Ch. 1-- Matter and Change
... Chemical Reactions When writing chemical reactions, the substances that ___________ react with each other are written on the _______ left and are called ...
... Chemical Reactions When writing chemical reactions, the substances that ___________ react with each other are written on the _______ left and are called ...
Additional background material on the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 1998
... reactions, a development, which has been of utmost importance for the application of quantum chemical tools in chemistry. Pople collected all this development into a computer program, GAUSSIAN, which was distributed freely to the chemical community for a number of years (today it is a commercial pro ...
... reactions, a development, which has been of utmost importance for the application of quantum chemical tools in chemistry. Pople collected all this development into a computer program, GAUSSIAN, which was distributed freely to the chemical community for a number of years (today it is a commercial pro ...
Chemistry for Changing Times
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
... • Elements might combine in more than one set of proportions – Each set makes up a new compound ...
Reactions of common metals and properties of
... 2 Na Æ 2 Na+ + 2 e2 H+ + 2 e- Æ H2(g) The two half-reactions combined can be written as: 2 Na + 2 H+ Æ 2 Na+ + H2(g) Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give chara ...
... 2 Na Æ 2 Na+ + 2 e2 H+ + 2 e- Æ H2(g) The two half-reactions combined can be written as: 2 Na + 2 H+ Æ 2 Na+ + H2(g) Atoms of the alkali metals are easily excited; even the flame of a Bunsen burner can excite their valence electrons. As the electrons jump back to lower energy levels, they give chara ...
Ink and paper
... 1- the cathode, which is the positive terminal a 2-node, which is the negative terminal, 3- the electrolyte, in the centre of the battery. ...
... 1- the cathode, which is the positive terminal a 2-node, which is the negative terminal, 3- the electrolyte, in the centre of the battery. ...
chapter02_part1_lecture - bloodhounds Incorporated
... number of protons (positively charged) is equal to the number of electrons ...
... number of protons (positively charged) is equal to the number of electrons ...
Ionic and Covalent Bonding
... • the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element’s atom ...
... • the electrons in the highest occupied energy level of an element’s atom ...
Chapter 7: Chemical Formulas and Chemical Compounds
... f. Know ammonium, acetate, chlorate, chlorite, hypochlorite, perchlorate, cyanide, bicarb, bissulfate, hydroxide, nitrate, nitrite, carbonate, chromate, dichromate, sulfate, sulfite, and phosphate. g. See Table 2 on page 226. ...
... f. Know ammonium, acetate, chlorate, chlorite, hypochlorite, perchlorate, cyanide, bicarb, bissulfate, hydroxide, nitrate, nitrite, carbonate, chromate, dichromate, sulfate, sulfite, and phosphate. g. See Table 2 on page 226. ...
iClicker PARTICIPATION Question: Development of the Modern
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
... 4. A compound is a combination of atoms of two or more elements in specific ratios (the law of definite composition). ...
Review for Midyear - 1 KEY - Ms. Robbins` PNHS Science Classes
... atoms and ions, and reactivity of pure elements. HS-PS1-2. Use the periodic table model to predict and design simple reactions that result in two main classes of binary compounds, ionic and molecular. Develop an explanation based on given observational data and the electronegativity model about the ...
... atoms and ions, and reactivity of pure elements. HS-PS1-2. Use the periodic table model to predict and design simple reactions that result in two main classes of binary compounds, ionic and molecular. Develop an explanation based on given observational data and the electronegativity model about the ...
Department of Chemistry First Year Syllabus
... Have an appreciation of the quantum mechanical basis of the Periodic Table Account for the horizontal and vertical trends for some atomic properties such as atomic size, ionisation potential, electron affinity and electronegativity Know how to describe chemical bonding in small molecules of the main ...
... Have an appreciation of the quantum mechanical basis of the Periodic Table Account for the horizontal and vertical trends for some atomic properties such as atomic size, ionisation potential, electron affinity and electronegativity Know how to describe chemical bonding in small molecules of the main ...
Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii on descending group II. The increase in both radii is due to the addition of one more electron shell on going down the group. However the ionic radius is always smaller than the atomic radius. Group II atoms tend to lose their outermost s-electro ...
... There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii on descending group II. The increase in both radii is due to the addition of one more electron shell on going down the group. However the ionic radius is always smaller than the atomic radius. Group II atoms tend to lose their outermost s-electro ...
Synthesis/Decomposition Reactions
... How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
... How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of synthesis reactions? How do you correctly identify, balance and predict the product(s) of decomposition reactions? ...
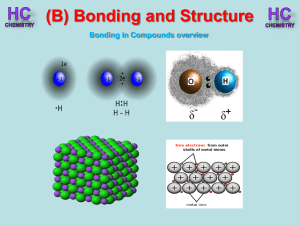
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... linked by strong covalent bonding, it has a high m.p. (2700oC). It is a hard substance as it is very difficult to break the covalent lattice. SiC is used as an abrasive for smoothing very hard materials. Each Si is bonded to 4 C’s and each C is bonded to 4 Si’s. Hence the chemical formula, SiC ...
... linked by strong covalent bonding, it has a high m.p. (2700oC). It is a hard substance as it is very difficult to break the covalent lattice. SiC is used as an abrasive for smoothing very hard materials. Each Si is bonded to 4 C’s and each C is bonded to 4 Si’s. Hence the chemical formula, SiC ...
The Chemical Basis of Life
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
... rates of chemical reactions, but are not consumed (used up) in the reaction. Enzymes are biological catalysts (proteins). ...
1 - mvhs-fuhsd.org
... e. Physical property: a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substances composition. EX: has a green color f. Chemical property: the ability of a substance to undergo a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original mat ...
... e. Physical property: a quality or condition of a substance that can be observed or measured without changing the substances composition. EX: has a green color f. Chemical property: the ability of a substance to undergo a change that produces matter with a different composition than the original mat ...
Hydrogen, Alkalis, and Alkaline Earths
... The Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen is an attractive fuel because of its high heat of combustion and zero pollution ...
... The Hydrogen Economy Hydrogen is an attractive fuel because of its high heat of combustion and zero pollution ...
Sugárkémiai áttekintés Schiller Róbert
... H· + R-CH2-CH2-R’ H2+ R-C·H-CH2-R’ Generally speaking: bond cleavage and bond formation. Main product usually H2 The failure of the organic moderated reactors. But: chemistry of the nuclear reactors!! ...
... H· + R-CH2-CH2-R’ H2+ R-C·H-CH2-R’ Generally speaking: bond cleavage and bond formation. Main product usually H2 The failure of the organic moderated reactors. But: chemistry of the nuclear reactors!! ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.