red shift blue shift
... Know the relationship between apparent magnitude (m), absolute magnitude (M) and distance (D): ...
... Know the relationship between apparent magnitude (m), absolute magnitude (M) and distance (D): ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... Complete each question or statement with as much information as we covered in class. 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
... Complete each question or statement with as much information as we covered in class. 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... • Definition of apparent magnitude – The magnitude of Vega is 0. – For every factor of 10 fainter, the magnitude is 2.5 greater. ...
... • Definition of apparent magnitude – The magnitude of Vega is 0. – For every factor of 10 fainter, the magnitude is 2.5 greater. ...
epsilon Aur
... Epsilon Aurigae is not the brightest eclipsing binary, nor is it the one with the deepest eclipses. What makes it distinctive is its long period of over 27 years, coupled with the mystery surrounding the nature of the secondary object in the system. The last primary eclipse took place during 1982-84 ...
... Epsilon Aurigae is not the brightest eclipsing binary, nor is it the one with the deepest eclipses. What makes it distinctive is its long period of over 27 years, coupled with the mystery surrounding the nature of the secondary object in the system. The last primary eclipse took place during 1982-84 ...
Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
... The term magnitude is used to describe the brightness of a star' Apparent magnitude is the brightness of a star as it appears from Earth. This brightness depends partly on how far away the star is. Absolute magnitude describes the actual brightness of a star without considering its distance from the ...
Main Sequence Stars
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
Problem set 1 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56Fe is 8.8MeV
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
... 1. The binding energy per nucleon for 56 Fe is 8.8 MeV per nucleon. Estimate the total energy released per kilogram of matter by the sequence of reactions which fuse hydrogen to iron. 2. The main sequence of the Pleiades cluster of stars consists of stars with mass less than 6M ; the more massive s ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
... 10. Be able to use an H-R diagram to plot the temperature, absolute magnitude, and luminosity of a star. Be able to use an H-R diagram to determine the stage in stellar evolution of a given star. 11. What are the stages in the life of a high mass star? A low mass star? Be able to give characteristic ...
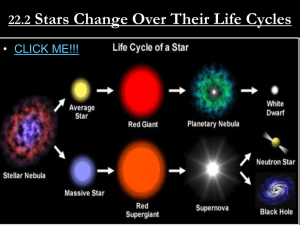
Life Cycle of Stars Flipbook Assignment
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. Completion: 1. Gather in groups of 3 (one for each mass type) 2. Share each flip book explaining the stages to the other two 3. Complete the worksheet provided. Life Cycle of Stars ...
... 4. Cut out pages and staple so that it flips in order from birth to death. Completion: 1. Gather in groups of 3 (one for each mass type) 2. Share each flip book explaining the stages to the other two 3. Complete the worksheet provided. Life Cycle of Stars ...
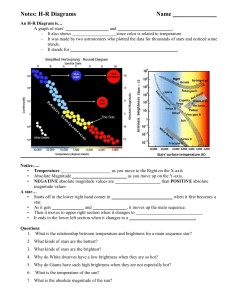
H-R Diagram Notes
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
chap17_f03_phints
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64X greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? HINT: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found ...
... A star is determined to have a surface temperature twice that of the Sun, and a luminosity 64X greater. What is this star’s radius, expressed in solar units ? HINT: Problem 4 is an application of the radius – luminosity – temperature relation for stars. Given two of these values, the third is found ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respectively. [Hint – you don’t need to know the absolute value of the solar luminosity] ...
... The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respectively. [Hint – you don’t need to know the absolute value of the solar luminosity] ...
Physical properties of stars
... The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their ...
... The size of the star The temperature of the star The distance of the star Pg. 444 scale of objects and their ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.