Alkenes 3 - ChemWeb (UCC)
... Reading assignment: Work through the practice problem on p. 200 of McMurry (5th Ed.) and problems 6.9 to 6.11 on p. 201. ...
... Reading assignment: Work through the practice problem on p. 200 of McMurry (5th Ed.) and problems 6.9 to 6.11 on p. 201. ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
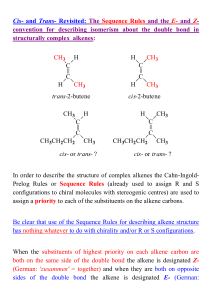
... 4. Write the Woodward Hoffmann rules for electrocyclization reaction. 5. Explain the change in the geometry of excited state molecule in a photochemical process and the variation in its physical property. 6. What is Norrish type I and II cleavage reactions? Give suitable examples. 7. What are the im ...
... 4. Write the Woodward Hoffmann rules for electrocyclization reaction. 5. Explain the change in the geometry of excited state molecule in a photochemical process and the variation in its physical property. 6. What is Norrish type I and II cleavage reactions? Give suitable examples. 7. What are the im ...
EXPERIMENT 1: Survival Organic Chemistry: Molecular Models
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
... manipulating molecular models helps their understanding of the spatial relationships of atoms in molecules. Using computer graphics will also provide a new way to view and manipulate molecular models. Finally, a simple understanding of organic compounds early in the semester will provide you with st ...
U. of Kentucky Chemistry 535 Synthetic Organic Chemistry Spring
... retrosynthetic analysis that leaves no doubt for the reader that you can make the molecule. You may start with molecules containing no less than eight carbon atoms. ...
... retrosynthetic analysis that leaves no doubt for the reader that you can make the molecule. You may start with molecules containing no less than eight carbon atoms. ...
Ethers, Sulfides, Epoxides
... haloform, HCX3 only occurs if there is an a methyl group, a methyl directly attached to the carbonyl. If done with iodine then the formation of iodoform, HCI3, a bright yellow precipitate, is a test for an a methyl group (iodoform test). ...
... haloform, HCX3 only occurs if there is an a methyl group, a methyl directly attached to the carbonyl. If done with iodine then the formation of iodoform, HCI3, a bright yellow precipitate, is a test for an a methyl group (iodoform test). ...
SCH4C: Chemistry, Grade 12, College Preparation
... 1. Which of the following is considered an inference from an observation? a. The precipitate was yellow. b. The metal sank in the water, it must be iron. c. A gas was released when lithium was dropped into water. d. Bubbles form from Alka-Seltzer tablets. 2. Which of the following is considered an o ...
... 1. Which of the following is considered an inference from an observation? a. The precipitate was yellow. b. The metal sank in the water, it must be iron. c. A gas was released when lithium was dropped into water. d. Bubbles form from Alka-Seltzer tablets. 2. Which of the following is considered an o ...
PPTB&W - Gmu - George Mason University
... (346 kJ/mol) vs C-O Bond (358 kJ/mol) is small Si-Si (226 kJ/mo) vs Si-O (368 kJ/mol) difference represents heat lost in bond formation ...
... (346 kJ/mol) vs C-O Bond (358 kJ/mol) is small Si-Si (226 kJ/mo) vs Si-O (368 kJ/mol) difference represents heat lost in bond formation ...
Types of reactions you know:
... b. CuLi and alkyl halide (use this if you need to add to the middle of a chain) ...
... b. CuLi and alkyl halide (use this if you need to add to the middle of a chain) ...
chemistry (paper 2)
... Functional series → double or triple bonds are functional groups. They are ‘add-ons’ that change the chemistry of a carbon chain ...
... Functional series → double or triple bonds are functional groups. They are ‘add-ons’ that change the chemistry of a carbon chain ...
Period 6
... • Substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboxyl group • Main ingredient of vinegar • Found in apples • Causes the stinging feeling in plants ...
... • Substituted hydrocarbon that contains one or more carboxyl group • Main ingredient of vinegar • Found in apples • Causes the stinging feeling in plants ...
CHM 235 Course Outline and Homework in McMurry (6th ed.)
... Bond dissociation energies (Ho = energy used to break bonds–energy gained by making bonds) Energy diagrams (reaction coordinates, transition states, reaction intermediates, RDS) ...
... Bond dissociation energies (Ho = energy used to break bonds–energy gained by making bonds) Energy diagrams (reaction coordinates, transition states, reaction intermediates, RDS) ...
Chapter 13 – Alcohols, Phenols, Ethers, and Thioethers
... tend to stick together much more strongly than alkanes and this affects their physical properties. Before going further, please remember that the effects of the –OH group decrease as the alkane chain becomes longer. Thus, any hydrogen bonding effects in methanol are much larger than those in 1-penta ...
... tend to stick together much more strongly than alkanes and this affects their physical properties. Before going further, please remember that the effects of the –OH group decrease as the alkane chain becomes longer. Thus, any hydrogen bonding effects in methanol are much larger than those in 1-penta ...
Alcohols - Miller, Jonathan
... (often larger molecular masses) formed when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst (small amount of conc. H2SO4). It is an equilibrium reaction. ...
... (often larger molecular masses) formed when an alcohol reacts with a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst (small amount of conc. H2SO4). It is an equilibrium reaction. ...
Fall.2008.Week9.Lesson.1 - reich
... unique formulas. I recognize to balance this reaction it requires 3 moles or 3 molecules on the left, BUT, I’m only speaking about the “types of molecules,” and I’m not invoking the coefficients. ...
... unique formulas. I recognize to balance this reaction it requires 3 moles or 3 molecules on the left, BUT, I’m only speaking about the “types of molecules,” and I’m not invoking the coefficients. ...
Print this page
... These are important in both artificial polymers and in biochemistry, not to mention organic chemistry in general. Alcohol: An oxygen atom singly-bound to one hydrogen atom and one carbon atom. ...
... These are important in both artificial polymers and in biochemistry, not to mention organic chemistry in general. Alcohol: An oxygen atom singly-bound to one hydrogen atom and one carbon atom. ...
aldehydes powerpoint
... • Tollens' reagent is a chemical reagent most commonly used to determine whether a known carbonyl-containing compound is an aldehyde or a ketone. It is usually ammoniacal silver nitrate, but can also be other mixtures, as long as aqueous diamminesilver(I) complex is present. It was named after its d ...
... • Tollens' reagent is a chemical reagent most commonly used to determine whether a known carbonyl-containing compound is an aldehyde or a ketone. It is usually ammoniacal silver nitrate, but can also be other mixtures, as long as aqueous diamminesilver(I) complex is present. It was named after its d ...
Chapter 2.3: Carbon Compounds
... 5. Examples: fats (3 fatty acid chains), phosopholipids (2 fatty acid chains), oils, waxes, ...
... 5. Examples: fats (3 fatty acid chains), phosopholipids (2 fatty acid chains), oils, waxes, ...
Survival Organic Laboratory
... simple Lewis structures, covalent bond, ionic bond, polar covalent bonds, sigma and pi bonds, single, double and triple bonds, bond lengths and angles, resonance, and bond dissociation energies. Your textbook will play an important role as a reference tool in this laboratory. Chapters and sections w ...
... simple Lewis structures, covalent bond, ionic bond, polar covalent bonds, sigma and pi bonds, single, double and triple bonds, bond lengths and angles, resonance, and bond dissociation energies. Your textbook will play an important role as a reference tool in this laboratory. Chapters and sections w ...
無投影片標題
... • Common reagents used: HCl, HBr, HI, PCl3 or PBr3 • The ease of substitution of alcohols: 3° alcohol > 2° alcohol > 1° alcohol > CH3OH • This is related to the stability of the reaction intermediate (i.e. stability of carbocations) ...
... • Common reagents used: HCl, HBr, HI, PCl3 or PBr3 • The ease of substitution of alcohols: 3° alcohol > 2° alcohol > 1° alcohol > CH3OH • This is related to the stability of the reaction intermediate (i.e. stability of carbocations) ...
Amines - MCAT Cooperative
... The building block is the hydrocarbon isoprene Terpene hydrocarbons have molecular formulas (C5H8)n ...
... The building block is the hydrocarbon isoprene Terpene hydrocarbons have molecular formulas (C5H8)n ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.