TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to determine ‘A’ values Conformational effects on reactivity - oxidation of axial vs equatorial alcohols, hydrolysis of axial vs equatorial esters haloketone conformations allylic strain, cyclohexenes six-membered heterocycles 4, 5, 7, ...
... Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to determine ‘A’ values Conformational effects on reactivity - oxidation of axial vs equatorial alcohols, hydrolysis of axial vs equatorial esters haloketone conformations allylic strain, cyclohexenes six-membered heterocycles 4, 5, 7, ...
Lecture 6
... bonds, C C-C C bonds Electrophilic: Such molecules do contain electro-negative atoms and are good oxidizing agents. agents They are often considered to be “reactive” reactive substrates. substrates These molecules do not require the presence of an empty orbital (18e- is OK) on the metal center in or ...
... bonds, C C-C C bonds Electrophilic: Such molecules do contain electro-negative atoms and are good oxidizing agents. agents They are often considered to be “reactive” reactive substrates. substrates These molecules do not require the presence of an empty orbital (18e- is OK) on the metal center in or ...
Chapter 13 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Hydrocarbon
... because the intermolecular forces holding the alkane molecules together are very weak London Dispersion forces (Van derWaals force). As a result of these weak intermolecular forces the temperature required to separate the molecules into the vapor state is low. The strength of Van der Waals forces is ...
... because the intermolecular forces holding the alkane molecules together are very weak London Dispersion forces (Van derWaals force). As a result of these weak intermolecular forces the temperature required to separate the molecules into the vapor state is low. The strength of Van der Waals forces is ...
Document
... •Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1973 (shared with Ernst Otto Fischer) for their pioneering work, performed independently, on the chemistry of the organometallic, so called sandwich compounds. ...
... •Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1973 (shared with Ernst Otto Fischer) for their pioneering work, performed independently, on the chemistry of the organometallic, so called sandwich compounds. ...
2.10 Reactions of alcohols
... reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary alcohols to produce ketones ...
... reaction with PCl5 and its use as a qualitative test for the presence of the –OH group iv. oxidation using potassium dichromate (VI) in dilute sulfuric acid on primary alcohols to produce aldehydes and carboxylic acids and on secondary alcohols to produce ketones ...
Preparation and Reaction of Carboxylic Acids - IDC
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
... nucleophilic group are important for preparing functional derivatives of carboxylic acids. The alcohols provide a usefulreference chemistry against which this class of transformations may be evaluated. In general, the hydroxyl group proved to be a poor leaving group, and virtually all alcohol reacti ...
Final Exam from 2006 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... CH3CH3 CH3OH an acetal a hemiacetal an alkene ...
... CH3CH3 CH3OH an acetal a hemiacetal an alkene ...
Document
... • Composite materials are formed when a reinforcing material (glass fiber, graphite fiber) is blended into a matrix material (usually a polymer). Composite materials are usually stiffer and stronger than the pure polymer matrix. ...
... • Composite materials are formed when a reinforcing material (glass fiber, graphite fiber) is blended into a matrix material (usually a polymer). Composite materials are usually stiffer and stronger than the pure polymer matrix. ...
The Chemistry of Life: Organic Compounds
... The properties of the major classes of biologically important organic compounds — carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids — are largely a consequence of the types and arrangement of functional groups they contain. When we know what kinds of functional groups are present in an organic comp ...
... The properties of the major classes of biologically important organic compounds — carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids — are largely a consequence of the types and arrangement of functional groups they contain. When we know what kinds of functional groups are present in an organic comp ...
Part (d) The Birch Reduction of Nitrogen
... As the constituents of poly amides (ie peptides) these functional groups are essential parts of biological systems. We can hydrolyse an amide bond in the laboratory, but require harsh acidic or basic conditions to do it ...
... As the constituents of poly amides (ie peptides) these functional groups are essential parts of biological systems. We can hydrolyse an amide bond in the laboratory, but require harsh acidic or basic conditions to do it ...
Ionic Bond Test - Dynamic Science
... 16) The diary of an organic chemist was found in his laboratory. The chemist was studying a group of compounds known as alkenes when he suddenly collapsed. The diary entry was incomplete and is shown here.”I have managed to isolate the compound hept……..” Which statement is true? a) The compound has ...
... 16) The diary of an organic chemist was found in his laboratory. The chemist was studying a group of compounds known as alkenes when he suddenly collapsed. The diary entry was incomplete and is shown here.”I have managed to isolate the compound hept……..” Which statement is true? a) The compound has ...
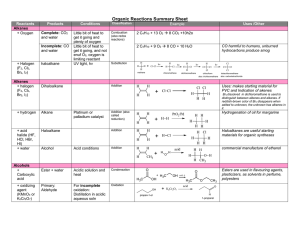
Organic Reactions Summary Sheet
... Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish-brown color of Br2 disappears when added to unknown, the unknown has alkenes in it. ...
... Br2 dissolved in dichloromethane is used to distinguish between alkenes and alkanes. If reddish-brown color of Br2 disappears when added to unknown, the unknown has alkenes in it. ...
Alcohols - Structure - University of Nebraska Omaha
... • The parent chain is the longest chain containing the -SH group. • Add -thiol to the name of the parent chain. • Sulfhydryl group has lower priority than hydroxyl. • Alternatively, indicate a lower priority -SH by the prefix mercapto. ...
... • The parent chain is the longest chain containing the -SH group. • Add -thiol to the name of the parent chain. • Sulfhydryl group has lower priority than hydroxyl. • Alternatively, indicate a lower priority -SH by the prefix mercapto. ...
Integrated Science Chapter 4 Notes Section 1: Compounds and
... Chemical structure – the arrangement of bonded atoms or ions within a substance Bond length – the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms Bond angle – the angle formed by two bonds to the same atom • Different structures give compound different properties Compound with networ ...
... Chemical structure – the arrangement of bonded atoms or ions within a substance Bond length – the average distance between the nuclei of two bonded atoms Bond angle – the angle formed by two bonds to the same atom • Different structures give compound different properties Compound with networ ...
C07B - Cooperative Patent Classification
... relating to chromatography is concerned 4. In this subclass, the last place priority rule is applied, i.e. at each hierarchical level, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place according to the type of reaction employed, noting the bond or ...
... relating to chromatography is concerned 4. In this subclass, the last place priority rule is applied, i.e. at each hierarchical level, in the absence of an indication to the contrary, classification is made in the last appropriate place according to the type of reaction employed, noting the bond or ...
Chapter Nine Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbon 1
... not found alone. It is derived from the corresponding alkane by removing one hydrogen atom .Alkyl radicals are given the symbol "R".Their general formula is (CnH2n+1).Its name is derived from the corresponding alkane by replacing the suffix (ane) by (yl). 22- The nomenclature of alkanes: (IUPAC syst ...
... not found alone. It is derived from the corresponding alkane by removing one hydrogen atom .Alkyl radicals are given the symbol "R".Their general formula is (CnH2n+1).Its name is derived from the corresponding alkane by replacing the suffix (ane) by (yl). 22- The nomenclature of alkanes: (IUPAC syst ...
TV RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Conformations of amides - Relationship between K and free energy difference between Z and E o amides ( also see later under A values) Conformational analysis of cyclic compounds - cyclohexanes, Chair, boat, twist conformations proof Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to de ...
... Conformations of amides - Relationship between K and free energy difference between Z and E o amides ( also see later under A values) Conformational analysis of cyclic compounds - cyclohexanes, Chair, boat, twist conformations proof Substituted cyclohexanes - ‘A’ values of various groups - how to de ...
LECTURE 3 Shape: Conformations of Cyclohexanes Cyclohexane
... In propane there are 6 methyl hydrogens and 2 methylene hydrogens and substitution of 1 each of these by chlorine leads to 1-chloropropane and 2chloropropane respectively. If all the C – H bonds were of equal reactivity then we should expect to see the 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane to be forme ...
... In propane there are 6 methyl hydrogens and 2 methylene hydrogens and substitution of 1 each of these by chlorine leads to 1-chloropropane and 2chloropropane respectively. If all the C – H bonds were of equal reactivity then we should expect to see the 1-chloropropane and 2-chloropropane to be forme ...
Section 5b and c: crude oil and synthetic polymers Fractional
... Nylon: condensation polymerization 5.17 recall that nylon is a condensation polymer 5.18 understand that the formation of a condensation polymer is accompanied by the release of a small molecule such as water or hydrogen chloride 5.19 recall the types of monomers used in the manufacture of nylon 5. ...
... Nylon: condensation polymerization 5.17 recall that nylon is a condensation polymer 5.18 understand that the formation of a condensation polymer is accompanied by the release of a small molecule such as water or hydrogen chloride 5.19 recall the types of monomers used in the manufacture of nylon 5. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.