Astronomy Toolkit
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
Review_game_and_answers
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
... 7- How are all galaxies moving in relation to every other galaxy? Away from each other ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
... expands to 10 – 100 times its original size The star has used all of its hydrogen fuel. The center shrinks. ...
Star
... -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
... -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is more dense! ...
After Dark in Allenspark
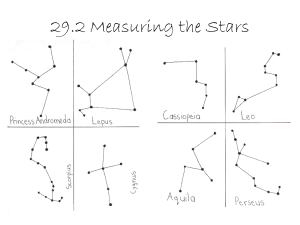
... star hop will be different, but here's one that works for me (and yes, I field tested it this time). Start with Orion, one of the most recognizable winter constellations. It'll be reasonably high in the south or southeast in the evening this month. My next step is to look past Orion's right shoulder ...
... star hop will be different, but here's one that works for me (and yes, I field tested it this time). Start with Orion, one of the most recognizable winter constellations. It'll be reasonably high in the south or southeast in the evening this month. My next step is to look past Orion's right shoulder ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _AWAY____ Diagram the correct sequence of a star’s life cycle. Write the formula for a fusion reaction. H + H ...
... The fact that the spectra of stars are shifted towards the red suggests that the stars are moving _AWAY____ Diagram the correct sequence of a star’s life cycle. Write the formula for a fusion reaction. H + H ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
... Evolution of low mass (red dwarf) stars, medium mass main sequence stars, massive stars, all from nebulae to their final phases ...
F03HW09
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
... Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparen ...
RFS_315_answers
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
... mass of a star the shorter it’s lifetime as it’s fuel is used much faster. Algol B is a dying K giant star but at only .81 solar masses, it is the LESS massive of the two. The dim companion has lost a great deal of mass to it’s closely orbiting partner. 15. Polaris is a variable star – what type of ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star brightens and dims is directly related to its _____. A. distance B. temperature C. composition ...
... to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star brightens and dims is directly related to its _____. A. distance B. temperature C. composition ...
astronomy 2 review sheet - Hicksville Public Schools
... PHOTOSPHERE, CHROMOSPHERE, CORONA 17. What is the solar wind? ELECTRICALLY CHARGED PARTICLES EXTENDING FROM THE CORONA. 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- ...
... PHOTOSPHERE, CHROMOSPHERE, CORONA 17. What is the solar wind? ELECTRICALLY CHARGED PARTICLES EXTENDING FROM THE CORONA. 18. Describe a meteor, meteoroid and a meteorite. METEOR- STREAK OF LIGHT AS A METE0ROID BURNS UP IN THE EARTH’S ATMOSPHERE. METEOROID- A CHUNK OF ROCK OR DUST IN SPACE. METEORITE- ...
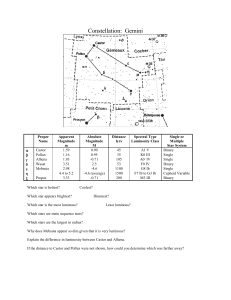
Gemini
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
... cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), it is of intermediate age, and contains some post-main sequence stars (including several yellow and ora ...
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...
... Starlight Brightness • Apparent Magnitude: How bright a star appears to be from earth when viewed with the unaided eye. Distance can cause a dimmer star to appear to be brighter than a brighter star that is farther away. • Absolute Magnitude: The amount of light (brightness) a star actually has. Th ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... 3. Is this statement sensible? Why, or why not? (20pt) If the Sun had been born as a high-mass star some 4.6 billion years ago, rather than as a low mass star, the planet Jupiter would probably have Earth-like conditions today, while earth would be hot like Venus. 4. Chapter 11, Problem 26. Stellar ...
... 3. Is this statement sensible? Why, or why not? (20pt) If the Sun had been born as a high-mass star some 4.6 billion years ago, rather than as a low mass star, the planet Jupiter would probably have Earth-like conditions today, while earth would be hot like Venus. 4. Chapter 11, Problem 26. Stellar ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.