Organic Structures
... level when a heteroatom is replaced by a carbon atom, for example when an alkyl halide reacts with cyanide. As the heteroatom is removed, the function group level of the original carbon falls by one, possibly to zero. The newly-introduced carbon is Level 3, as it has three bonds to a nitrogen atom, ...
... level when a heteroatom is replaced by a carbon atom, for example when an alkyl halide reacts with cyanide. As the heteroatom is removed, the function group level of the original carbon falls by one, possibly to zero. The newly-introduced carbon is Level 3, as it has three bonds to a nitrogen atom, ...
Exam 1 Solution Key
... You have seen this reaction (or a very similar one) in the last four weeks. However, the expertise we are expecting to acquire in organic chemistry will allow us to “predict” the products of such reactions. Our starting point for the reaction is that both reactants are reactive. ...
... You have seen this reaction (or a very similar one) in the last four weeks. However, the expertise we are expecting to acquire in organic chemistry will allow us to “predict” the products of such reactions. Our starting point for the reaction is that both reactants are reactive. ...
Chemdraw B&W - Pennsylvania State University
... • Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
... • Protonation of OH converts into water as the leaving group • Result is iminium ion, which loses proton • Acid is required for loss of OH – too much acid blocks RNH2 ...
CH 19
... four-membered ring to yield alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide, (Ph)3P=O • Formation of the ylide is shown below ...
... four-membered ring to yield alkene and triphenylphosphine oxide, (Ph)3P=O • Formation of the ylide is shown below ...
Unit 2 Summary - A
... the hydrolysis of bromoethane: C2H5Br + NaOH C2H5OH + NaBr the fermentation of glucose: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 the hydration of ethane: C2H4 + H2O C2H5OH (o) describe the benefits of developing chemical processes with a high atom economy in terms of fewer waste materials; Why is it an advantag ...
... the hydrolysis of bromoethane: C2H5Br + NaOH C2H5OH + NaBr the fermentation of glucose: C6H12O6 2C2H5OH + 2CO2 the hydration of ethane: C2H4 + H2O C2H5OH (o) describe the benefits of developing chemical processes with a high atom economy in terms of fewer waste materials; Why is it an advantag ...
Organic Compounds
... other electrons. This means that each carbon atom forms 4 bonds. • The 4 bonds are in the form of a tetrahedron, a triangular pyramid. • Carbon can form long chains and rings, especially with hydrogens attached. ...
... other electrons. This means that each carbon atom forms 4 bonds. • The 4 bonds are in the form of a tetrahedron, a triangular pyramid. • Carbon can form long chains and rings, especially with hydrogens attached. ...
CfE Higher Chemistry Homework Unit 2: Natures Chemistry
... butanone (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
... butanone (a) Name the two products formed by the dehydration of butan-2-ol (b) Name a reagent which could be used to oxidise butan-2-ol to butanone. ...
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of t ...
... dehydration, an E1 reaction. In this experiment, a mixture of concentrated phosphoric acid and concentrated sulfuric acid is used to prepare cyclohexene from cyclohexanol via an E1 reaction. The mechanism of this E1 reaction involves three steps. First, is the rapid (and reversible) protonation of t ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: OXIDATION
... solution, and so must be tertiary. CH3 CH3-C-CH3 OH (There are other ways you might have drawn this. Your structure is right if you have three CH3 groups and an OH all attached to the same carbon atom.) C is a secondary alcohol, because it doesn’t produce an aldehyde on oxidation. It can only be CH3 ...
... solution, and so must be tertiary. CH3 CH3-C-CH3 OH (There are other ways you might have drawn this. Your structure is right if you have three CH3 groups and an OH all attached to the same carbon atom.) C is a secondary alcohol, because it doesn’t produce an aldehyde on oxidation. It can only be CH3 ...
Chapter 17: Aldehydes and Ketones: Nucleophilic Addition to the
... The Wittig reaction is highly selective for ketones and aldehydes; esters, lactones, nitriles and amides will not react but are tolerated in the substrate. Acidic groups (alcohols, amine and carboxylic acids) are not tolerated. O O ...
... The Wittig reaction is highly selective for ketones and aldehydes; esters, lactones, nitriles and amides will not react but are tolerated in the substrate. Acidic groups (alcohols, amine and carboxylic acids) are not tolerated. O O ...
Slide 1
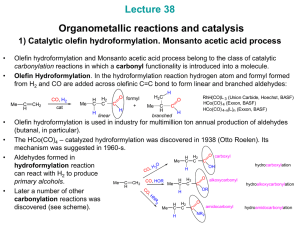
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
... Olefin hydroformylation and Monsanto acetic acid process belong to the class of catalytic carbonylation reactions in which a carbonyl functionality is introduced into a molecule. Olefin Hydroformylation. In the hydroformylation reaction hydrogen atom and formyl formed from H2 and CO are added across ...
An Introduction to Organic Chemistry
... extensive, indiscriminate mixture of halogenated hydrocarbons that is very expensive to separate. Reactivity: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 >> I2 Provides an albeit prohibitively expensive route to useful compounds since polarity (and thus chemical reactivity) has been introduced. Cracking This is enormously impor ...
... extensive, indiscriminate mixture of halogenated hydrocarbons that is very expensive to separate. Reactivity: F2 > Cl2 > Br2 >> I2 Provides an albeit prohibitively expensive route to useful compounds since polarity (and thus chemical reactivity) has been introduced. Cracking This is enormously impor ...
Study Guide for Exam 2-‐ Aldehydes and Ketones
... writing) at solving the synthesis on your own. During review sessions, any student that asks about the syntheses will be asked to go to the board to present what they have worked out so far. ...
... writing) at solving the synthesis on your own. During review sessions, any student that asks about the syntheses will be asked to go to the board to present what they have worked out so far. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chem 101/lecture 1-2
... Because each carbon is trigonal planar, ethylene is a flat molecule with thickness due to the pi-electrons. ...
... Because each carbon is trigonal planar, ethylene is a flat molecule with thickness due to the pi-electrons. ...
CHM 253L Organic Chemistry Laboratory I
... R #8 Record the energies for each cyclic hydrocarbon (cyclopropane through cyclohexane) as Hf per CH2. See Table 5.1 on page 200 of the Jones text. D #8 How well do your calculated (experimental) heats of formation per CH2 for the series of cyclic hydrocarbons cyclic hydrocarbon (cyclopropane throu ...
... R #8 Record the energies for each cyclic hydrocarbon (cyclopropane through cyclohexane) as Hf per CH2. See Table 5.1 on page 200 of the Jones text. D #8 How well do your calculated (experimental) heats of formation per CH2 for the series of cyclic hydrocarbons cyclic hydrocarbon (cyclopropane throu ...
Kekulé structure of benzene
... There are many different types of isomers, including those in which the molecules have different functional groups. Different functional groups different classes, different reactivities. E.g. C2H6O describes both an alcohol and ether ...
... There are many different types of isomers, including those in which the molecules have different functional groups. Different functional groups different classes, different reactivities. E.g. C2H6O describes both an alcohol and ether ...
Lecture #3 – Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... a. AMINO GROUP: (Your “basic” relative) -NH2 a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Organic compounds in this group are called amines. b. Because glycine has an amine group and a carboxylic acid, compounds with both are called something very important – amino acids – t ...
... a. AMINO GROUP: (Your “basic” relative) -NH2 a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and the carbon skeleton. Organic compounds in this group are called amines. b. Because glycine has an amine group and a carboxylic acid, compounds with both are called something very important – amino acids – t ...
Aldehydes and ketones
... When some aldehyde is added to Tollens reagent and the mixture warmed, a redox reaction occurs. ...
... When some aldehyde is added to Tollens reagent and the mixture warmed, a redox reaction occurs. ...
Worked out problems
... Analyze: We are given the structural formulas for two compounds, the first an alkene and the second an alkyne, and asked to name the compounds. Plan: In each case the name is based on the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the multiple bond. In the case of th ...
... Analyze: We are given the structural formulas for two compounds, the first an alkene and the second an alkyne, and asked to name the compounds. Plan: In each case the name is based on the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous carbon chain that contains the multiple bond. In the case of th ...
Organic Compounds
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. 90% of compounds contain Carbon Carbon has a unique ability to bond with itself in complex covalent bonds. A single molecular formula may have several structures. ...
... Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds. 90% of compounds contain Carbon Carbon has a unique ability to bond with itself in complex covalent bonds. A single molecular formula may have several structures. ...
Organometallic Compounds - Reagents
... Functional Group Interconversion (FGI): the process of converting one functional group into another by substitution, addition, elimination, reduction, or oxidation ...
... Functional Group Interconversion (FGI): the process of converting one functional group into another by substitution, addition, elimination, reduction, or oxidation ...
File
... Organic Reactions, Combustion The most common type of reaction that organic compounds undergo is combustion. Hydrocarbons are carbon-hydrogen compounds • used as fuels; gasoline is a mixture of different ...
... Organic Reactions, Combustion The most common type of reaction that organic compounds undergo is combustion. Hydrocarbons are carbon-hydrogen compounds • used as fuels; gasoline is a mixture of different ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.