Chapter 1
... – A way to classify organic compounds into families. – They determine the chemical and physical properties of a compound. – They undergo the same types of chemical reactions. ...
... – A way to classify organic compounds into families. – They determine the chemical and physical properties of a compound. – They undergo the same types of chemical reactions. ...
Carbonyl Compounds_ Properties and Reactions
... Carbonyls show a limited/lack of hydrogen bonding between molecules, whereas the corresponding alcohol will show extensive intermolecular H bonding. Weaker polarity means aldehydes and ketones mix well with polar solvents such as water and will dissolve many organic compounds. ...
... Carbonyls show a limited/lack of hydrogen bonding between molecules, whereas the corresponding alcohol will show extensive intermolecular H bonding. Weaker polarity means aldehydes and ketones mix well with polar solvents such as water and will dissolve many organic compounds. ...
Functional groups and homologous series
... propane C3H8 If one of the hydrogen atoms is removed what is left is known as an alkyl radical R – (e.g methyl CH3–; ethyl C2H5–). When other atoms or groups are attached to an alkyl radical they can form a different series of compounds. These atoms or groups attached are known as functional groups ...
... propane C3H8 If one of the hydrogen atoms is removed what is left is known as an alkyl radical R – (e.g methyl CH3–; ethyl C2H5–). When other atoms or groups are attached to an alkyl radical they can form a different series of compounds. These atoms or groups attached are known as functional groups ...
Nucleophilic Substitution
... interconversion of functional groups. Of particular importance are the reactions of alkyl halides (R-X) and alcohols (R-OH) For alcohols, the range of substitution reactions possible can be increased by utilising the tosylates (R-OTs), an alternative method of converting the -OH to a better leaving ...
... interconversion of functional groups. Of particular importance are the reactions of alkyl halides (R-X) and alcohols (R-OH) For alcohols, the range of substitution reactions possible can be increased by utilising the tosylates (R-OTs), an alternative method of converting the -OH to a better leaving ...
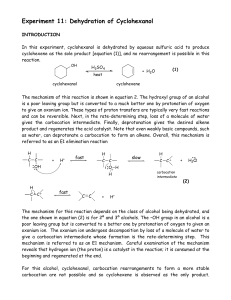
Dehydration of Cyclohexanol
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
... carbocations derived from certain 2°alcohols may undergo rearrangement to form more stable carbocations. This can result in the formation of rearranged isomeric alkenes. Both 2° and 3° alcohols primarily undergo the E1 reaction under these conditions, whereas for 1° alcohols and methyl alcohol, symm ...
2.10 Alcohols notes - A
... - it uses a lot of energy - the ethene comes from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource Ethanol for use in industry is manufactured during this process. 2. Ethanol as a fuel Ethanol is a useful fuel; it burns with a clean flame and is increasingly used in cars: C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3 ...
... - it uses a lot of energy - the ethene comes from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource Ethanol for use in industry is manufactured during this process. 2. Ethanol as a fuel Ethanol is a useful fuel; it burns with a clean flame and is increasingly used in cars: C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3 ...
Macromolecules polymers carbohydrates lipids proteins nucleic
... Diversity results from the unique combination of these subunits How are macromolecules formed? Terms: Polymerization—chemical reactions that link two or more small molecules to form larger molecules with repeating structural units Condensation Reaction—polymerization reaction which form covalent lin ...
... Diversity results from the unique combination of these subunits How are macromolecules formed? Terms: Polymerization—chemical reactions that link two or more small molecules to form larger molecules with repeating structural units Condensation Reaction—polymerization reaction which form covalent lin ...
H + - uaschemistry
... • A group that donates electrons, such as CH3, will make the anion less stable (stronger conjugate base) and the acid weaker. • Q: What would the order of pKa, from largest to smallest, be for ethanol, phenol, 2-methylphenol, and 2,4,6-trinitrophenol? ...
... • A group that donates electrons, such as CH3, will make the anion less stable (stronger conjugate base) and the acid weaker. • Q: What would the order of pKa, from largest to smallest, be for ethanol, phenol, 2-methylphenol, and 2,4,6-trinitrophenol? ...
Answers - Final Exam 2013
... e. An alkyne containing at least 3 carbon atoms, that produces an achiral diol when treated with H2 and Lindlar catalyst, followed by OsO4 and then aqueous NaHSO3, or when treated with Na in liquid NH3, followed by MCPBA and then aqueous H2SO4, and an alkyne also containing at least 3 carbon atoms t ...
... e. An alkyne containing at least 3 carbon atoms, that produces an achiral diol when treated with H2 and Lindlar catalyst, followed by OsO4 and then aqueous NaHSO3, or when treated with Na in liquid NH3, followed by MCPBA and then aqueous H2SO4, and an alkyne also containing at least 3 carbon atoms t ...
Mill Hill County High School
... - it uses a lot of energy - the ethene comes from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource Ethanol for use in industry is manufactured during this process. 2. Ethanol as a fuel Ethanol is a useful fuel; it burns with a clean flame and is increasingly used in cars: C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3 ...
... - it uses a lot of energy - the ethene comes from crude oil, which is a non-renewable resource Ethanol for use in industry is manufactured during this process. 2. Ethanol as a fuel Ethanol is a useful fuel; it burns with a clean flame and is increasingly used in cars: C2H6O(l) + 3O2(g) 3CO2(g) + 3 ...
T. V. RajanBabu Chemistry, 730 Autumn 1997
... Conformation of butane and van der Waals and gauche interactions Conformations of CH3XHn, ethers, amines, alcohols Conformations of terminal alkenes, carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) Conformations of dienes, enals and enones Conformations of esters Conformations of amides - Relationship be ...
... Conformation of butane and van der Waals and gauche interactions Conformations of CH3XHn, ethers, amines, alcohols Conformations of terminal alkenes, carbonyl compounds (aldehydes and ketones) Conformations of dienes, enals and enones Conformations of esters Conformations of amides - Relationship be ...
730-2005 topics
... Conformation of butane and van der Waals and gauche interactions Conformations of CH3XHn, ethers, amines, alcohols ...
... Conformation of butane and van der Waals and gauche interactions Conformations of CH3XHn, ethers, amines, alcohols ...
MATERIAL FOR GRADE 9 FINAL EXAM 2016
... • Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. • Differentiate ionic and covalent bonding. • Explain why most chemical bonding is neither purely ionic nor purely covalent. • Classify bonding type according to electronegativity differences. Covalent bonding and molecular compounds • Define molecule an ...
... • Explain why most atoms form chemical bonds. • Differentiate ionic and covalent bonding. • Explain why most chemical bonding is neither purely ionic nor purely covalent. • Classify bonding type according to electronegativity differences. Covalent bonding and molecular compounds • Define molecule an ...
Atomic Structure
... d. What is carbon’s valence number? What does that mean? 4, can make 4 covalent bonds with other atoms Fluorine: a. How many valence electrons does fluorine have? What is an easy way to figure out this answer? 7, look at its period in the periodic table b. How many covalent bonds is fluorine most li ...
... d. What is carbon’s valence number? What does that mean? 4, can make 4 covalent bonds with other atoms Fluorine: a. How many valence electrons does fluorine have? What is an easy way to figure out this answer? 7, look at its period in the periodic table b. How many covalent bonds is fluorine most li ...
Chemistry Lesson 40 Organic Chemistry
... f. Know these for the test! g. Some compounds have more than one functional group – such as amino acids, which contain an amine (C-N) group and an organic acid (COOH) group. h. Naming organic compounds with functional groups involves using the alkane name, and adding the prefix/suffix for the funct ...
... f. Know these for the test! g. Some compounds have more than one functional group – such as amino acids, which contain an amine (C-N) group and an organic acid (COOH) group. h. Naming organic compounds with functional groups involves using the alkane name, and adding the prefix/suffix for the funct ...
Organic Dyes as Photoredox Catalysts
... The Nicewicz group applied Mes–Acr+ as a photoredox catalyst for the intramolecular antiMarkovnikov hydroetherification and hydroamination of olefins to form cyclic ethers and amines, respectively.1 Intermolecular reactions with amines,2a carboxylic acids,1 and mineral acids2b are also possible unde ...
... The Nicewicz group applied Mes–Acr+ as a photoredox catalyst for the intramolecular antiMarkovnikov hydroetherification and hydroamination of olefins to form cyclic ethers and amines, respectively.1 Intermolecular reactions with amines,2a carboxylic acids,1 and mineral acids2b are also possible unde ...
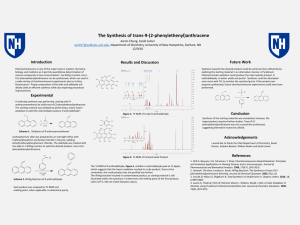
Here is the Original File - University of New Hampshire
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
... chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans-9-(2phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent experiments due to its blue fluorescence2. Proper pre ...
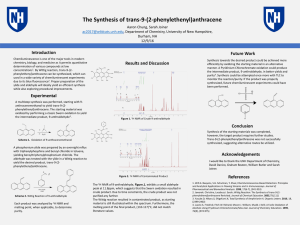
The Synthesis of trans-9-(2
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
... Chemiluminescence is one of the major tools in modern chemistry, biology, and medicine as it permits quantitative determination of various compounds at low concentrations1. By Wittig reaction, trans9-(2-phenylethenyl)anthracene can be synthesized, which can used in a wide variety of chemiluminescent ...
IR spectroscopy
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
... organic molecules have a lot of C-C and C-H bonds within their structure spectra obtained will have peaks in the 1400 cm-1 to 800 cm-1 range this is referred to as the “fingerprint” region the pattern obtained is characteristic of a particular compound the frequency of any absorption is also affecte ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.