Heptan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol with a relatively longer carbon chain. Since simple alcohols with short carbon chains are more soluble in water than those with longer carbon chains, a solubility test can be used to identify the two compounds. Dissolve a sample of an equal amount of either ...
... chain. Heptan-2-ol is a secondary alcohol with a relatively longer carbon chain. Since simple alcohols with short carbon chains are more soluble in water than those with longer carbon chains, a solubility test can be used to identify the two compounds. Dissolve a sample of an equal amount of either ...
Alkanes In alkanes, the C-C bonds are weaker than the C
... In alkanes, the C-C bonds are weaker than the C-H bonds. Ionisation of the molecule results in greatly reduced bond strengths. Due to the delocalised nature of the charge, all bonds are weakened equally. The mass spectra of unbranched alkanes show groups of ions separated by 14Da. This separation is ...
... In alkanes, the C-C bonds are weaker than the C-H bonds. Ionisation of the molecule results in greatly reduced bond strengths. Due to the delocalised nature of the charge, all bonds are weakened equally. The mass spectra of unbranched alkanes show groups of ions separated by 14Da. This separation is ...
10.5 Carbonyl Compounds (a) describe: (i) the
... (a) describe: (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) des ...
... (a) describe: (i) the formation of aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols respectively using Cr2O72-/H+ (ii) the reduction of aldehydes and ketones e.g. using NaBH4 (b) describe the mechanism of nucleophilic addition reactions of hydrogen cyanide with aldehydes and ketones (c) des ...
hydrogen bonds and van der Waals bonds
... Waals attractions can become important when two macromolecular surfaces fit very close together, because many atoms are involved. Note that when two atoms form a covalent bond, the centers of the two atoms (the two atomic nuclei) are much closer together than the sum of the two van der Waals radii. ...
... Waals attractions can become important when two macromolecular surfaces fit very close together, because many atoms are involved. Note that when two atoms form a covalent bond, the centers of the two atoms (the two atomic nuclei) are much closer together than the sum of the two van der Waals radii. ...
Introduction to Organic Chemistry
... Portions of large molecules may be hydrophobic and other portions of the same molecule may be hydrophilic. ...
... Portions of large molecules may be hydrophobic and other portions of the same molecule may be hydrophilic. ...
Chapter 4: Carbon and Molecular Diversity
... 1. % of C, O, H, N, S, P are uniform from individual to individual and from species to species a. Atoms in an organic molecule can be arranged many different ways C. Know the terms and contributions made by the following: (Table Activity) 1. George Washington Carver 2. Jons Jakob Berzelius (Swedish ...
... 1. % of C, O, H, N, S, P are uniform from individual to individual and from species to species a. Atoms in an organic molecule can be arranged many different ways C. Know the terms and contributions made by the following: (Table Activity) 1. George Washington Carver 2. Jons Jakob Berzelius (Swedish ...
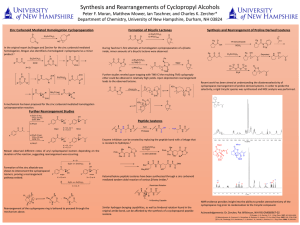
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
... Further studies reveled upon trapping with TMS-Cl the resulting TMS cycloproply ether could be obtained in relatively high yields. Upon deprotection rearrangement leads to the observed lactone. ...
... Further studies reveled upon trapping with TMS-Cl the resulting TMS cycloproply ether could be obtained in relatively high yields. Upon deprotection rearrangement leads to the observed lactone. ...
Q1. Give I.U.P.A..C Name of the following Organic Compound. 1 CH
... Q11. At a site low grades copper ores are available and Zinc and iron scraps are also available. Which of the two scraps would be more suitable for reducing the leached copper ore and why? ...
... Q11. At a site low grades copper ores are available and Zinc and iron scraps are also available. Which of the two scraps would be more suitable for reducing the leached copper ore and why? ...
COURSE: Organic chemistry ACADEMIC YEAR:2016/2017 TYPE
... nitrogen, amines, sp2 nitrogen, s nitrogenp. Compounds containing oxygen: sp3 oxygen, alcohols, ethers, sp2 oxyen, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. Compounds containing sulfur. Alkyl halides (15 hours). Sterochemistry: conformations, chirality (10 hours). The organic re ...
... nitrogen, amines, sp2 nitrogen, s nitrogenp. Compounds containing oxygen: sp3 oxygen, alcohols, ethers, sp2 oxyen, aldehydes and ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. Compounds containing sulfur. Alkyl halides (15 hours). Sterochemistry: conformations, chirality (10 hours). The organic re ...
Nugget
... improved solubility of the organometallic compounds. Currently we are working on optimization of the crystallization conditions for the ruthenium products. Ruthenium ditriflate analog of the carborane complexes oxidizes alcohols to yield aldehydes (or ketones). We continued the kinetic and thermodyn ...
... improved solubility of the organometallic compounds. Currently we are working on optimization of the crystallization conditions for the ruthenium products. Ruthenium ditriflate analog of the carborane complexes oxidizes alcohols to yield aldehydes (or ketones). We continued the kinetic and thermodyn ...
16.2: Structure and Bonding in Ethers and Epoxides
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers The O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
... The ether oxygen is sp3-hybridized and tetrahedral. In general, the C-O bonds of ethers have low reactivity. 16.3: Physical Properties of Ethers The O-H group of alcohols act as both an H-bond donor (Lewis acid) and H-bond acceptor (Lewis base). Ethers are only H-bond acceptors (Lewis base) 16.4: Cr ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.