fo-Balancing Chemical Notes
... In this reaction, all of the compounds have the correct formulas. The next step is to select the 'simplest' element. Either carbon (C) or hydrogen (H) could be used. For this example, we will select carbon. Following step #3, we change the coefficients in front of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon dioxi ...
... In this reaction, all of the compounds have the correct formulas. The next step is to select the 'simplest' element. Either carbon (C) or hydrogen (H) could be used. For this example, we will select carbon. Following step #3, we change the coefficients in front of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) and carbon dioxi ...
Make Your Own Summary 1. single displacement reaction 2
... double displacement, since two ionic compounds will usually swap ions decomposition, since the only reaction possible for a single compound is to break down into simpler substances single displacement, since the activity series for metals shows aluminum is more reactive than iron double displacement ...
... double displacement, since two ionic compounds will usually swap ions decomposition, since the only reaction possible for a single compound is to break down into simpler substances single displacement, since the activity series for metals shows aluminum is more reactive than iron double displacement ...
Chapter 14 – Aldehydes and Ketones
... practical way of making aldehydes on the large scale. The major reason is cost and this can be seen in the use of silver and copper reagents respectively. On the industrial scale, when compounds are frequently made in thousand to million pound quantities, the use of this much precious or semi-precio ...
... practical way of making aldehydes on the large scale. The major reason is cost and this can be seen in the use of silver and copper reagents respectively. On the industrial scale, when compounds are frequently made in thousand to million pound quantities, the use of this much precious or semi-precio ...
Drawing Organic Structures Functional Groups
... 1. Parent is longest C chain containing both carbons of C=C 2. Number chain so C=C has lowest possible number • If the double bond is equidistant from both ends, start numbering at end nearest the first substituent • Show location of C=C by first number • Alkenes with >1 C=C use “-adiene”, “-atriene ...
... 1. Parent is longest C chain containing both carbons of C=C 2. Number chain so C=C has lowest possible number • If the double bond is equidistant from both ends, start numbering at end nearest the first substituent • Show location of C=C by first number • Alkenes with >1 C=C use “-adiene”, “-atriene ...
Alkenes - Gadjah Mada University
... CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 Hydrogenation requires high temperatures and pressures as well as the presence of a catalyst (e.g. Ni). ...
... CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 Hydrogenation requires high temperatures and pressures as well as the presence of a catalyst (e.g. Ni). ...
Organic Chemistry PPT including assignments File
... hydrocarbon that we have talked about: alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acids, amines, esters In the chart, include ...
... hydrocarbon that we have talked about: alkane, alkene, alkyne, alcohol, carboxylic acids, amines, esters In the chart, include ...
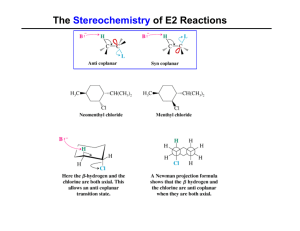
The Stereochemistry of E2 Reactions
... Dehydration of Alcohols: E1 Mechanism Rate Limiting Step ...
... Dehydration of Alcohols: E1 Mechanism Rate Limiting Step ...
Survey on Conditions Catalysis of Chemical Reactions
... manganese. To confer good solubility in the organic solvent, these catalysts are often derived nd ethylhexanoic acid, which are highly lipophilic. These catalysts initiate radical chain reactions, autoxidation that produce organic radicals that combine with oxygen to give from naphthenic acids ahydr ...
... manganese. To confer good solubility in the organic solvent, these catalysts are often derived nd ethylhexanoic acid, which are highly lipophilic. These catalysts initiate radical chain reactions, autoxidation that produce organic radicals that combine with oxygen to give from naphthenic acids ahydr ...
Fun With Predicting Reaction Products
... reaction to occur, both reactants and only one of the products must be soluble in water. If you look up the solubilities on a chart, you’ll find that Ag2SO3 is partly soluble in water, and all of the other compounds are totally soluble in water. This tells us that this reaction will not occur. ...
... reaction to occur, both reactants and only one of the products must be soluble in water. If you look up the solubilities on a chart, you’ll find that Ag2SO3 is partly soluble in water, and all of the other compounds are totally soluble in water. This tells us that this reaction will not occur. ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
ppt file
... cm-1 is the unit for wavenumber (n) (The numbers of waves within 1 cm) n is directly proportional to energy (unlike wavelength) 4. Bonds absorb energy equal to their natural vibrational energy - it is quantized. This absorption of energy causes a change in dipole moment for the bond. 5. Upon absorpt ...
... cm-1 is the unit for wavenumber (n) (The numbers of waves within 1 cm) n is directly proportional to energy (unlike wavelength) 4. Bonds absorb energy equal to their natural vibrational energy - it is quantized. This absorption of energy causes a change in dipole moment for the bond. 5. Upon absorpt ...
Hein and Arena
... of reactions involved in making compounds that can be used in a separate process to manufacture an energy-rich compound called ATP. A reaction early in the citric acid cycle involves the oxidation of an alcohol. Of the two reactants shown below (each is a reactant somewhere in the cycle), which can ...
... of reactions involved in making compounds that can be used in a separate process to manufacture an energy-rich compound called ATP. A reaction early in the citric acid cycle involves the oxidation of an alcohol. Of the two reactants shown below (each is a reactant somewhere in the cycle), which can ...
Handout 5
... 5) If there are three or more substituents, they are listed alphabetically in the name; numbering of the substituted ring carbons is chosen so that the lowest possible sum numbers results. Numbering in the ring may be clockwise or counterclockwise. ...
... 5) If there are three or more substituents, they are listed alphabetically in the name; numbering of the substituted ring carbons is chosen so that the lowest possible sum numbers results. Numbering in the ring may be clockwise or counterclockwise. ...
Functional Groups
... Humic Substances: a general category of naturally occurring, biogenic, heterogeneous organic substances that can generally be characterized as being yellow to black in color, of high molecular weight, and refractory. Humin: that fraction of the humic material that is insoluble in water at all pH va ...
... Humic Substances: a general category of naturally occurring, biogenic, heterogeneous organic substances that can generally be characterized as being yellow to black in color, of high molecular weight, and refractory. Humin: that fraction of the humic material that is insoluble in water at all pH va ...
Biol 1020 Ch. 4: organic molecules
... based on organic compounds organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to either: ...
... based on organic compounds organic compounds have at least one carbon atom covalently bound to either: ...
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Epoxides
... • Do you remember the 3 exceptions for E2 reactions in terms of predicting the major products? • Usually, the more substituted alkene is the major product except if there is a big bulky base, possibility of conjugation or a Fluorine LG. • Here, the quaternary ammonium salt is a relatively slow LG ju ...
... • Do you remember the 3 exceptions for E2 reactions in terms of predicting the major products? • Usually, the more substituted alkene is the major product except if there is a big bulky base, possibility of conjugation or a Fluorine LG. • Here, the quaternary ammonium salt is a relatively slow LG ju ...
GRADE 12A: Chemistry 5
... central atom. A group of electrons might be a lone pair of electrons, a single, double or triple covalent bond. Ask students to model various atoms in molecules (e.g. the carbon in methane could be represented by twisting two bilobar balloons together). The lobes automatically arrange themselves int ...
... central atom. A group of electrons might be a lone pair of electrons, a single, double or triple covalent bond. Ask students to model various atoms in molecules (e.g. the carbon in methane could be represented by twisting two bilobar balloons together). The lobes automatically arrange themselves int ...
Staff demonstrating hours for level-3 Inorganic Lab
... Level-3 Organometallics L3a Synthesis of stable metal alkyl compounds (2) Metal hydride plus alkene This is the reverse of the -elimination reaction and is an example of the general insertion reaction. These involve insertion of small molecules into transition metal-X bonds. In this case that of an ...
... Level-3 Organometallics L3a Synthesis of stable metal alkyl compounds (2) Metal hydride plus alkene This is the reverse of the -elimination reaction and is an example of the general insertion reaction. These involve insertion of small molecules into transition metal-X bonds. In this case that of an ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.