* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download F03HW09
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
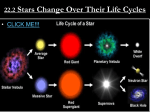
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Physics 121 Chapter 8 RQ: 1,4,14 P: 1,7,11 RQ 1: Why are earth-based parallax measurements limited to the nearest stars? Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparent motions. Therefore, we are limited to the only the nearest stars. If Earth’s orbit were larger, we could measure the parallax of stars at greatest distance. RQ 4: What does luminosity measure that is different from what absolute visual magnitude measure? The luminosity is a measure of the total amount of energy emitted by a star in one second. The absolute visual magnitude is related to the portion of the total luminosity emitted only in the visible portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. Consequently, the absolute visual magnitude ignores energy in the gamma-ray, x-ray, ultraviolet, infrared, and radio. RQ 14: What is the most common kind of star? The most common types of stars are the red dwarfs(lower main sequence stars) and the white dwarfs. Problems P 1: If a star has a parallax of 0.05 seconds of arc, what is its distance in pc? in AU? 1 , p parallax .05 p 1 d .05seconds of arc d 20pc d 206,265 AU d 1 pc 200 pc d 4.125 10 6 AU P 7: If a star is 10 times the radius of the sun and half as hot, what will its luminosity be? (Hint: See By the Numbers 8-3.) L R L R 2 4 T T ; R 10 R , T 2 T 2 4 10 R T L L R 2T 1 L 100 L 16 L 6.25 L P 11: If two stars orbit each other with a period of 6 years and a separation of 4 AU, what is there total mass?(Hint: See By the Numbers 8-4.) M A M B M tot M tot p2 4 AU 3 6 years 2 64 36 1.78 solar masses M tot M tot a3