* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
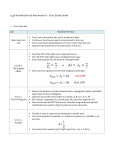
Name Date Class Chapter 4.2 Astronomy Review The Scale of the Universe Understanding Main Ideas If the statement is true, write true. If the statement is false, change the underlined word or words to make the statement true. 1. The spacecraft Voyager is 16,000,000,000 km away from Earth. That is the same as 1.6 × 1010 km. An astronomer says that his house cost $2.9 × 105. That is 2. $2,900,000. 3. A light-year is a measure of time on an astronomical scale. 4. Astronomers often use parallax to measure distances to stars. 5. Refraction makes nearby stars look like they shift position against the background of stars between winter and summer viewings from Earth. 6. The solar system is all of space and everything in it. Building Vocabulary Write a definition for each of these terms on the lines below. 7. light-year 8. parallax 9. universe 10. scientific notation 135D Name Date Class The Scale of the Universe Read the passage and study the table below. Then use a separate sheet of paper to answer the questions that follow. The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnitude. Third magnitude stars were half as bright as second magnitude stars, and so on. Modern astronomers have changed Hipparchus’s system a little. In the modern system, an object of magnitude 1 appears 100 times as bright as one of magnitude of 6. This means that if two objects are separated by one unit of magnitude, the brighter object appears about 2.5 times as bright as the dimmer one. A star of magnitude 1 is about 2.5 times as bright as a star of magnitude 2. Using this scale, the dimmer the object, the larger the magnitude number. What about very bright objects? Remember, the brighter an object appears, the lower the magnitude number. Very bright objects have negative magnitudes. Sirius, the brightest star in the sky (except for the sun), has a magnitude of −1.5. Venus is the brightest planet. Its brightness varies, but at its brightest, its magnitude is −4. The suns magnitude is −26.5. Object Apparent Magnitude −26.50 Sun Venus (maximum brightness) −4.00 Mars (maximum brightness) −2.00 Procyon 0.36 Regulus 1.36 Dimmest visible to the naked eye 6.00 Dimmest visible with binoculars 10.00 1. What is the difference between the magnitudes of the bright stars Regulus and Procyon? Which is brighter? How much brighter is it than the dimmer one? 2. How much brighter is Venus than Mars? 3. What is the difference between the magnitude of the dimmest star that is visible with the naked eye and the magnitude of the dimmest star that can be seen with binoculars? How much brighter is the former than the latter? Name Date Class The Scale of the Universe Write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 1. In space, light travels at a speed of about 300,000,000 m/s. Which expresses that speed correctly in scientific notation? A 300,000 km/s B 3 × 109 m/s C 3 × 108 m/s D 3 × 107 m/s 2. A star is 9 × 1012 meters from Earth. What is that number in expanded form? A 900,000,000,000 meters B 9,000,000,000,000 meters C 90,000,000,000,000 meters D 9.0 × 1012 meters 3. After six months, an astronomer notices that star A moves a greater distance than star B. Which conclusion is correct? A Star A is closer than star B. B Star A and star B are equally far away. C Star A is farther away than star B. D More observations are necessary to determine which star is farther away. 4. A star looks like it’s located one place in the sky in January and a different place in June. What is this phenomenon called? A a light-year B parallax C refraction D scientific notation Fill in the blank to complete each statement. 5. uses powers of ten to write very large or very small numbers in shorter form. 6. The is made up of all of space and everything in it. 7. A light-year is a measure of . 8. Astronomers use to measure the distance to stars that are within several hundred light-years of Earth. 9. The distance light travels through space in a year is one 10. Parallax is the apparent change of at it from different places. . of an object when you look 135F