Thermochimica Acta Thermodynamics of hydrogen bonding and van
... wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them useful in separation processes, for example, they showed good efficiency ...
... wide range in polarity allows them to be fully miscible with polar substances (water, amides, alcohols, etc.) [6–8], as well as able to dissolve non-polar compounds (aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons) [9]. This fact makes them useful in separation processes, for example, they showed good efficiency ...
Chemistry
... Idea of de Broglie matter waves, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, atomic orbitals, Schrödinger wave equation, significance of ψ and ψ2 , quantum numbers, radial and angular wave functions and probability distribution curves, shapes of s, p, and d orbitals. Aufbau and Pauli’s exclusion principles, H ...
... Idea of de Broglie matter waves, Heisenberg uncertainty principle, atomic orbitals, Schrödinger wave equation, significance of ψ and ψ2 , quantum numbers, radial and angular wave functions and probability distribution curves, shapes of s, p, and d orbitals. Aufbau and Pauli’s exclusion principles, H ...
Chemicals: What`s in? What`s out?
... acid—HCl, nitric acid—HNO3, sulfuric acid—H2SO4 (corrosive, serious burn and eye hazard) Copper sulfate (toxic) ...
... acid—HCl, nitric acid—HNO3, sulfuric acid—H2SO4 (corrosive, serious burn and eye hazard) Copper sulfate (toxic) ...
ChemFinalgeocities
... b. A gas and a solid produce a liquid. c. The compound will be shiny and odorless. d. It is impossible to predict its specific properties. Noble gases _____. a. form no compounds b. form compounds easily c. form no compounds that occur naturally in the environment d. do not obey the octet rule Oppos ...
... b. A gas and a solid produce a liquid. c. The compound will be shiny and odorless. d. It is impossible to predict its specific properties. Noble gases _____. a. form no compounds b. form compounds easily c. form no compounds that occur naturally in the environment d. do not obey the octet rule Oppos ...
Here
... 4. Set up products with dots and charges as necessary. 5. Do the charges add up to zero? F. Crystal Lattice 1. A 3-D arrangement so that each (+) charged ion is surrounded by (-) ion and vice versa 2. Lattice energy – the energy required to separate 1 mol of ions from an ionic compound – the greater ...
... 4. Set up products with dots and charges as necessary. 5. Do the charges add up to zero? F. Crystal Lattice 1. A 3-D arrangement so that each (+) charged ion is surrounded by (-) ion and vice versa 2. Lattice energy – the energy required to separate 1 mol of ions from an ionic compound – the greater ...
CHAPTER 10 - NUCLEAR PHYSICS
... electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melting and boiling points 3. Conduct electricity when melt ...
... electrons can be shared by two atoms. When two pairs are shared the chemical bond is called a double bond. When three pairs are shared it is called a triple bond. Characteristics of Ionic Compounds 1. Crystalline solids made of ions 2. High melting and boiling points 3. Conduct electricity when melt ...
Chapter 5 Notes: The Structure of Matter
... Shows the exact number of atoms of each element Subscripts (written below) = how many atoms of the element ...
... Shows the exact number of atoms of each element Subscripts (written below) = how many atoms of the element ...
6.7 – Ionic Compounds
... Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. Ionic attractions result in high melting points. Most ionic compounds can dissolve in water to become an aqueous solution with ions that are free to move around. Therefore, ionic compounds do not conduct ...
... Properties of Ionic Compounds – Most ionic compounds are crystalline solids at room temperature. Ionic attractions result in high melting points. Most ionic compounds can dissolve in water to become an aqueous solution with ions that are free to move around. Therefore, ionic compounds do not conduct ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... - Solid ionic compounds are crystals with a regular 3D arrangement of alternating ions. The crystal contains only ions, and does not contain separate discrete molecules. Its formula unit gives the proportions, but not any structural information. Naming Compounds - Chemical nomenclature is a systemat ...
... - Solid ionic compounds are crystals with a regular 3D arrangement of alternating ions. The crystal contains only ions, and does not contain separate discrete molecules. Its formula unit gives the proportions, but not any structural information. Naming Compounds - Chemical nomenclature is a systemat ...
LIST OF TOPICS COVERED DURING THIS COURSE
... Periodic table 4 main groups of the periodic table (and characteristics) periodic trends (atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity) review of Bohr-Rutherford diagram ionic compounds (properties, formation, structure, naming, and bonding) molecular element ...
... Periodic table 4 main groups of the periodic table (and characteristics) periodic trends (atomic radius, ionic radius, ionization energy, electron affinity, electronegativity) review of Bohr-Rutherford diagram ionic compounds (properties, formation, structure, naming, and bonding) molecular element ...
File
... definite proportions). Electrolysis Reactions: Carried out in a Hoffman’s apparatus (shown to the right), it splits water compounds into oxygen molecules and hydrogen molecules Water Oxygen + Hydrogen H2O O2 +H2 The electrolysis reaction proves that compounds are made of more than one kind o ...
... definite proportions). Electrolysis Reactions: Carried out in a Hoffman’s apparatus (shown to the right), it splits water compounds into oxygen molecules and hydrogen molecules Water Oxygen + Hydrogen H2O O2 +H2 The electrolysis reaction proves that compounds are made of more than one kind o ...
Ch. 10 – Stoichiometry Stoichiometry – relates molar ratios between
... (numbers) of any compound to the moles (numbers) of any other compound in the equation. These molar ratios are used to 'convert' between any two compounds, whether they are reactants or products. This allows us to calculate moles of reactants needed, ...
... (numbers) of any compound to the moles (numbers) of any other compound in the equation. These molar ratios are used to 'convert' between any two compounds, whether they are reactants or products. This allows us to calculate moles of reactants needed, ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
... 1. __Condensation___ occurs when a gas becomes a liquid. 2. All matter is made up of tiny particles called __atoms___. 3. When a solid becomes a liquid, _melting_____ occurs. 4. An _element_____ is made up of only one type of atom. 5. __freezing___ changes a liquid into a solid. 6. A mixture is made ...
General Chemistry I
... How many grams of magnesium oxide will result when 10.0 g of magnesium ribbon is burned in air? 2Mg (s) + O2 (s) ...
... How many grams of magnesium oxide will result when 10.0 g of magnesium ribbon is burned in air? 2Mg (s) + O2 (s) ...
The format of this test is MULTIPLE CHOICE
... 6. Which nonmetal elements can form triple bonds? Nitrogen family 7. Which nonmetal elements can only form single bond? Halogens 8. What major assumption of the VSEPR theory means that bond angles will be as large as possible and that compound will exist in 3 dimensional space? Unpaired electron clo ...
... 6. Which nonmetal elements can form triple bonds? Nitrogen family 7. Which nonmetal elements can only form single bond? Halogens 8. What major assumption of the VSEPR theory means that bond angles will be as large as possible and that compound will exist in 3 dimensional space? Unpaired electron clo ...
Chemistry Standard Outline
... affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a catalyst. SC5a. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical proc ...
... affected by changing concentration, temperature, or pressure and the addition of a catalyst. SC5a. Demonstrate the effects of changing concentration, temperature, and pressure on chemical reactions. SC6. Students will understand the effects motion of atoms and molecules in chemical and physical proc ...
pdf AP Chemistry Summer Assignment 2014 Dr. Hart`s classes
... The Modern View of Atomic Structure and Atomic Weights: Exercises: pp. 71,72: # 17, 20, 23, 25, 29, 31 17. The radius of an atom of krypton (Kr) is about 1.9 Å (10-10 m). a) Express this distance in nanometers (nm) and in picometers (pm). b) How many krypton atoms would have to be lined up to span 1 ...
... The Modern View of Atomic Structure and Atomic Weights: Exercises: pp. 71,72: # 17, 20, 23, 25, 29, 31 17. The radius of an atom of krypton (Kr) is about 1.9 Å (10-10 m). a) Express this distance in nanometers (nm) and in picometers (pm). b) How many krypton atoms would have to be lined up to span 1 ...
What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry
... What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of properties’ composition, changes and use of matter. Chemistry is divided into five main areas: analytical chemistry, biochemistry, inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry and physical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the study of th ...
... What Can I Do With a Major In Chemistry? Chemistry is the study of properties’ composition, changes and use of matter. Chemistry is divided into five main areas: analytical chemistry, biochemistry, inorganic chemistry, organic chemistry and physical chemistry. Analytical chemistry is the study of th ...
Chemistry Standards Checklist
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
... a. Trace the source on any large disparity between estimated and calculated answers to problems. b. Consider possible effects of measurement errors on calculations. ...
the ap chemistry summer assignment
... general chemistry class, but AP Chemistry is very different. Rather than memorizing how to do particular types of problems, you must really understand the chemistry and be able to apply it to different kinds of problems. AP Chemistry is a difficult course. To succeed you must keep up with the assign ...
... general chemistry class, but AP Chemistry is very different. Rather than memorizing how to do particular types of problems, you must really understand the chemistry and be able to apply it to different kinds of problems. AP Chemistry is a difficult course. To succeed you must keep up with the assign ...
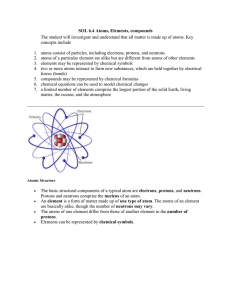
Atoms, Elements, Compounds File
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
... SOL 6.4 Atoms, Elements, compounds The student will investigate and understand that all matter is made up of atoms. Key concepts include ...
summer learning G10
... top of the test-tube, it relit, proving that oxygen gas was also produced. A fine black solid, copper(II) oxide, was left in the test-tube. a. Assess which substances are reactants and which are products. ...
... top of the test-tube, it relit, proving that oxygen gas was also produced. A fine black solid, copper(II) oxide, was left in the test-tube. a. Assess which substances are reactants and which are products. ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.