Life Cycle of a Star
... Supernova gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses Occurs after a massive star uses up its fuel source Neutron Star a star that has collapsed to a point at which all particles are neutrons A neutron star that spins and sends out beams of radiation is called a pulsar ...
... Supernova gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses Occurs after a massive star uses up its fuel source Neutron Star a star that has collapsed to a point at which all particles are neutrons A neutron star that spins and sends out beams of radiation is called a pulsar ...
Stars
... range greatly in size from large supergiants to very small dwarfs. Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
... range greatly in size from large supergiants to very small dwarfs. Our star, the Sun, is considered to be average in comparison to the size of other stars. ...
HR DIAGRAM ACTIVITY
... use pages 627-628 to help you 1. Of the stars plotted which is nearest to the end of its life? ________________ (name of star) Explain how you determined this. ...
... use pages 627-628 to help you 1. Of the stars plotted which is nearest to the end of its life? ________________ (name of star) Explain how you determined this. ...
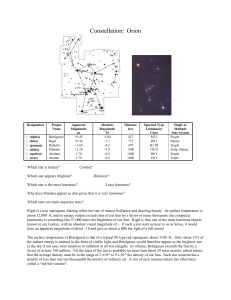
Orion
... greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellation Orion. The linear extend of this giant cloud is well several hundreds of light years. It can be visualized by l ...
... greatest Earth-bound observatories and the Hubble Space Telescope. It is the main part of a much larger cloud of gas and dust which extends over 10 degrees well over half the constellation Orion. The linear extend of this giant cloud is well several hundreds of light years. It can be visualized by l ...
The Hertzsprung – Russell Diagram Star Data Table
... Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell discovered a relationship between the brightness of a star and the surface temperature of a star. The graph of a star’s absolute magnitude versus its temperature is called an ...
... Danish astronomer Ejnar Hertzsprung and American astronomer Henry Russell discovered a relationship between the brightness of a star and the surface temperature of a star. The graph of a star’s absolute magnitude versus its temperature is called an ...
TU Muscae and the Early-type Overcontact Binaries
... Binary orbital plane is oriented so that the two stars pass in front of one another as seen from Earth. The light curve is rich in information about the two stars. ...
... Binary orbital plane is oriented so that the two stars pass in front of one another as seen from Earth. The light curve is rich in information about the two stars. ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... The shrinking, spinning region begins to flatten into a disk with a central concentration called a protostar ...
... The shrinking, spinning region begins to flatten into a disk with a central concentration called a protostar ...
Planetarium Activity 1 Learning to measure brightness and Limiting
... Things to review before you come: Constellations, naming conventions of stars in constellations, apparent magnitude, and magnitude scale, Greek Letters Task 1 Instructions 1. You will be shown five popular constellations (Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Leo, Ursa Minor and Orion) fix their position in the s ...
... Things to review before you come: Constellations, naming conventions of stars in constellations, apparent magnitude, and magnitude scale, Greek Letters Task 1 Instructions 1. You will be shown five popular constellations (Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Leo, Ursa Minor and Orion) fix their position in the s ...
100 X size of Sun - East Penn School District
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
... • In the magnitude scale, lower numbers are associated with brighter stars. • Star A has an apparent magnitude = 5.4 and star B has an apparent magnitude = 2.4. Which star is brighter? • We can't actually move stars around, but we can calculate how bright a star would be if placed at the agreed-upon ...
Homework, November 16, 2006 AST110-6
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
... how many stars have Earth-like planets, nor do we know the likelihood that such planets might harbor advanced civilizations like our own. However, some stars can probably be ruled out as candidates for advanced civilizations. For example, given that it took a few billion years for humans to evolve o ...
Homework 4
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
... 1. If a protostar is forming out of a cold molecular cloud, how can its luminosity be upto one hundred times as large as the luminosity of the star it will become? ...
d 2
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
... • Some have names that go back to ancient times (e.g. Castor and Pollux, Greek mythology) • Some were named by Arab astronomers (e.g. Aldebaran, Algol, etc.) • Since the 17th century we use a scheme that lists stars by constellation – in order of their apparent brightness – labeled alphabetically in ...
Star Life Cycle and classroom textbooks for research!
... 2. Find a diagram on the internet showing the life cycle of a star and paste it in your document. (2 pts) 3. Find a “Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram” and paste it in your document. (2pts) 4. Using the diagrams above Answer the following questions. (1 pt each) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. ...
... 2. Find a diagram on the internet showing the life cycle of a star and paste it in your document. (2 pts) 3. Find a “Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram” and paste it in your document. (2pts) 4. Using the diagrams above Answer the following questions. (1 pt each) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. k. l. ...
Chapter 21
... Parallax is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places. To measure parallax shift, astronomers look at the same star at two different times of year, when Earth is on different sides of the _______________. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Look on page 758 a ...
... Parallax is the apparent change in position of an object when you look at it from different places. To measure parallax shift, astronomers look at the same star at two different times of year, when Earth is on different sides of the _______________. The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Look on page 758 a ...
A star is a - Trimble County Schools
... – Most do not look like what they are named for Common Constellations • Ursa Major (Big Dipper) • Ursa Minor (Little Dipper) • Draco the Dragon • Orion • Zodiac Animals Constellation stars • Astronomers use constellations to locate _____________________________ • Stars within a constellation are nam ...
... – Most do not look like what they are named for Common Constellations • Ursa Major (Big Dipper) • Ursa Minor (Little Dipper) • Draco the Dragon • Orion • Zodiac Animals Constellation stars • Astronomers use constellations to locate _____________________________ • Stars within a constellation are nam ...
Johnathan - WordPress.com
... two stars in the dipper opposite the handle to point to the North Star. ...
... two stars in the dipper opposite the handle to point to the North Star. ...
AST 207 Homework 5 Due 14 October 2011
... a. (not graded) What is the absolute magnitude of the hottest main-sequence stars? b. (not graded) Why are there no hotter main-sequence stars? c. Stars with a color B-V=0.6 span a range of 5 magnitudes. (not graded) What property of the stars accounts for this observation? (not graded) What is the ...
... a. (not graded) What is the absolute magnitude of the hottest main-sequence stars? b. (not graded) Why are there no hotter main-sequence stars? c. Stars with a color B-V=0.6 span a range of 5 magnitudes. (not graded) What property of the stars accounts for this observation? (not graded) What is the ...
Chapter 21 power point - Laconia School District
... Light-year • The distance that light travels in a year. ...
... Light-year • The distance that light travels in a year. ...
Stars - BrainBytes
... Middle aged star predicted to keep shining for 5 billion more years Diameter: 870,000 miles wide ...
... Middle aged star predicted to keep shining for 5 billion more years Diameter: 870,000 miles wide ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.