Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... The HR diagram below shows two main sequence stars, X and Y, and our Sun. ...
... The HR diagram below shows two main sequence stars, X and Y, and our Sun. ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
... gives the distances in light years, the formula had to be modified to M =m+5-5 logD/3.26 . Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 l ...
Physics 127 Descriptive Astronomy Homework #16
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
... 10-5. The star Zubenelgenubi (from Arabic for “scorpion’s southern claw”) has apparent magnitude 2.75 while the star Sulafat (Arabic for “tortoise”) has apparent magnitude 3.25. Which star appears brighter? From this information alone, what can you conclude about the luminosities of these stars? Exp ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... stars and galaxies – Distance that light travels in one year – 300,000 km/s = speed of light – 9.5 trillion km in one year – Sun in 8 light minutes from Earth – Proxima Centauri: closest star to Earth (other than the sun) is 4.2 light years away Sirius (brightest star): 9 ly Polaris: 700 ly ...
... stars and galaxies – Distance that light travels in one year – 300,000 km/s = speed of light – 9.5 trillion km in one year – Sun in 8 light minutes from Earth – Proxima Centauri: closest star to Earth (other than the sun) is 4.2 light years away Sirius (brightest star): 9 ly Polaris: 700 ly ...
Stars from Afar
... an object into colors and photographs the resulting spectrum. Astronomers use spectrographs to get information about stars, including their chemical compositions and temperatures. ...
... an object into colors and photographs the resulting spectrum. Astronomers use spectrographs to get information about stars, including their chemical compositions and temperatures. ...
Ch 29 Sun and Solar Activity
... atmosphere, disrupt longrange radios, satell. & radar • solar flame animation ...
... atmosphere, disrupt longrange radios, satell. & radar • solar flame animation ...
Name
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
... If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. ...
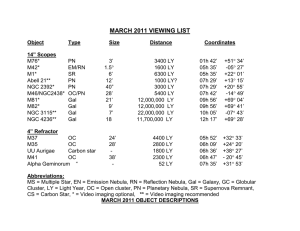
March
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
... adjoining galaxy M82 had a close encounter about 600 million years ago, resulting in a prolonged period of intense new star formation that continues today. This is a prime candidate for the east scope. M82 is an irregular galaxy of 8th magnitude in the constellation Ursa Major (URR-suh-MAY-jer). Als ...
Structure of the Universe
... Star types • Main sequence – Average size – As temperature increases, so does luminosity • Giant stars – Large, bright, cool stars – Red, orange or yellow in color – 10 or more times brighter then the sun • Super giants – High luminosity, high temperature – 100 to 1000 times bigger then the sun – ...
... Star types • Main sequence – Average size – As temperature increases, so does luminosity • Giant stars – Large, bright, cool stars – Red, orange or yellow in color – 10 or more times brighter then the sun • Super giants – High luminosity, high temperature – 100 to 1000 times bigger then the sun – ...
Stars
... Nebula: large amount of gas & dust spread out in an immense volume Protostar: earliest stage in a star’s life White Dwarf: remaining hot core of a star after outer layers expand & drift out into ...
... Nebula: large amount of gas & dust spread out in an immense volume Protostar: earliest stage in a star’s life White Dwarf: remaining hot core of a star after outer layers expand & drift out into ...
stars and constellations
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
Astronomy Chapter 13 Name
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
... D. A type of binary star in which the spectrum lines exhibit a changing Doppler shift as a result of the orbital motion of one star around the other ...
The Stars
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
... Plotting the Properties of Stars Two astronomers created a special kind of graph that compares star brightness with their ________________ ________________. When this was plotted it showed that these properties are related. For example, as the temperature of a star __________________, its colour bec ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... 3 billion stars can be seen through telescopes on the surface 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble ...
... 3 billion stars can be seen through telescopes on the surface 6000 can be seen with the unaided eye Over a trillion stars can be seen with the Hubble ...
name - New York Science Teacher
... 1. Name the brightest star in the known universe. _____________________________ 2. What is its magnitude? ________________________ 3. Are the brightest stars low magnitude or high magnitude? ______________________________ 4. Make a top 10 list of the names of the 10 brightest stars in the known univ ...
... 1. Name the brightest star in the known universe. _____________________________ 2. What is its magnitude? ________________________ 3. Are the brightest stars low magnitude or high magnitude? ______________________________ 4. Make a top 10 list of the names of the 10 brightest stars in the known univ ...
Extension worksheet – Topic 6 - Cambridge Resources for the IB
... variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
... variation of its luminosity is 12 days. Using the relation M 2.83log10 T 1.81 between period T (in days) and average absolute magnitude M calculate the distance to this star. ...
Understanding Stars
... – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing – like Celsius and Fahrenheit The H-R diagram • Hertzsprung ...
... – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • Big luminosities are bright – 1 order of magnitude is roughly equal to 20 units of luminosity Absolute Magnitude and Luminosity • 2 different ways of measuring the same thing – like Celsius and Fahrenheit The H-R diagram • Hertzsprung ...
Name: Notes – #45 The Diverse Sizes of Stars 1. A Hertzsprung
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
... of energy stars emit is proportional to their surface temperature to the ______ power. 4. A star that is twice as hot as another star with the same surface area emits ______ times more energy per second. 5. What is the equation for the luminosity of a star? 6. Super giants tend to have surface tempe ...
HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.