
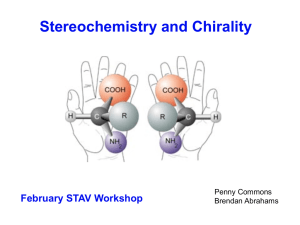
Asymmetry and Stereoisomers
... • the carbon atom with reference to valence number, bond strength, stability of carbon bonds with other elements and the formation of isomers to explain carbon compound diversity, including identification of chiral centres in optical isomers of simple organic compounds and distinction between cis- a ...
... • the carbon atom with reference to valence number, bond strength, stability of carbon bonds with other elements and the formation of isomers to explain carbon compound diversity, including identification of chiral centres in optical isomers of simple organic compounds and distinction between cis- a ...
C h e m g u i d e ... ALCOHOLS: THE REACTION WITH SODIUM
... a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you have an alcohol. What else might cause the result you described in part (b)? d) Suppose you added a small ...
... a) Why is it important to test the pH of the liquid before adding the sodium? b) What would you observe if the liquid was actually an alcohol? c) Observing this isn’t enough to be sure that you have an alcohol. What else might cause the result you described in part (b)? d) Suppose you added a small ...
reactions of alcohols
... complex ion of [Ag(NH3)2]+ . • Conditions: heat gently • Reaction: aldehydes only are oxidised by Tollen’s reagent into a carboxylic acid and the silver(I) ions are reduced to silver atoms coating the inside of the test tube . The silver coating the inside of test tube is called a silver mirror. ...
... complex ion of [Ag(NH3)2]+ . • Conditions: heat gently • Reaction: aldehydes only are oxidised by Tollen’s reagent into a carboxylic acid and the silver(I) ions are reduced to silver atoms coating the inside of the test tube . The silver coating the inside of test tube is called a silver mirror. ...
Exam 2
... Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical results of the Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 mechanism -If given a reaction be able to ...
... Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical results of the Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 mechanism -If given a reaction be able to ...
CHEM 210 Nomenclature Lecture
... • When an OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group. • Because the functional group is at C1, the 1 is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered in a clockwise or counterclockwise fashion to give the next substituent the lowest number. ...
... • When an OH group is bonded to a ring, the ring is numbered beginning with the OH group. • Because the functional group is at C1, the 1 is usually omitted from the name. • The ring is then numbered in a clockwise or counterclockwise fashion to give the next substituent the lowest number. ...
3. Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes
... Functional group - collection of atoms at a site that have a characteristic behavior in all molecules where it occurs The group reacts in a typical way, generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example, the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way ...
... Functional group - collection of atoms at a site that have a characteristic behavior in all molecules where it occurs The group reacts in a typical way, generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example, the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way ...
St.Mont Fort School Bhopal Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Q 1 Give
... 12. CCl4 and water are immiscible whereas ethanol and water are miscible in all proportions. Correlate this behaviour with molecular structure of these compounds. 13. State Henry’s Law ? What is the significance ? 14. Derive an equation to express that relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solu ...
... 12. CCl4 and water are immiscible whereas ethanol and water are miscible in all proportions. Correlate this behaviour with molecular structure of these compounds. 13. State Henry’s Law ? What is the significance ? 14. Derive an equation to express that relative lowering of vapour pressure for a solu ...
Answer Key - OISE-IS-Chemistry-2011-2012
... 1. Carbon is able to form large numbers of organic compounds because carbon can a. form 4 bonds b. form single, double and triple bonds c. form chains, rings, spheres and sheets d. the carbon-carbon bond is very stable e. all of the above 2. From the following list, select the two molecules that are ...
... 1. Carbon is able to form large numbers of organic compounds because carbon can a. form 4 bonds b. form single, double and triple bonds c. form chains, rings, spheres and sheets d. the carbon-carbon bond is very stable e. all of the above 2. From the following list, select the two molecules that are ...
Study guide/lecture topics
... Retrosynthetic analysis This chapter provides detail on retrosynthetic formalisms called “synthons” that are NOT AT ALL required for this course, but that some may find helpful for synthetic ...
... Retrosynthetic analysis This chapter provides detail on retrosynthetic formalisms called “synthons” that are NOT AT ALL required for this course, but that some may find helpful for synthetic ...
Survival Organic Chemistry
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
UNIT_3_PART_5[3]
... When the metal involved in the ionic bond has more than one oxidations state/possible charge we need to identify which ion it is. This usually occurs with the transition metals. Any ion that appears on your common ion sheet more than once is one of these types of metals. There are 2 ways to do thi ...
... When the metal involved in the ionic bond has more than one oxidations state/possible charge we need to identify which ion it is. This usually occurs with the transition metals. Any ion that appears on your common ion sheet more than once is one of these types of metals. There are 2 ways to do thi ...
Organic reactions and mechanisms
... The classical structural theory of organic reactions The reactions of organic compounds were explained based on their structural formulae. They are essentially molecular in nature. The classical ‘structural theory’ visualized that the chemical behavior of an organic compound was determined by the fu ...
... The classical structural theory of organic reactions The reactions of organic compounds were explained based on their structural formulae. They are essentially molecular in nature. The classical ‘structural theory’ visualized that the chemical behavior of an organic compound was determined by the fu ...
9/13/2016 Nomenclature (Naming) Rules IUPAC has designed a
... Alkanes can be joined at the ends to make ring compounds. In order to do this, two hydrogens must be lost. Thus, the general formula for cycloalkanes is CnH2n. Rule 1: Count the number of C's in the ring. If greater than or equal to the largest substituent chain, the ring is the parent. If a substit ...
... Alkanes can be joined at the ends to make ring compounds. In order to do this, two hydrogens must be lost. Thus, the general formula for cycloalkanes is CnH2n. Rule 1: Count the number of C's in the ring. If greater than or equal to the largest substituent chain, the ring is the parent. If a substit ...
Organic for Chem II
... CH4 CH3CH3 CH3CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 ...
... CH4 CH3CH3 CH3CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 ...
Part 1
... a) thing you’re naming the compound after (double bond if alkene; -OH group if alcohol, etc) note: for multiple double bonds -diene, -triene, -tetraene b) first branch/substituent group c) If both ends have the same first branching number, then number chain to minimize position of second branch (an ...
... a) thing you’re naming the compound after (double bond if alkene; -OH group if alcohol, etc) note: for multiple double bonds -diene, -triene, -tetraene b) first branch/substituent group c) If both ends have the same first branching number, then number chain to minimize position of second branch (an ...
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL
... (b) Suggest two changes to experiment C which would increase the speed of the reaction and explain why the speed would increase. The volume of the acid, the concentration of the acid and the mass of magnesium used were kept the same. change 1 ......................................................... ...
... (b) Suggest two changes to experiment C which would increase the speed of the reaction and explain why the speed would increase. The volume of the acid, the concentration of the acid and the mass of magnesium used were kept the same. change 1 ......................................................... ...
paper 14 organic synthesis: disconnection approach - e
... Syllabus for Post-Graduate Course in Chemistry ...
... Syllabus for Post-Graduate Course in Chemistry ...
Ch. 8 Carbon Chemistry
... B. Form stable compounds with halogen family C. If Hydrogen is substituted, entirely different compound is made D. A substituted hydrocarbon is when atoms of other elements replace one or more atom/s. ...
... B. Form stable compounds with halogen family C. If Hydrogen is substituted, entirely different compound is made D. A substituted hydrocarbon is when atoms of other elements replace one or more atom/s. ...
Cell Molecules
... Are the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions, and give each molecule its unique properties. – Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. ...
... Are the components of organic molecules that are most commonly involved in chemical reactions, and give each molecule its unique properties. – Functional groups are attachments that replace one or more hydrogen atoms to the carbon skeleton of the hydrocarbon. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.











![UNIT_3_PART_5[3]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/013887813_1-e384d1258759e65beb0bedcc6881c6f9-300x300.png)









