View PDF - Cypress HS
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
... calculate the value of ∆H for the complete combustion of one mole of pentane. (d) Under identical conditions, a sample of an unknown gas effuses into a vacuum at twice the rate that a sample of pentane gas effuses. Calculate the molar mass of the unknown gas. (e) The structural formula of one isomer ...
Topic 7 Assessed Homework - A
... C8H18 is obtained by the catalytic cracking of suitable heavy fractions. State what is meant by the term cracking and name the catalyst used in catalytic cracking. Write an equation to show how one molecule of C14H30 is cracked to form one molecule of C8H18 and one molecule of another hydrocarbon. E ...
... C8H18 is obtained by the catalytic cracking of suitable heavy fractions. State what is meant by the term cracking and name the catalyst used in catalytic cracking. Write an equation to show how one molecule of C14H30 is cracked to form one molecule of C8H18 and one molecule of another hydrocarbon. E ...
ch04 by Dr. Dina
... “Straight-chain” alkanes have a zig-zag orientation when they are in their most straight orientation ...
... “Straight-chain” alkanes have a zig-zag orientation when they are in their most straight orientation ...
Non-Heme Iron Catalyzed Oxidation of Alkanes to Alcohols via
... (MPPH) or phenylperacetic acid (PPAA) to produce a highly reactive iron-based intermediate exclusively through a pathway characterized by heterolytic O-O bond cleavage will be detailed. Low temperature reactions of the diferrous complex with either oxygen atom donor molecules, MPPH or PPAA cleanly g ...
... (MPPH) or phenylperacetic acid (PPAA) to produce a highly reactive iron-based intermediate exclusively through a pathway characterized by heterolytic O-O bond cleavage will be detailed. Low temperature reactions of the diferrous complex with either oxygen atom donor molecules, MPPH or PPAA cleanly g ...
chem 464l survival guide
... As an exercise, draw all the resonance structures for an ester. Which resonance structure most clearly illustrates the electrophilic character of an ester? Now draw all the resonance forms for a ketone. Which resonance form(s) illustrate why the ester is less electrophilic than a ketone (i.e. the on ...
... As an exercise, draw all the resonance structures for an ester. Which resonance structure most clearly illustrates the electrophilic character of an ester? Now draw all the resonance forms for a ketone. Which resonance form(s) illustrate why the ester is less electrophilic than a ketone (i.e. the on ...
Document
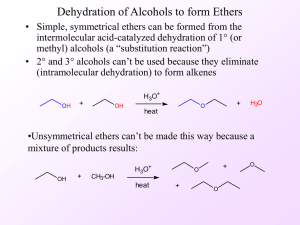
... • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the reaction of (CH3)3COCH3 with HI, the 3° alkyl group undergoes nucleophilic substi ...
... • When 2° or 3° alkyl groups are bonded to the ether oxygen, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN1 mechanism involving a carbocation. With methyl or 1° R groups, the C—O bond is cleaved by an SN2 mechanism. Example: In the reaction of (CH3)3COCH3 with HI, the 3° alkyl group undergoes nucleophilic substi ...
Carbon Chemistry
... molecules by bonding to four other atoms • Carbon compounds range from simple molecules to complex ones • Carbon has four valence electrons and may form single, double, triple, or quadruple bonds ...
... molecules by bonding to four other atoms • Carbon compounds range from simple molecules to complex ones • Carbon has four valence electrons and may form single, double, triple, or quadruple bonds ...
Rates of Hydrolysis of Some Halogeno-compounds
... the preparation of alcohols, ethers, esters, nitrides and amines when substitution occurs with by —OH, —OR, —OOCCH3, —CN and —NH2 groups respectively. ...
... the preparation of alcohols, ethers, esters, nitrides and amines when substitution occurs with by —OH, —OR, —OOCCH3, —CN and —NH2 groups respectively. ...
c - Down the Rabbit Hole
... • Vitalism (life force outside physical & chemical laws) Berzelius • Mechanism (all natural phenomena are governed by physical & chemical laws) Miller • Carbon unparalleled in its ability to form molecules that are large, complex and diverse. Why? ...
... • Vitalism (life force outside physical & chemical laws) Berzelius • Mechanism (all natural phenomena are governed by physical & chemical laws) Miller • Carbon unparalleled in its ability to form molecules that are large, complex and diverse. Why? ...
Alkanes File
... Starter: Name your compound, draw its full structural formula and skeletal formula, and identify all functional groups present ...
... Starter: Name your compound, draw its full structural formula and skeletal formula, and identify all functional groups present ...
Download PDF
... Course Textbook: “Organic Chemistry,” by Smith, 4th ed; class interaction “CPS RF keypad” to be registered to the course; will be used for daily in-class quizzes. “Connect” on-line or take home problem sets will be assigned about every 3rd day to be turned in on specific dates and graded. Optional C ...
... Course Textbook: “Organic Chemistry,” by Smith, 4th ed; class interaction “CPS RF keypad” to be registered to the course; will be used for daily in-class quizzes. “Connect” on-line or take home problem sets will be assigned about every 3rd day to be turned in on specific dates and graded. Optional C ...
alcohols - profpaz.com
... · This rule is summarized as Saytzeff’s rule, which states that during intramolecular dehydration, if there is a choice of positions for the carboncarbon double bond, the preferred location is the one that generally gives the more highly substituted alkene – that is, the alkene with the most al ...
... · This rule is summarized as Saytzeff’s rule, which states that during intramolecular dehydration, if there is a choice of positions for the carboncarbon double bond, the preferred location is the one that generally gives the more highly substituted alkene – that is, the alkene with the most al ...
Unit 1 Chemistry
... Stanley Miller was able to synthesize simple amino acids but it shows us how complicated life simplest pieces are and how unlikely it is that they would have ...
... Stanley Miller was able to synthesize simple amino acids but it shows us how complicated life simplest pieces are and how unlikely it is that they would have ...
Chemical Reactions
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
... Don’t forget about the diatomic elements! (Br, I, N, Cl, H, O, F) For example, Oxygen is O2 as an element. In a compound, it can’t be a diatomic element because it’s not an element anymore, it’s a compound! ...
Document
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
... the carbon skeleton of the organic molecule. (Do not confuse this functional group with the hydroxide ion, OH–.) ...
The Baylis–Hillman reaction is an organic reaction of an aldehyde
... shifted toward modifications of the Henry Reaction to overcome this synthetic challenge. One of the most frequently employed ways to induce enantio- or diastereoselectivity in the Henry Reaction has been through the use of chiral metal catalysts in which the nitro group and carbonyl oxygen coordinat ...
... shifted toward modifications of the Henry Reaction to overcome this synthetic challenge. One of the most frequently employed ways to induce enantio- or diastereoselectivity in the Henry Reaction has been through the use of chiral metal catalysts in which the nitro group and carbonyl oxygen coordinat ...
Experiment 2. Reduction of copper (II) hydroxide with glucose in
... 5.3. Chemical properties of glucose: formation of helates, О– and N– glycosides, alkylation, acetylation. 5.4. The formulas to know: glucose, fructose, ribose, desoxyribose and their derivatives (glycone, glycarone, glycurone acids, glucosamine’s, phosphor esters). 6. The questions for individual le ...
... 5.3. Chemical properties of glucose: formation of helates, О– and N– glycosides, alkylation, acetylation. 5.4. The formulas to know: glucose, fructose, ribose, desoxyribose and their derivatives (glycone, glycarone, glycurone acids, glucosamine’s, phosphor esters). 6. The questions for individual le ...
Chem 350 Jasperse Ch. 6 Summary of Reaction Types, Ch. 4
... with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a reactive species, whether strong anion or an acid, to start the first step a. If acidic, ...
... with the reaction classification above a. If the reaction is cationic, don’t show anionic intermediates b. If the reaction is anionic, don’t show cationic intermediates 4. Usually conditions are ionic. 5. Use a reactive species, whether strong anion or an acid, to start the first step a. If acidic, ...
2.7 INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL GROUPS
... As we have seen, the number of possible organic compounds is virtually limitless. How can anyone learn the chemistry of all of them? Fortunately, we do not need to learn an entire new set of chemical reactions for each new compound encountered. A particular arrangement or group of atoms has very sim ...
... As we have seen, the number of possible organic compounds is virtually limitless. How can anyone learn the chemistry of all of them? Fortunately, we do not need to learn an entire new set of chemical reactions for each new compound encountered. A particular arrangement or group of atoms has very sim ...
102 Lecture Ch14b
... alcohols all the way to carboxylic acids • Secondary alcohols can be oxidized with either reagent PCC ...
... alcohols all the way to carboxylic acids • Secondary alcohols can be oxidized with either reagent PCC ...
alcohol - Portal UniMAP
... is one which electron transfer occurs In organic chemistry this tends to have a significance more on par of oxygen content Oxidation reactions as ones in which carbon gains bonds to oxygen Reduction reactions as ones in which carbon atoms lose bonds to oxygen. ...
... is one which electron transfer occurs In organic chemistry this tends to have a significance more on par of oxygen content Oxidation reactions as ones in which carbon gains bonds to oxygen Reduction reactions as ones in which carbon atoms lose bonds to oxygen. ...
Preparation of Alcohols
... A: Substitution only. Hydroxide nucleophile; difficult reaction because of competing elimination (E2). See Carey Chpt. 8. B: Hydration can go in two ways to give different regioselectivities. Oxymercuration-demercuration gives Markovnikov product, hydroboration/oxidation gives opposite. Generally cl ...
... A: Substitution only. Hydroxide nucleophile; difficult reaction because of competing elimination (E2). See Carey Chpt. 8. B: Hydration can go in two ways to give different regioselectivities. Oxymercuration-demercuration gives Markovnikov product, hydroboration/oxidation gives opposite. Generally cl ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.