Stars - TeacherWeb
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
... using this as your topic sentence: “The three main characteristics used for classifying stars are size, temperature and brightness.” • Your paragraph should include, in addition to the topic sentence, three detail sentences each followed by an example sentence and finished off with a conclusion sent ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
... 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate distance of the following in AU: (a) Sun to the E ...
chap17_s05_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
Weekly Homework Questions #3, Sep. 14, 2010
... Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a) Fomalhaut is 0.36 magnitudes brighter than Aldebaran (b) Fomalhaut is 1.45 magnitudes fainter than Aldebaran (c) Fomalhaut is 2.07 magnitudes brighter than Alde ...
... Aldebaran, the brightest star in the constellation of Taurus, which will also be visible this fall? How much brighter or fainter is it? (a) Fomalhaut is 0.36 magnitudes brighter than Aldebaran (b) Fomalhaut is 1.45 magnitudes fainter than Aldebaran (c) Fomalhaut is 2.07 magnitudes brighter than Alde ...
chap17_f04_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
Maui Stargazing April Observing List DEEP SPACE OBJECTS
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
... ASTERISMS - In astronomy, an asterism is an informal pattern of stars recognized in the Earth's night sky. It may be part of an official constellation or it may be composed of stars from more than one constellation. CONSTELLATIONS - In modern astronomy, a constellation is a specific area of the cel ...
Use this form to take notes in class about stars
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
... Stars of Spectral Classes B to M 9. What color is our sun? ___________what class is it in? ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
labex7
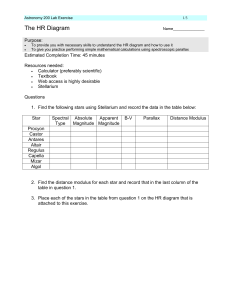
... 4. From the absolute magnitude that you found for each star determine the star’s luminosity in solar units. (Hint – the absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.84. Polaris has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitu ...
... 4. From the absolute magnitude that you found for each star determine the star’s luminosity in solar units. (Hint – the absolute magnitude of the Sun is 4.84. Polaris has an absolute magnitude of -3.66. This means that Polaris is 4.84 - (-3.66) = 8.5 magnitudes brighter than the Sun. Use the magnitu ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Chapter 30.1
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
... Circumpolar: stars that never go below the horizon. (Circling stars). Different stars become visible during different seasons. Three actual motions: ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of _____________________ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of _____________________ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
... Stars that glow blue-white are the hottest (15,000 degrees Celsius) Rigel ...
Characteristics of Stars
... • Brightness of a star as it appears from earth • Brightest stars have lowest #s • Dimmest stars have highest #s ...
... • Brightness of a star as it appears from earth • Brightest stars have lowest #s • Dimmest stars have highest #s ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
observingopenclusters-2-2-1
... Are they all at the same distance? Do they contain the same kinds of stars? ...
... Are they all at the same distance? Do they contain the same kinds of stars? ...
Pistol Star of the Pistol Nebula
... 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 S ...
... 10^6.3) and appears to have more than 150 Solar-masses, having been resolved as a single star down to a projected separation of 110 AUs (Figer et al, 1998). Indeed, the star may have started with as much as 200 to 250 Solar-masses but has been violently shedding much of its substance. With over 40 S ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far ...
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.