+ 2 HCL(aq) CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
... Subscript: A number that represents how many atoms of an element are in a compound. Compound: A substance made of the combined atoms of two or more elements. Chemical Formula: States what elements a compound contains and the exact number of atoms of these elements. Oxidation Number: positive or nega ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
periodic table - Mesa Community College
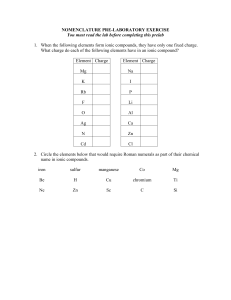
... 1. IONIC BINARY COMPOUNDS: metal or hydrogen with a nonmetal 2. COVALENT BINARY COMPOUNDS: two nonmetals 3. IONIC TERNARY COMPOUNDS: metal or hydrogen or ammonium with polyatomic anion 4. BINARY ACIDS: a binary compound of hydrogen and a non-metal, dissolved in water, e.g., HCl (aq). The (aq) means ...
... 1. IONIC BINARY COMPOUNDS: metal or hydrogen with a nonmetal 2. COVALENT BINARY COMPOUNDS: two nonmetals 3. IONIC TERNARY COMPOUNDS: metal or hydrogen or ammonium with polyatomic anion 4. BINARY ACIDS: a binary compound of hydrogen and a non-metal, dissolved in water, e.g., HCl (aq). The (aq) means ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus 2013 Mawhiney
... 1) The Chemical Elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. 2) Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement o ...
... 1) The Chemical Elements are fundamental building materials of matter, and all matter can be understood in terms of arrangements of atoms. These atoms retain their identity in chemical reactions. 2) Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement o ...
Ch. 8 Notes (Chemical Reactions) Teacher Relearn
... Just use your ion sheet and find the names of the ions. cation name ...
... Just use your ion sheet and find the names of the ions. cation name ...
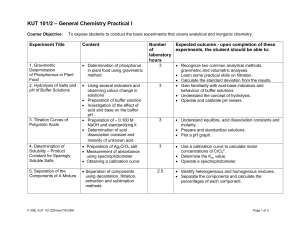
KUT 101/2 – General Chemistry Practical I
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
... • Differentiate the primary and secondary standards. • Differentiate the equivalence and end-points. • Choose suitable indicators for acid-base titration. • Determine the amount of acid in an unknown. • Know a quantitative technique of volumetric analysis. • Understand the definition of BOD (Biochem ...
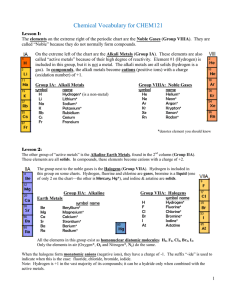
Vocabulary CHEM121
... first and subscripts are used to indicate the number of ions (if more than 1). The name is that of the metal followed by that of the non-metal with the “-ide” ending to indicate the homonuclear anion. ...
... first and subscripts are used to indicate the number of ions (if more than 1). The name is that of the metal followed by that of the non-metal with the “-ide” ending to indicate the homonuclear anion. ...
Word Equations • a summary
... Reactions in which one element “displaces” or replaces another in a compound. The general formula is an element reacting with a compound to produce a new element and a new compound. A metal (cation) can displace another metal (cation) or hydrogen: X + YZ Y + XZ eg. 1 Mg + ZnCl2 Zn + MgCl2 ...
... Reactions in which one element “displaces” or replaces another in a compound. The general formula is an element reacting with a compound to produce a new element and a new compound. A metal (cation) can displace another metal (cation) or hydrogen: X + YZ Y + XZ eg. 1 Mg + ZnCl2 Zn + MgCl2 ...
green chemistry
... break down to innocuous substances after use so that they do not accumulate in the environment. 5. Analyze in real time to prevent pollution: Include in-process real-time monitoring and control during syntheses to minimize or eliminate the formation of byproducts. 6. Minimize the potential for accid ...
... break down to innocuous substances after use so that they do not accumulate in the environment. 5. Analyze in real time to prevent pollution: Include in-process real-time monitoring and control during syntheses to minimize or eliminate the formation of byproducts. 6. Minimize the potential for accid ...
Chapter 3: The Structure of Matter
... natural elements •A natural element is one that is found in nature ...
... natural elements •A natural element is one that is found in nature ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... E. A change in the number of protons results in a change of element F. A change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed ...
... E. A change in the number of protons results in a change of element F. A change in the number of neutrons results in an isotope G. A change in the number of electrons results in an ion IV. Compounds and mixtures A. When two or more atoms bond covalently, they form a molecule B. A compound is formed ...
Ionic Equations
... If product is a gas that has a low solubility in water, reaction in solution is driven to produce the gas Tums relief Any carbonate with an acid NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) = NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
... If product is a gas that has a low solubility in water, reaction in solution is driven to produce the gas Tums relief Any carbonate with an acid NaHCO3(s) + HCl(aq) = NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) ...
Revised Syllabus - M. Sc. First Year - Chemistry
... i) Limitations of Crystal field theory, Nephelauxatic effect ii) Linear Combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO), iii) Molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear (from hydrogen to neon molecule) & heteronuclear diatomic molecules heteronuclear diatomic molecules iv) Molecular orbital theory for coordin ...
... i) Limitations of Crystal field theory, Nephelauxatic effect ii) Linear Combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO), iii) Molecular orbital diagrams for homonuclear (from hydrogen to neon molecule) & heteronuclear diatomic molecules heteronuclear diatomic molecules iv) Molecular orbital theory for coordin ...
(EXAMPLES: DNA and RNA) NUCLEIC ACIDS contain atoms of
... Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: ...
... Your personal notes, summary of the lesson, and/or questions that you may have: ...
Chapter 2
... electrons is shared Double covalent bond – 2 pairs of electrons shared Triple covalent bond – 3 pairs of electrons shared ...
... electrons is shared Double covalent bond – 2 pairs of electrons shared Triple covalent bond – 3 pairs of electrons shared ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.