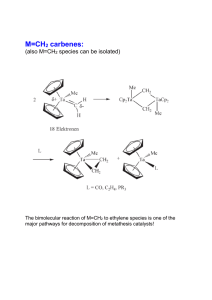
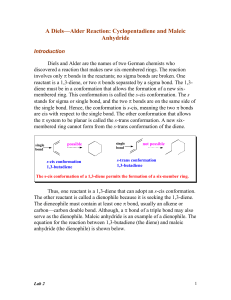
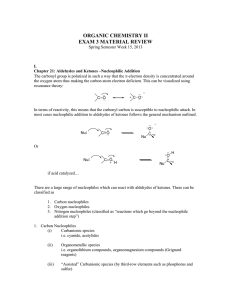
Section 5b and c: crude oil and synthetic polymers Fractional
... As addition polymers are not reactive (they are inert which is one of the properties essential for their uses) they are biodegradable. This means that bacteria are unable to decompose plastics when left in nature. Condensation polymerization 5.20 understand that some polymers, such as nylon, form by ...
... As addition polymers are not reactive (they are inert which is one of the properties essential for their uses) they are biodegradable. This means that bacteria are unable to decompose plastics when left in nature. Condensation polymerization 5.20 understand that some polymers, such as nylon, form by ...
Microwave-Assisted Sulfamide Synthesis
... selective [1,5]. A novel transition-metal-catalyzed process for making unsymmetric sulfamides that was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or ...
... selective [1,5]. A novel transition-metal-catalyzed process for making unsymmetric sulfamides that was recently reported has several limitations, especially with ortho-isomers [1]. Even though other available methods report high yields, they either require reagents that are not readily accessible or ...
L-13
... the reaction and led to the production of allylated product 3a in 80% yield (entry 2).[6] Strong Lewis acids such as AlCl3 or BF3・OEt2 were not effective for the allylation (entries 3 and 4), probably because these catalysts are not stable under protic conditions. Sc(OTf)3 only gave a low yield of 3 ...
... the reaction and led to the production of allylated product 3a in 80% yield (entry 2).[6] Strong Lewis acids such as AlCl3 or BF3・OEt2 were not effective for the allylation (entries 3 and 4), probably because these catalysts are not stable under protic conditions. Sc(OTf)3 only gave a low yield of 3 ...
functional group review
... CH3-O-CH2CH3 ethyl methyl ether Can H-bond weakly with water, but not so polar to be water soluble. ...
... CH3-O-CH2CH3 ethyl methyl ether Can H-bond weakly with water, but not so polar to be water soluble. ...
Free Radical Chemistry and the Preparation of Alkyl
... To determine the relative amounts of each isomer product that forms: Relative amount 1o = (number of 1o H) x (reactivity factor for 1o) Relative amount 2o = (number of 2o H) x (reactivity factor for 2o) Relative amount 3o = (number of 3o H) x (reactivity factor for 3o) Divide each relative amount by ...
... To determine the relative amounts of each isomer product that forms: Relative amount 1o = (number of 1o H) x (reactivity factor for 1o) Relative amount 2o = (number of 2o H) x (reactivity factor for 2o) Relative amount 3o = (number of 3o H) x (reactivity factor for 3o) Divide each relative amount by ...
Chapter 13 – Organic Chemistry
... The double bond in C4 H8 can be placed in three different positions (after the first or second carbon in a straight chain or after the first carbon of a branched chain) to produce three isomers. In addition, groups cannot rotate about double bonds like they can about single bonds because the rotatio ...
... The double bond in C4 H8 can be placed in three different positions (after the first or second carbon in a straight chain or after the first carbon of a branched chain) to produce three isomers. In addition, groups cannot rotate about double bonds like they can about single bonds because the rotatio ...
1-16 polymers
... work. Changing pH can break the hydrogen bonding, e.g. hair perms or curdling of milk with OJ. Starch and cellulose, polymers of sugar All carbohydrates have hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2:1, the same as for water; hence the name of carbohydrate. All sugars contain a carbonyl group as a ketyl ...
... work. Changing pH can break the hydrogen bonding, e.g. hair perms or curdling of milk with OJ. Starch and cellulose, polymers of sugar All carbohydrates have hydrogen and oxygen in the ratio of 2:1, the same as for water; hence the name of carbohydrate. All sugars contain a carbonyl group as a ketyl ...
carbonyl group
... which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic or aromatic group. The –CH=O group characteristic of aldehydes is often called ...
... which is perhaps the most important functional group in organic chemistry. Aldehydes have at least one hydrogen atom attached to the carbonyl carbon atom. The remaining group may be another hydrogen atom or any aliphatic or aromatic group. The –CH=O group characteristic of aldehydes is often called ...
DMC (double metal cyanide) catalyst DMC catalyst is used
... DMC catalyst is used for epoxide polymerization, that is, for polymerizing alkylene oxides such as propylene oxide and ethylene oxide to yield high molecular weight polether polyols. In conventional base catalyzed oxyalkylation reaction, propylene oxide and certain other alkylene oxides are subject ...
... DMC catalyst is used for epoxide polymerization, that is, for polymerizing alkylene oxides such as propylene oxide and ethylene oxide to yield high molecular weight polether polyols. In conventional base catalyzed oxyalkylation reaction, propylene oxide and certain other alkylene oxides are subject ...
MS - Past Papers.org
... equation for straight chain alkane converted into a branched chain alkane equation could be in the form of: ...
... equation for straight chain alkane converted into a branched chain alkane equation could be in the form of: ...
p. 634 - 643
... 6. Hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds are called alkenes. The simplest alkene is ethylene, C2H4. Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with a carboncarbon triple bond. The simplest in the series is acetylene, C2H2 . 7. Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions such as hydrogenatio ...
... 6. Hydrocarbons with carbon-carbon double bonds are called alkenes. The simplest alkene is ethylene, C2H4. Alkynes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with a carboncarbon triple bond. The simplest in the series is acetylene, C2H2 . 7. Unsaturated hydrocarbons undergo addition reactions such as hydrogenatio ...
Production of NMOCs and Trace Organics During the
... Ultimate NMOC yields vary substantially among MSW components Lab-scale NMOC and HAP yields are considerably lower than regulatory estimates NMOC production is characterized by an initial “burst”, followed by much more gradual release ...
... Ultimate NMOC yields vary substantially among MSW components Lab-scale NMOC and HAP yields are considerably lower than regulatory estimates NMOC production is characterized by an initial “burst”, followed by much more gradual release ...
Lab 2 - Academic Computer Center
... centrifugation technique as demonstrated by the instructor and described below. Alternatively, collect your crystals on a Hirsh funnel. Centrifugation Technique: Insert the large end of the plug from the microkit into the Craig tube. Obtain a 12 cm piece of thin copper wire. Wrap two or three turns ...
... centrifugation technique as demonstrated by the instructor and described below. Alternatively, collect your crystals on a Hirsh funnel. Centrifugation Technique: Insert the large end of the plug from the microkit into the Craig tube. Obtain a 12 cm piece of thin copper wire. Wrap two or three turns ...
Alcohols General formula R-OH hydroxyl group Nomenclature
... Note that all of the reactions are reversible. Therefore the alkene has to be removed from the solution as rapidly as it is formed. The slow rate-determining step is the formation of the carbocation. Tertiary ...
... Note that all of the reactions are reversible. Therefore the alkene has to be removed from the solution as rapidly as it is formed. The slow rate-determining step is the formation of the carbocation. Tertiary ...
organic chemistry ii
... Note that the carboxylic acid hydroxyl oxygen is protonated and subsequently dehydrated (not the alcohol hydroxyl) An intramolecular esterification of a - (or -) hydroxycarboxylic acid would give a cyclic ester, which is referred to as a “lactone” ...
... Note that the carboxylic acid hydroxyl oxygen is protonated and subsequently dehydrated (not the alcohol hydroxyl) An intramolecular esterification of a - (or -) hydroxycarboxylic acid would give a cyclic ester, which is referred to as a “lactone” ...
Depending on C, where the
... Contains -OH hydroxyl group • Common formula is R-OH – alcohols: R is alkyl group (e. g. methyl, ethyl...) – phenols: R is aryl (e. g. phenyl) ...
... Contains -OH hydroxyl group • Common formula is R-OH – alcohols: R is alkyl group (e. g. methyl, ethyl...) – phenols: R is aryl (e. g. phenyl) ...
Chapter 7- Alcohols
... Covalent OH bond ~ 480 kJ mol-1 Hydrogen bond ~ 20-40 kJ mol-1 Much weaker but has important effects (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols ar ...
... Covalent OH bond ~ 480 kJ mol-1 Hydrogen bond ~ 20-40 kJ mol-1 Much weaker but has important effects (i) Boiling points of alcohols are higher than would be predicted based on molecular weight - Extra energy required to break the intermolecular hydrogen bonds (ii) Lower molecular weight alcohols ar ...
Chapter 24 Organic Chemistry
... organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. none of these. ...
... organic bases that react with water to produce ammonia. organic acids that react with water to produce ammonia. organic bases that react with acids to form ammonium salts. organic acids that react with bases to form ammonium salts. none of these. ...
Chapter 13 - U of L Class Index
... loss of hydrogen atoms or a gain of oxygen atoms. Conversely, reduction can be defined as a gain of hydrogen atoms or a loss of oxygen atoms. In organic chemistry we can list different functional groups at different levels of oxidation or reduction. Shown below are the different stages of oxidation ...
... loss of hydrogen atoms or a gain of oxygen atoms. Conversely, reduction can be defined as a gain of hydrogen atoms or a loss of oxygen atoms. In organic chemistry we can list different functional groups at different levels of oxidation or reduction. Shown below are the different stages of oxidation ...
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... If it is A AC2 (with Nu), the intermediate and reactant (the protonated starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an induc ...
... If it is A AC2 (with Nu), the intermediate and reactant (the protonated starting material) are both positively charged. Electronegative groups would destabilize both. However, the effect may be greater on the reactant because the positive charge is transferred to the carbonyl carbon by both an induc ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.