Midterm Review Sample Content Questions
... C. K3PO4 G. Fe(OH)3 D. SnCO3 H. HClO4 I. HBr 28. Write the formula for the following compounds. A. ammonia E. cadmium oxalate B. chromium (III) cyanide F. lithium oxide C. acetic acid G. sulfur dioxide D. silver nitrite H. cobalt (II) chloride heptahydrate ...
... C. K3PO4 G. Fe(OH)3 D. SnCO3 H. HClO4 I. HBr 28. Write the formula for the following compounds. A. ammonia E. cadmium oxalate B. chromium (III) cyanide F. lithium oxide C. acetic acid G. sulfur dioxide D. silver nitrite H. cobalt (II) chloride heptahydrate ...
Physical Properties
... Pure Substances • A pure substance has well defined physical and chemical properties. • Pure substances can be classified as elements or compounds. • Compounds can be further reduced into two or more elements. • Elements consist of only one type of atom. They cannot be decomposed or further simplifi ...
... Pure Substances • A pure substance has well defined physical and chemical properties. • Pure substances can be classified as elements or compounds. • Compounds can be further reduced into two or more elements. • Elements consist of only one type of atom. They cannot be decomposed or further simplifi ...
Atomic Structure, Molecular Structure & Bonding
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-me ...
... Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-me ...
Fall - Physical Chemistry Division
... NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN STRONGLY CORRELATED ELECTRONS Strongly correlated electrons represent one of the key challenges of modern electronic structure in chemistry and physics. Many molecular processes involving energy transfer through excited states or transition metal catalysis, as well as exotic mate ...
... NEW DEVELOPMENTS IN STRONGLY CORRELATED ELECTRONS Strongly correlated electrons represent one of the key challenges of modern electronic structure in chemistry and physics. Many molecular processes involving energy transfer through excited states or transition metal catalysis, as well as exotic mate ...
Chemistry Content Standards
... b. Experimentally determine indicators of a chemical reaction specifically precipitation, gas evolution, water production, and changes in energy to the system. c. Apply concepts of the mole and Avogadro’s number to conceptualize and calculate • Empirical/molecular formulas, • Mass, moles and molecul ...
... b. Experimentally determine indicators of a chemical reaction specifically precipitation, gas evolution, water production, and changes in energy to the system. c. Apply concepts of the mole and Avogadro’s number to conceptualize and calculate • Empirical/molecular formulas, • Mass, moles and molecul ...
Unit 13 - Electrochemistry
... the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. Electrode: A conductor used to establish electrical contact wit ...
... the relationship between electric forces and chemical reactions. Voltage: The potential difference or electromotive force, measured in volts; it represents the amount of work that moving an electric charge between two points would take. Electrode: A conductor used to establish electrical contact wit ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... plate; and the rest went through the magnetic field without deflection. Thus, there were three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma rays (neutral). By performing other experiments and using this information, Rutherford created an atomic model different from Thoms ...
... plate; and the rest went through the magnetic field without deflection. Thus, there were three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma rays (neutral). By performing other experiments and using this information, Rutherford created an atomic model different from Thoms ...
Chapter 1: The Nature of Analytical Chemistry
... composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation by ...
... composition of samples. – 4. Spectroscopic methods based on interaction of electromagnetic radiation with analyte atoms & molecules, or on the production of radiation by ...
AEED Sustainability - June 17, 2004
... eliminate health and environmental hazards in the manufacture and use of chemicals. • Clean technology – prevent formation of waste • Environmentally-benign chemistry • Rational, deliberate design at the molecular level • Consideration of health and environmental effects of both the process and the ...
... eliminate health and environmental hazards in the manufacture and use of chemicals. • Clean technology – prevent formation of waste • Environmentally-benign chemistry • Rational, deliberate design at the molecular level • Consideration of health and environmental effects of both the process and the ...
Stoichiometry - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... identify limitations of a given classification system and identify alternative ways of classifying to accommodate anomalies distinguish between scientific questions and technological problems select and use apparatus and material safely provide a statement that addresses the problem or answe ...
... identify limitations of a given classification system and identify alternative ways of classifying to accommodate anomalies distinguish between scientific questions and technological problems select and use apparatus and material safely provide a statement that addresses the problem or answe ...
Unit 1 science of chemistry
... Elements are the simplest form of matter that has its unique set of properties. Ex. Gold is an element. All atoms of gold have the same properties. Elements are shown in the Periodic Table. There are more than 100 elements, most of them occur naturally. Elements are represented by one (a cap ...
... Elements are the simplest form of matter that has its unique set of properties. Ex. Gold is an element. All atoms of gold have the same properties. Elements are shown in the Periodic Table. There are more than 100 elements, most of them occur naturally. Elements are represented by one (a cap ...
Ionic Bonding
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
... 7. Water is known for its many anomalous properties. Use your knowledge of intermolecular forces and intramolecular bonding to explain theoretically why lakes freeze from top to bottom. 8. Using Table 3 (page 85), predict whether each of the following moleculeswould be polar or nonpolar. (a) CH3OH(l ...
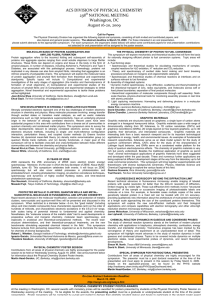
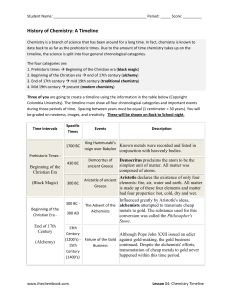
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
Organic Chemistry
... structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (by synthesis or by other means) of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives. These compounds may contain any number of other elements, including hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, the halogens as well as phosphorus, silicon, ...
... structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation (by synthesis or by other means) of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives. These compounds may contain any number of other elements, including hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, the halogens as well as phosphorus, silicon, ...
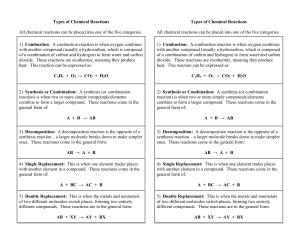
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
primes - The Institute of Mathematical Sciences
... that the British chemist Henry Cavendish discovered that water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. Cavendish was very shy. He did not even complete his college degree. Luckily he came from a rich family and he could build a chemistry lab at home. At that time neither hydrogen nor oxygen were recognized ...
... that the British chemist Henry Cavendish discovered that water is made of hydrogen and oxygen. Cavendish was very shy. He did not even complete his college degree. Luckily he came from a rich family and he could build a chemistry lab at home. At that time neither hydrogen nor oxygen were recognized ...
Study Guide for Ch. 1
... Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and rounding of numbers. Convert numbers between scientific notation and stan ...
... Temperature scales and their details. Differentiate between solutions, colloids, and suspensions. Understand the physical properties involved in determining solids, liquids, & gases. Use significant figures in calculations and rounding of numbers. Convert numbers between scientific notation and stan ...
PowerPoint Template
... masses of B that combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... masses of B that combine with a fixed mass of A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers. ...
Chapter 12
... Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons Alkanes are the least reactive organic compounds. However, two major reactions are common: •Combustion –R (some hydrocarbon) + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy –very exothermic reaction. –If the quantity of O2 is insufficient, it will form a poison called carbon monoxide ( ...
... Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons Alkanes are the least reactive organic compounds. However, two major reactions are common: •Combustion –R (some hydrocarbon) + O2 → CO2 + H2O + energy –very exothermic reaction. –If the quantity of O2 is insufficient, it will form a poison called carbon monoxide ( ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.