* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Starlight and What it Tells Us
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
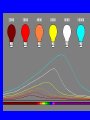
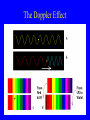
Starlight and What it Tells Us Brightness of Stars • Variations in distance and intrinsic brightness • Scale based on one by Hipparcos 500 B.C. • Magnitude: Large Numbers = Fainter – One magnitude = 2.5 x – Five magnitudes = 100 x Magnitudes • • • • • • • • Planet around nearby star: Pluto: Faintest Naked-Eye Star: Big Dipper Stars: Sirius (Brightest Star) Venus Full Moon Sun 30 13 6 2 -1.6 -4 -12 -27 Absolute Magnitude • Altair and Deneb are about equally bright as seen from Earth • Altair is 16 l.y. away, Deneb 1600 • Hence Deneb must be about 10,000 times brighter Absolute Magnitude • How bright a star would be at a distance of 32.6 l.y. (10 parsecs) • Sun: 4.5 (inconspicuous naked-eye star) • Altair: 2.2 • Deneb: -7.1 (bright as crescent moon) – Note: Deneb - Altair about 10 magnitudes = 100 x 100 = 10,000 times Black-Body Radiation • Objects Emit Radiation Because They Are Hot • Why “Black”? Because None of the Radiation is Reflected from Some Other Source • The Sun Emits Black-Body Radiation, the Moon Does Not Why Black-Body Radiation is so Important • Color is directly related to temperature • Temperature is the only determinant of color • Energy per unit area is the same if temperature is the same – If two stars have the same color and distance, difference in brightness is due to difference in size – Dwarf and giant stars are literally dwarfs or giants Spectroscopy • Different atoms absorb or emit specific wavelengths of light • When light spread into a spectrum, the absorbed wavelengths show up as dark (missing) bands • These spectral lines are indicators of: – Chemical composition – Physical conditions The Solar Spectrum Spectral Lines are Affected By: • Electrical and Magnetic Fields • Number of Electrons Atoms Have Lost (Indicates Temperature and Pressure) • Motion (Doppler Effect) • Blue-shifted if Motion Toward Observer • Red-shifted if Motion Away From Observer The Doppler Effect What the Doppler Effect Tells Us • Radial Motion • Rotation of Stars – Approaching side of star blue-shifted, receding side red-shifted • Unseen Companions (Stars or Planets) – Star oscillates around center of mass • Surface and Interior Motions – Changes in Size – Interior Oscillations