Oxidation of alcohols and aldehydes
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
... Further oxidation of a primary alcohol • Using a process known as REFLUX, the reaction contents are continually heated at their boiling point temperature, so HOTTER and LONGER heating then alcohol conversion to an aldehyde • Still uses acidified potassium dichromate Primary + Oxidising Carboxylic ...
Crazy Carbon - Cloudfront.net
... ex. Vision involves light changing chemical rhodopsin from one geometric isomer to another. ...
... ex. Vision involves light changing chemical rhodopsin from one geometric isomer to another. ...
Organic Unit - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... 4. Do any groups have the same general formula? b) Two Physical Properties - The presence of a functional group has a major effect on the physical properties of a compound. Intermolecular forces determine many physical properties, such as solubility and boiling point: - hydrocarbons – have only weak ...
... 4. Do any groups have the same general formula? b) Two Physical Properties - The presence of a functional group has a major effect on the physical properties of a compound. Intermolecular forces determine many physical properties, such as solubility and boiling point: - hydrocarbons – have only weak ...
Isomers
... Optical isomers can be distinguished by the way they interact with plane polarized light. One enantiomer will rotate polarized light to the right, the other to the left. Racemic mixture equal amounts of both enantiomers does ...
... Optical isomers can be distinguished by the way they interact with plane polarized light. One enantiomer will rotate polarized light to the right, the other to the left. Racemic mixture equal amounts of both enantiomers does ...
Chapter 4 Carbon Chemistry
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
c - Tan Lam
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
Synthesizing Organic Compounds
... Note: The questions are taken from the Nelson Chemistry 12 textbook. Nelson (2003). Synthesizing Organic Compounds, Chemistry 12 (pg. 82) 1. A food additive that is named as a single ingredient is often a mixture of many compounds. For example, a typical “artificial strawberry flavour” found in a mi ...
... Note: The questions are taken from the Nelson Chemistry 12 textbook. Nelson (2003). Synthesizing Organic Compounds, Chemistry 12 (pg. 82) 1. A food additive that is named as a single ingredient is often a mixture of many compounds. For example, a typical “artificial strawberry flavour” found in a mi ...
Review
... Mono-substituted cyclohexanes: equatorial substituents are more stable (1,3-diaxial interactions); tert-butylcyclohexane Disubstituted cyclohexanes: cis/trans-isomerism; comparison of stability (the fewer are the axial substituents, the more stable is the disubstituted cyclohexane. Fused rings (cis ...
... Mono-substituted cyclohexanes: equatorial substituents are more stable (1,3-diaxial interactions); tert-butylcyclohexane Disubstituted cyclohexanes: cis/trans-isomerism; comparison of stability (the fewer are the axial substituents, the more stable is the disubstituted cyclohexane. Fused rings (cis ...
Solution Key - Chemistry With BT
... Is the stereoisomer obtained in the reaction above optically active? Explain. No, it is not possible to obtain a chiral product from an achiral reactant unless chiral reaction conditions are utilized, such as enzyme catalysis ...
... Is the stereoisomer obtained in the reaction above optically active? Explain. No, it is not possible to obtain a chiral product from an achiral reactant unless chiral reaction conditions are utilized, such as enzyme catalysis ...
functional groups
... phosphorus bound to four oxygen atoms (three with single bonds and one with a double bond). • A phosphate group connects to the carbon backbone via one of its oxygen atoms. • Phosphate groups are anions with two negative charges as two protons have dissociated from the oxygen atoms. • One function o ...
... phosphorus bound to four oxygen atoms (three with single bonds and one with a double bond). • A phosphate group connects to the carbon backbone via one of its oxygen atoms. • Phosphate groups are anions with two negative charges as two protons have dissociated from the oxygen atoms. • One function o ...
Phy Properties - Rosebank Progress College
... temperature. Alkenes – two to four gasses, 5 to15 liquids and more than 15 are solids at room temperature. Alkynes – two to four gasses, 5 to 17 liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. ...
... temperature. Alkenes – two to four gasses, 5 to15 liquids and more than 15 are solids at room temperature. Alkynes – two to four gasses, 5 to 17 liquids and more than 17 solids at room temperature. ...
... 6. How will you prepare phenyl methyl ether from phenol using Williamson’s synthesis? 7. What happens when calcium acetate is heated? Give its equation. 8. What is Norrish type –I reaction. 9. What is trans esterification. 10. Arrange the following in terms of increasing acid strength and give reaso ...
activity 1-071510 - ids
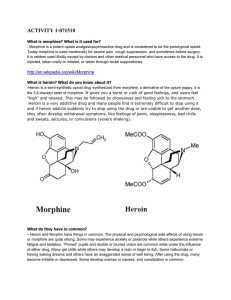
... heroin addicts because the drug is so much stronger and easier to come by. Both morphine addiction and heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
... heroin addicts because the drug is so much stronger and easier to come by. Both morphine addiction and heroin addiction are deadly diseases that require medical treatment. ...
Honors Chemistry Name Julien Period _____ Date Chapter 17
... STEP 2: Number the chain starting at the end closer to the —OH. For simple alcohols, the common name gives the name of the carbon chain as an alkyl group (ends with yl) followed by alcohol. 1-propanol is commonly called propyl alcohol. Alcohols with one or two carbon atoms do not require a number f ...
... STEP 2: Number the chain starting at the end closer to the —OH. For simple alcohols, the common name gives the name of the carbon chain as an alkyl group (ends with yl) followed by alcohol. 1-propanol is commonly called propyl alcohol. Alcohols with one or two carbon atoms do not require a number f ...
Document
... • Imine formation is also a nucleophilic addition. • There is a different end result here, though as elimination of water occurs. • The initial reaction is attack of the amine on the carbonyl to give the alkoxide intermediate as normal. • Following protonation of the alkoxide and loss of the proton ...
... • Imine formation is also a nucleophilic addition. • There is a different end result here, though as elimination of water occurs. • The initial reaction is attack of the amine on the carbonyl to give the alkoxide intermediate as normal. • Following protonation of the alkoxide and loss of the proton ...
Organic Chemistry Chapter 2 - Snow College | It's SNOWing
... • Name is written as one word • For four groups attached to a nitrogen, use alkyl groups and then ammonium • IUPAC – replace the e with amine • N – designates the alkyl group is attached to the N and not a C ...
... • Name is written as one word • For four groups attached to a nitrogen, use alkyl groups and then ammonium • IUPAC – replace the e with amine • N – designates the alkyl group is attached to the N and not a C ...
Functional Groups
... Your mind map should have at least produce a mind map to four sections including: summarise the following classes Functional group of compounds and their Name of functional group characteristic functional groups: ...
... Your mind map should have at least produce a mind map to four sections including: summarise the following classes Functional group of compounds and their Name of functional group characteristic functional groups: ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 14. a) Write the mechanism for the reduction of CH3COOC2H5 by LAH. b) How will you prepare isobutyl alcohol using a Grignard reagent? 15. An amide(A) having molecular formula C3H7ON on hydrolysis gives an acid C3H6O2(B) which upon chlorination in the presence of red phosphorus produces a chloroacid( ...
... 14. a) Write the mechanism for the reduction of CH3COOC2H5 by LAH. b) How will you prepare isobutyl alcohol using a Grignard reagent? 15. An amide(A) having molecular formula C3H7ON on hydrolysis gives an acid C3H6O2(B) which upon chlorination in the presence of red phosphorus produces a chloroacid( ...
Alcohols
... Secondary alcohols are prepared from Grignard reagent and aldehyde other than formaldehyde. ...
... Secondary alcohols are prepared from Grignard reagent and aldehyde other than formaldehyde. ...
Powerpoint on chapter 4 and 5
... √ CH2O formula; √ multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups and 1 carbonyl (C=O) group: aldehyde (aldoses) sugar ketone sugar √ cellular respiration; √ raw material for amino acids and fatty acids – Pentoses (5 carbons) – Hexoses (6 carbons) – Can be a ring or linear. ...
... √ CH2O formula; √ multiple hydroxyl (-OH) groups and 1 carbonyl (C=O) group: aldehyde (aldoses) sugar ketone sugar √ cellular respiration; √ raw material for amino acids and fatty acids – Pentoses (5 carbons) – Hexoses (6 carbons) – Can be a ring or linear. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.