Chemistry B1A - Bakersfield College
... Some iron wire weighing 5.6 g is placed in a beaker and covered with 15.1 g of hydrochloric acid. The acid reacts with the metal and gives off hydrogen gas, which escapes into the surrounding air. After reaction the contents of the beaker weighs 20.4 g. What is the mass of hydrogen produced? Write t ...
... Some iron wire weighing 5.6 g is placed in a beaker and covered with 15.1 g of hydrochloric acid. The acid reacts with the metal and gives off hydrogen gas, which escapes into the surrounding air. After reaction the contents of the beaker weighs 20.4 g. What is the mass of hydrogen produced? Write t ...
Exam 1 Format and Review
... homework assignments, and (4) additional recommended text problems (in syllabus). The exam will test not only your problem solving skills, but also your conceptual understanding of the material and your ability to integrate concepts. Questions on the exam will be in the format of multiple choice, sh ...
... homework assignments, and (4) additional recommended text problems (in syllabus). The exam will test not only your problem solving skills, but also your conceptual understanding of the material and your ability to integrate concepts. Questions on the exam will be in the format of multiple choice, sh ...
C1a - Mr Corfe
... down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical reaction where a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler compounds or elements whe ...
... down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSITION – is a chemical reaction where a single compound breaks up into two or more simpler compounds or elements whe ...
naming-and-formulas-chem-1-ab
... sodium, 67.49 g chromium and 72.67 g oxygen. What is the empirical formula? ...
... sodium, 67.49 g chromium and 72.67 g oxygen. What is the empirical formula? ...
Presentation
... covalently bonded units, or molecules. • Covalent compounds are formed between nonmetals. • Prefixes are used to indicate number of each type of element in the compound. • Write the prefixes as indicated on the next slide…. ...
... covalently bonded units, or molecules. • Covalent compounds are formed between nonmetals. • Prefixes are used to indicate number of each type of element in the compound. • Write the prefixes as indicated on the next slide…. ...
Chapter 10 Handouts - Bakersfield College
... 10-16. Naming Compounds •A compound ending in -ide usually is composed of only two elements. Hydroxides which contain the OH- ion are an exception. Sodium Chloride=NaCl •A compound ending in -ate contains oxygen and two or more other elements. Calcium Sulfate=CaSO4 •When the same pair of elements oc ...
... 10-16. Naming Compounds •A compound ending in -ide usually is composed of only two elements. Hydroxides which contain the OH- ion are an exception. Sodium Chloride=NaCl •A compound ending in -ate contains oxygen and two or more other elements. Calcium Sulfate=CaSO4 •When the same pair of elements oc ...
Chemistry 11 – Course Outcomes
... Use electron affinity to explain formation of ions and explain how the formation of ionic compounds occurs State octet rule Give an electron dot diagram (Lewis dot diagram) of atoms forming ions and ionic bonding (3 equations) Use model for the structure of an ionic compound to explain its propertie ...
... Use electron affinity to explain formation of ions and explain how the formation of ionic compounds occurs State octet rule Give an electron dot diagram (Lewis dot diagram) of atoms forming ions and ionic bonding (3 equations) Use model for the structure of an ionic compound to explain its propertie ...
Unit 4 Evolution
... Science Starter: Copy and answer. Can a phase change produce new compounds? No, because chemical changes occur. ...
... Science Starter: Copy and answer. Can a phase change produce new compounds? No, because chemical changes occur. ...
Unit Description - Honors Chemistry
... orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element using orbital notation, electron configuration, and Lewis structures (5.3) Identify electron configuration that co ...
... orbital diagrams of the elements (5.3) Relate valence electrons to Lewis (electron dot) structures (5.3) Describe the ground-state arrangement of electrons in atoms of any element using orbital notation, electron configuration, and Lewis structures (5.3) Identify electron configuration that co ...
FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... 7) Draw a graph of temperature vs. energy showing the phase changes. Be sure to label all the phases, phase changes, melting points, boiling points etc. 8) For each of the following write whether it is a mechanical mixture (M), an element (E) or a compound (C). a) carbon b) sugar c) milk d) muddy wa ...
... 7) Draw a graph of temperature vs. energy showing the phase changes. Be sure to label all the phases, phase changes, melting points, boiling points etc. 8) For each of the following write whether it is a mechanical mixture (M), an element (E) or a compound (C). a) carbon b) sugar c) milk d) muddy wa ...
Elements, Compounds and Mixtures
... chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of two or more atoms. • Ex. (H2O) ...
... chemical compound that can take place in a chemical reaction. • Has the same chemical properties of that element or compound. • Some molecules consist of two atoms of the same element. • Ex. O2 • Other molecules consists of two or more atoms. • Ex. (H2O) ...
4.5b.notes
... Simple equations can be balanced by adding coefficients by trial and error / common sense a. Balance compounds first b. Add coefficients only. Do not change subscripts c. If you add a coefficient to a compound, balance all of those atoms first before moving on d. Make sure that all of the coefficien ...
... Simple equations can be balanced by adding coefficients by trial and error / common sense a. Balance compounds first b. Add coefficients only. Do not change subscripts c. If you add a coefficient to a compound, balance all of those atoms first before moving on d. Make sure that all of the coefficien ...
2011-2012 Summer Packet - Tenafly Public Schools
... D Physical & chemical properties: A physical property is a characteristic of matter that can be determined without changing the chemical formula of the substance. These properties include density, freezing point, or melting point (same point) boiling point, hardness, electrical conductivity, malleab ...
... D Physical & chemical properties: A physical property is a characteristic of matter that can be determined without changing the chemical formula of the substance. These properties include density, freezing point, or melting point (same point) boiling point, hardness, electrical conductivity, malleab ...
American-Journal-of-Oil-and-Chemical-Technologies
... In conclusion, continuing with our previous works on synthesizing supramolecular compounds containing pyridinedicarboxylic acid N-oxides [9-11], two new coordination complexes have been synthesized and characterized. The red shift of bands ʋas(COO−), ʋs(COO−), and ʋas(COO−) and ʋ(NO) confirm formati ...
... In conclusion, continuing with our previous works on synthesizing supramolecular compounds containing pyridinedicarboxylic acid N-oxides [9-11], two new coordination complexes have been synthesized and characterized. The red shift of bands ʋas(COO−), ʋs(COO−), and ʋas(COO−) and ʋ(NO) confirm formati ...
AP Chapter Five Outline
... solution. Commonly water is produced in acid-base neutralization reactions H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l) c) formation of a gaseous molecular compound that evolves from the solution 2 HCl (aq) + Na2S (aq) 2 NaCl (aq) + H2S (g) B. Precipitation Reactions: when in an exchange react ...
... solution. Commonly water is produced in acid-base neutralization reactions H2SO4 (aq) + 2NaOH (aq) Na2SO4 (aq) + 2H2O (l) c) formation of a gaseous molecular compound that evolves from the solution 2 HCl (aq) + Na2S (aq) 2 NaCl (aq) + H2S (g) B. Precipitation Reactions: when in an exchange react ...
Chem 1411 Chapt2
... Ex. O2, H2, HBr, C3H8O Compound- At least two different types of elements chemically combined. NaCl, HBr, H2SO4 Types of MoleculesDiatomic- O2, H2, N2, Br2, F2, I2, Cl2, CO, NaCl, Polyatomic- P4, S8, H2O, C2H5OH Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and an ...
... Ex. O2, H2, HBr, C3H8O Compound- At least two different types of elements chemically combined. NaCl, HBr, H2SO4 Types of MoleculesDiatomic- O2, H2, N2, Br2, F2, I2, Cl2, CO, NaCl, Polyatomic- P4, S8, H2O, C2H5OH Types of CompoundsIonic- Consists of metals and non-metals (Or in general cations and an ...
Chapter 10
... Predicting Products of Synthesis Reactions For Synthesis Reactions For metals that only form one cation, determine the charge on the ion of each element (metallic and nonmetallic) and form a compound from the two ions. If one of the elements forms more than one cation or 2 nonmetals are combined ...
... Predicting Products of Synthesis Reactions For Synthesis Reactions For metals that only form one cation, determine the charge on the ion of each element (metallic and nonmetallic) and form a compound from the two ions. If one of the elements forms more than one cation or 2 nonmetals are combined ...
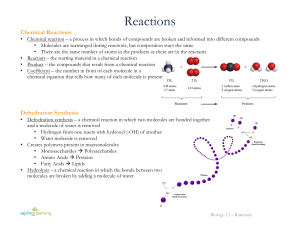
Reactions
... • Creates polymers present in macromolecules • Monosaccharides à Polysaccharides • Amino Acids à Proteins • Fatty Acids à Lipids • Hydrolysis – a chemical reaction in which the bonds between two molecules are broken by adding a molecule of water ...
... • Creates polymers present in macromolecules • Monosaccharides à Polysaccharides • Amino Acids à Proteins • Fatty Acids à Lipids • Hydrolysis – a chemical reaction in which the bonds between two molecules are broken by adding a molecule of water ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.