* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Cycle of a Star
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
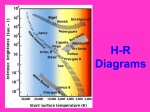
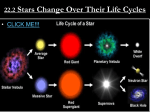
Life Cycle of a Star 1st Stage of Life Ball of gas and dust that is pulled together by gravity Nuclear fusion starts as gas cloud becomes denser and hotter Nuclear Fusion hydrogen atoms fuse into helium Creates the intense energy found in stars Four types of stars make up the life of a star Main Sequence Giants Super Giants White Dwarfs Main Sequence (the Sun) 2nd stage Longest stage Hydrogen changes into helium which creates enormous amounts of energy The size of the star does not change much Giants and Supergiants 3rd stage Main Sequence star becomes a red giant Red giant star that expands and cools once it loses all its hydrogen Center shrinks and atmosphere grows large and cools Dwarf small hot star that is the leftover center of an older star Final stage Can shine for billions of years before they extinguish White Hertzprung-Russell Diagram Shows the relationship between a star’s surface temperature and absolute magnitude Used to study the lives of stars Most stars lie along the main sequence portion of the diagram Age of stars Average stars become red giants then white dwarfs More massive stars explode into a variety of objects Supernova gigantic explosion in which a massive star collapses Occurs after a massive star uses up its fuel source Neutron Star a star that has collapsed to a point at which all particles are neutrons A neutron star that spins and sends out beams of radiation is called a pulsar Black Hole an object that is so massive that light cannot escape its gravity Remnants of a supernova Astronomers can detect black holes by using X-ray telescopes Question 1 What sun? kind of a star is the Answer Main Sequence Question 2 What is the H-R diagram? Answer A graph that shows the relationship between a star’s temperature and absolute magnitude Question 3 What are the four main types of stars? Answer Main-Sequence Giants and Supergiants White Dwarfs