* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars from Afar
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
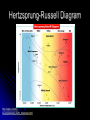
HR Diagram Learning About Stars Astronomers study the universe using tools to collect the electromagnetic radiation given off by stars and galaxies. Most large telescopes today have spectrographs. A spectrograph (spek truh graf) breaks the light from an object into colors and photographs the resulting spectrum. Astronomers use spectrographs to get information about stars, including their chemical compositions and temperatures. Through studying this information we are able to piece together theories about the life cycle of stars. Classifying Stars Stars can be classified in three ways: Size – How massive the star is Temperature – A stars color reveals its temperature. Red stars have a cooler temperature, and blue stars have a warmer temperature. Brightness/Magnitude – The amount of light a star gives off depends on its size and temperature. Apparent and Absolute Magnitude Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as seen from Earth. Absolute magnitude is brightness of a star as if it were 32.6 light years from Earth. The brightness of the stars is compared to the brightness of our Sun. We call this luminosity. HR Diagram An HR diagram shows the two most important characteristics of stars, which are temperature and absolute magnitude (brightness) and/or luminosity. Scientists plot the surface temperatures of stars and their brightness on a graph. Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram http://aspire.cosmicray.org/labs/star_life/hr_interactive.html