Synthesis_of_Organometallic_Compounds
... • less application in organic synthesis than palladium compounds, probably because their chemistry is more complicated. ...
... • less application in organic synthesis than palladium compounds, probably because their chemistry is more complicated. ...
4.5: Bonding in Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... 4.4: Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides - Alcohols and alkyl halides are classified as according to the degree of substitution of the carbon bearing the halogen or -OH group OH primary (1°) : one alkyl substituent secondary (2°) : two alkyl substituents tertiary (3°) : three alkyl substituents 2- ...
... 4.4: Classes of Alcohols and Alkyl Halides - Alcohols and alkyl halides are classified as according to the degree of substitution of the carbon bearing the halogen or -OH group OH primary (1°) : one alkyl substituent secondary (2°) : two alkyl substituents tertiary (3°) : three alkyl substituents 2- ...
Unit 13 Organic Chem R
... They say a picture is worth a thousand words. The design of the IUPAC naming system is such that it takes far less than a thousand words to name a specific molecule’s structure. © 2011, Mark Rosengarten ...
... They say a picture is worth a thousand words. The design of the IUPAC naming system is such that it takes far less than a thousand words to name a specific molecule’s structure. © 2011, Mark Rosengarten ...
Functional Groups
... Functional Groups functional group: an atom, or group of atoms (with specific connectivity), exhibiting identical chemical reactivity regardless of the molecule containing it; the reactivity of individual functional groups dictates the reactivity of the molecule of which they are a part ...
... Functional Groups functional group: an atom, or group of atoms (with specific connectivity), exhibiting identical chemical reactivity regardless of the molecule containing it; the reactivity of individual functional groups dictates the reactivity of the molecule of which they are a part ...
Chapter 20 Amines-part 2
... t Coupling with phenol occurs best in slightly alkaline solution l Generates a phenoxideion that couples more rapidly l If the solution is too alkaline, a nonreactive diazohydroxide ...
... t Coupling with phenol occurs best in slightly alkaline solution l Generates a phenoxideion that couples more rapidly l If the solution is too alkaline, a nonreactive diazohydroxide ...
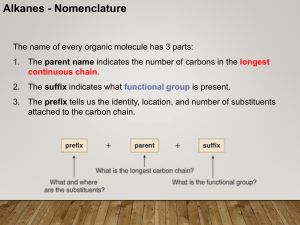
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture 1
... • In the IUPAC system, change the –ane ending of the parent alkane name to the suffix –yne. • Choose the longest continuous chain that contains both atoms of the triple bond and number the chain to give the triple bond the lower number. ...
... • In the IUPAC system, change the –ane ending of the parent alkane name to the suffix –yne. • Choose the longest continuous chain that contains both atoms of the triple bond and number the chain to give the triple bond the lower number. ...
Document
... At the right hand side of the spectrum, the peaks become more complicated, but since the same compound produces exactly the same pattern, this region can be used to identify a particular compound, so this is called the "fingerprint region". A chemist would look at the key peaks to determine the type ...
... At the right hand side of the spectrum, the peaks become more complicated, but since the same compound produces exactly the same pattern, this region can be used to identify a particular compound, so this is called the "fingerprint region". A chemist would look at the key peaks to determine the type ...
reactions of alcohols with alkenes over an aluminum
... Figure 1. Mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction of 2-methyl pent-2-ene with alcohols (Al-montmorillonite catalyst). methyl t-butyl ether when using a clay catalyst (Bylina et al.. 1980: Adams et al.. 1981b). At this temperature methanol is the only alcohol to form a di-alkyl ether. whereas Balla ...
... Figure 1. Mechanism for the acid-catalyzed reaction of 2-methyl pent-2-ene with alcohols (Al-montmorillonite catalyst). methyl t-butyl ether when using a clay catalyst (Bylina et al.. 1980: Adams et al.. 1981b). At this temperature methanol is the only alcohol to form a di-alkyl ether. whereas Balla ...
03 AP Bio Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life
... “CNOPS” can combine together to make double and triple covalent bonds • However, when two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, the atoms joined to the carbons are in the same plane as the carbons • Why is this important? Because the shape of a molecule dictates its reactivity, thus its functio ...
... “CNOPS” can combine together to make double and triple covalent bonds • However, when two carbon atoms are joined by a double bond, the atoms joined to the carbons are in the same plane as the carbons • Why is this important? Because the shape of a molecule dictates its reactivity, thus its functio ...
Chemistry 3719L – Week 9 Reduction of Benzil with Sodium
... • Filter the solid, dry for 15 minutes then weigh the product and obtain the melting point. • If possible you should obtain an IR spectrum of your product to compare with that of the benzil starting material. This information will be used in your report to prove that the functional group conversion ...
... • Filter the solid, dry for 15 minutes then weigh the product and obtain the melting point. • If possible you should obtain an IR spectrum of your product to compare with that of the benzil starting material. This information will be used in your report to prove that the functional group conversion ...
Review Questions
... VESPR theory-know the shapes [linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, pyramidal, bent, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral, square planar Orbitals: s, p, d, f and hybridized orbitals sp, sp2, sp3 Formation of single, double and triple bonds Problems: 1. Draw Lewis Structure for each of the followin ...
... VESPR theory-know the shapes [linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, pyramidal, bent, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral, square planar Orbitals: s, p, d, f and hybridized orbitals sp, sp2, sp3 Formation of single, double and triple bonds Problems: 1. Draw Lewis Structure for each of the followin ...
Qualitative Identification of Functional Groups
... Zinc Chloride in HCl (a.k.a Lucas Test) • Tests for the presence of secondary and tertiary alcohols only. • Low molecular mass alcohols are polar and water soluble. In this reaction they are changed to alkyl halides which are insoluble in water. A positive test will be the presence of an insoluble ...
... Zinc Chloride in HCl (a.k.a Lucas Test) • Tests for the presence of secondary and tertiary alcohols only. • Low molecular mass alcohols are polar and water soluble. In this reaction they are changed to alkyl halides which are insoluble in water. A positive test will be the presence of an insoluble ...
Alcohol Solubility
... Hexadecane refers to 16 Carbons. The structure of n-hexadecanol is as follows: CH3(CH2)15 OH What would explain why it is a solid, rather than a liquid? Hexadecanol is a solid because it has a bulky alkyl group in which all the Carbons are having covalent bonds and as covalent compounds are more str ...
... Hexadecane refers to 16 Carbons. The structure of n-hexadecanol is as follows: CH3(CH2)15 OH What would explain why it is a solid, rather than a liquid? Hexadecanol is a solid because it has a bulky alkyl group in which all the Carbons are having covalent bonds and as covalent compounds are more str ...
First palladium- and nickel-catalyzed oxidative
... Early work from our laboratory employed preformed imidoosmium(VIII) reagents, which display unprecedented reactivity and selectivity toward selective diamination [3]. In addition, chiral versions of these reactions allowed for the development of diastereoselective [4] and enantioselective [5] alkene ...
... Early work from our laboratory employed preformed imidoosmium(VIII) reagents, which display unprecedented reactivity and selectivity toward selective diamination [3]. In addition, chiral versions of these reactions allowed for the development of diastereoselective [4] and enantioselective [5] alkene ...
5 · Chemical Reactions
... You will be given a periodic table and a solubility chart. No other resources are allowed. You have fifty (50) minutes to complete this test, unless other arrangements have been made. Please transfer your answers for questions in Sections 1 and 2 onto the Answer Document. Work for these questions wi ...
... You will be given a periodic table and a solubility chart. No other resources are allowed. You have fifty (50) minutes to complete this test, unless other arrangements have been made. Please transfer your answers for questions in Sections 1 and 2 onto the Answer Document. Work for these questions wi ...
Aldehydes and Ketones - University of Nebraska Omaha
... Aldehydes and Ketones Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones • Both aldehydes and ketones have a carbonyl group, a carbon atom doubly bonded to an oxygen atom, C=O. • Aldehydes have a carbonyl group bonded to an H atom. • Ketones have a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. ...
... Aldehydes and Ketones Structure of Aldehydes and Ketones • Both aldehydes and ketones have a carbonyl group, a carbon atom doubly bonded to an oxygen atom, C=O. • Aldehydes have a carbonyl group bonded to an H atom. • Ketones have a carbonyl group bonded to two carbon atoms. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.