
Carbon Compounds
... So far we have learned that structural formula as only a single bond between any two carbon atoms. One bond, one dash. However, two carbon atoms can form a single bond, a double bond, or a triple bond. A carbon atom can also form a single or double bond with an oxygen atom. Structural form ...
... So far we have learned that structural formula as only a single bond between any two carbon atoms. One bond, one dash. However, two carbon atoms can form a single bond, a double bond, or a triple bond. A carbon atom can also form a single or double bond with an oxygen atom. Structural form ...
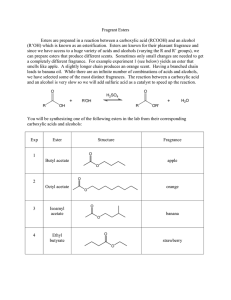
Fragrant Esters Esters are prepared in a reaction between a
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
... can prepare esters that produce different scents. Sometimes only small changes are needed to get a completely different fragrance. For example experiment 1 (see below) yields an ester that smells like apple. A slightly longer chain produces an orange scent. Having a branched chain leads to banana oi ...
to get Period 1 8
... Scientists classify organic compounds into different categories. The simplest organic compounds are the hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only the atoms of hydrogen and carbon. Methane is the main gas in metro gas. Its used to heat homes. Propane is used in portable stoves And ...
... Scientists classify organic compounds into different categories. The simplest organic compounds are the hydrocarbons. A hydrocarbon is a compound that contains only the atoms of hydrogen and carbon. Methane is the main gas in metro gas. Its used to heat homes. Propane is used in portable stoves And ...
Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming
... not consumed. In addition, [Ru3(CO)12] proved an unsuitable starting material to access the same reaction product. Despite NMR data strongly suggesting alkene binding to the nitrosyl ligands of a ruthenium complex, the structure of the product could not be assigned by NMR spectroscopy alone. Attempt ...
... not consumed. In addition, [Ru3(CO)12] proved an unsuitable starting material to access the same reaction product. Despite NMR data strongly suggesting alkene binding to the nitrosyl ligands of a ruthenium complex, the structure of the product could not be assigned by NMR spectroscopy alone. Attempt ...
Document
... Alkanes contain the most hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms, as there as only single carbon-carbon bonds, whereas alkenes and alkynes contain less hydrogen atoms due to the presence of double or triple carbon-carbon bonds ...
... Alkanes contain the most hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon atoms, as there as only single carbon-carbon bonds, whereas alkenes and alkynes contain less hydrogen atoms due to the presence of double or triple carbon-carbon bonds ...
ch 1: organic chemistry
... compared to a carboxylic the functional group is similar but is missing the OH group i.e. the –OH is replaced by an –OR group therefore esters are less polar, less soluble in water and have lower melting and boiling points than their parent acids acidity of carboxylic acids is from the H on ...
... compared to a carboxylic the functional group is similar but is missing the OH group i.e. the –OH is replaced by an –OR group therefore esters are less polar, less soluble in water and have lower melting and boiling points than their parent acids acidity of carboxylic acids is from the H on ...
Exam 2 review sheet
... preparation of ethers: (a) Williamson ether synthesis using SN2 reaction of RO- plus RX, intramolecular to form cyclic ethers; (b) peroxyacid plus alkene (syn addition) to form epoxides reactions of ethers: (a) cleavage using strong acid HX; (b) ring-opening reactions of epoxides, mechanisms for aci ...
... preparation of ethers: (a) Williamson ether synthesis using SN2 reaction of RO- plus RX, intramolecular to form cyclic ethers; (b) peroxyacid plus alkene (syn addition) to form epoxides reactions of ethers: (a) cleavage using strong acid HX; (b) ring-opening reactions of epoxides, mechanisms for aci ...
Chem 150 Unit 2 - Hydrocarbons & Functional Groups
... The number of the first carbon in the double or triple bond is included in the name to locate the double or triple bond. ...
... The number of the first carbon in the double or triple bond is included in the name to locate the double or triple bond. ...
ALCOHOLS
... deep blue solution containing a complex copper(II) ion is formed. When aliphatic aldehydes are warmed with Fehling’s solution, they reduce it to copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, which appears as a brick red precipitate. There is no reaction with ketones. RCHO + 2Cu2+ + 5OH- ...
... deep blue solution containing a complex copper(II) ion is formed. When aliphatic aldehydes are warmed with Fehling’s solution, they reduce it to copper(I) oxide, Cu2O, which appears as a brick red precipitate. There is no reaction with ketones. RCHO + 2Cu2+ + 5OH- ...
functional groups - Beal Science Dept.
... 1. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hy ...
... 1. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hy ...
Functional Group Handout
... E. Amides: contain a carbonyl group. The carbon atom of the carbonyl group is bonded to another carbon atom and a nitrogen atom. Amides can be primary secondary or tertiary. The nitrogen atom of the primary amide is bonded to the carbonyl carbon and two hydrogens. The nitrogen atom of a secondary am ...
... E. Amides: contain a carbonyl group. The carbon atom of the carbonyl group is bonded to another carbon atom and a nitrogen atom. Amides can be primary secondary or tertiary. The nitrogen atom of the primary amide is bonded to the carbonyl carbon and two hydrogens. The nitrogen atom of a secondary am ...
Chemistry 223 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... Show the mechanism for: presence of AlCl3 ...
... Show the mechanism for: presence of AlCl3 ...
Organic Models
... bond with each other as well as with atoms of other elements. Each carbon atom, however, may make only four covalent bonds. When carbon atoms bond with each other, they form a carbon chain. Compounds containing carbon chains may become a homologous series. A homologous series is a set of compounds t ...
... bond with each other as well as with atoms of other elements. Each carbon atom, however, may make only four covalent bonds. When carbon atoms bond with each other, they form a carbon chain. Compounds containing carbon chains may become a homologous series. A homologous series is a set of compounds t ...
Ch. 14 Alcohols, Ethers, & Thiols
... • 1o alcohols are more difficult to dehydrate. They require high temperatures in concentrate H2SO4 • 2o alcohols require lower temperatures • 3o alcohols are the easiest to dehydrate and undergo dehydration only slightly above room temperature ...
... • 1o alcohols are more difficult to dehydrate. They require high temperatures in concentrate H2SO4 • 2o alcohols require lower temperatures • 3o alcohols are the easiest to dehydrate and undergo dehydration only slightly above room temperature ...
Heck Reactions
... natural product total synthesis." Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2945-2963. Beletskaya, I. P.; Cheprakov, A. V. "The Heck reaction as a sharpening stone of palladium catalysis." Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009-3066. ...
... natural product total synthesis." Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2945-2963. Beletskaya, I. P.; Cheprakov, A. V. "The Heck reaction as a sharpening stone of palladium catalysis." Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 3009-3066. ...
CHAPTER 4 CARBON AND THE MOLECULAR DIVERSITY OF LIFE
... 1. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hy ...
... 1. Functional groups contribute to the molecular diversity of life • The components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions are known as functional groups. • Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hy ...
TASK CARD: Modeling Activity Gumdrop Macromolecules (pgs. 166
... this bonding process, two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen are removed from the linking sugars. These atoms join together to produce a molecule of water. Hence, this type of sugar bonding is called dehydration synthesis. 1. Construct a second model of the glucose model. 2. Place both models ...
... this bonding process, two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen are removed from the linking sugars. These atoms join together to produce a molecule of water. Hence, this type of sugar bonding is called dehydration synthesis. 1. Construct a second model of the glucose model. 2. Place both models ...
Chemistry 250A -- Exam #3 Answer Key -
... hydrogen in this orientation and therefore elimination proceeds to give only the product shown. By contrast, the second reaction proceeds via an E1 mechanism as shown below. (The absence of a strong base makes the E2 mechanism unfavorable.) In the E1 mechanism the leaving group leaves first, produci ...
... hydrogen in this orientation and therefore elimination proceeds to give only the product shown. By contrast, the second reaction proceeds via an E1 mechanism as shown below. (The absence of a strong base makes the E2 mechanism unfavorable.) In the E1 mechanism the leaving group leaves first, produci ...
- Cypress HS
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
View PDF - Cypress HS
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Chapter 25
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.

![Synthesis of [RuCl2(NO)2(THF)] and its Double CN BondForming](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001773792_1-763ad0089529123821e01ed17077bbf2-300x300.png)




















