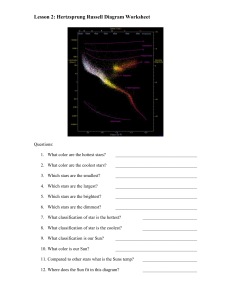
Stars are classified by how hot they are (temperature)
... and brightness of stars on a graph 1913, American astronomer Henry Norris Russell made similar graphs Although they used different data, they came up with the same graphs Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram ...
... and brightness of stars on a graph 1913, American astronomer Henry Norris Russell made similar graphs Although they used different data, they came up with the same graphs Hertzsprung-Russell (H-R) diagram ...
On my webpage, find the link Star Life Cycle and use it to answer the
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
... A Solar Mass is equal to the mass of the Sun. If, for example, a star has 2 solar masses, it means it has twice as much mass as the Sun. Click the “brown dwarf” link in Option 1 6. How many solar masses are brown dwarfs on average? ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
... turns out, the system is anything but typical or uninteresting. KOI-54 has been found to be a close binary system, consisting of nearly twin A stars in highly eccentric (e = 0.83) 41.8 day orbits about their mutual center of mass. These main sequence stars reside right at the bottom of the instabili ...
It is evident from our observations of impact craters on planets and
... In order to understand the stars, astronomers must determine accurate stellar distances. Stellar (heliocentric) parallax was used for determining distances to stars in Lab # 6. But the heliocentric parallax method breaks down beyond 100 parsecs (300 LY). In space, telescopes have increased our abili ...
... In order to understand the stars, astronomers must determine accurate stellar distances. Stellar (heliocentric) parallax was used for determining distances to stars in Lab # 6. But the heliocentric parallax method breaks down beyond 100 parsecs (300 LY). In space, telescopes have increased our abili ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
molecular clouds
... • Hydrogen and helium are the predominant components of the ISM, but it is enriched with heavier elements from earlier stars (created in stellar fusion and supernova explosions). ...
... • Hydrogen and helium are the predominant components of the ISM, but it is enriched with heavier elements from earlier stars (created in stellar fusion and supernova explosions). ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
... 3. How does the sun compare to the other stars on the main sequence? (Hint: The sun’s color is …..What part of the main sequence is it in – upper left, lower left, etc.?) ...
Chapter 8 lesson 4 Notes
... Stars form when matter comes together and starts to give off energy. ...
... Stars form when matter comes together and starts to give off energy. ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Stars, H-R and Life Cycle of Star
... between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. ...
... between the average surface temperature of stars and their absolute magnitude. ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... • Strictly speaking: L = (4πR2 )(σT 4 ) where R is the radius of a star. On the other hand, L = f · (4πr2 ) → T = (f r2 /R2 σ)1/4 • The basic idea of UBV Photometry is to measure the proportions of radiant energy put out by a thermal body at ultraviolet (U), blue (B), and visual (V) wavelength • fV ...
... • Strictly speaking: L = (4πR2 )(σT 4 ) where R is the radius of a star. On the other hand, L = f · (4πr2 ) → T = (f r2 /R2 σ)1/4 • The basic idea of UBV Photometry is to measure the proportions of radiant energy put out by a thermal body at ultraviolet (U), blue (B), and visual (V) wavelength • fV ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
... 3) As you move across the X axis of the diagram, what happens to surface temperature? Surface temperature decreases 4) Where is the sun found within the H-R diagram? In the Main Sequence 5) Sketch an H-R diagram and label the main sequence, white dwarf, and giant/super giant regions on the diagram. ...
Magnitude Scale
... distance can be determined. • Difficult to accurately measure luminosity for one star – Use spectra to get spectral type and class ...
... distance can be determined. • Difficult to accurately measure luminosity for one star – Use spectra to get spectral type and class ...
Stars and their Properties
... Proper Motion is the measurement of a star’s physical motion Must be measured in parallel with Parallax o The Moving Cluster Method – Stars converge to a central point if you are moving backwards in space at very high speed – Used to 1,000 parsecs Sun is not in a star cluster Convergent Poin ...
... Proper Motion is the measurement of a star’s physical motion Must be measured in parallel with Parallax o The Moving Cluster Method – Stars converge to a central point if you are moving backwards in space at very high speed – Used to 1,000 parsecs Sun is not in a star cluster Convergent Poin ...
Quiz #4 – The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Stars
... Two stars that are in close orbit around each other are called ___________ binary stars. ...
... Two stars that are in close orbit around each other are called ___________ binary stars. ...
stars and galaxies – study guide
... 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellation is Orion. 26. White dwarf stars are hot, faint, Earth-sized stars. 27. A black hole is the densest object in the universe, and ...
... 23. On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by temperature and absolute magnitude. 24. What is the next stage of the sun? Red Giant 25. An example of a winter constellation is Orion. 26. White dwarf stars are hot, faint, Earth-sized stars. 27. A black hole is the densest object in the universe, and ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
... 1. What types of radiation make up the electromagnetic spectrum? 2. Define the three types of spectra. 3. How do scientists determine the elements present in a star. 4. How can scientists determine whether a star is moving toward or away from Earth? 5. How does a reflecting telescope differ from a r ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.