Notes - CH 12
... Neptune to about 50AU from the sun. Only discovered in 1992 Pluto is the largest known member of the Kuiper Belt This discovery is what helped Pluto ...
... Neptune to about 50AU from the sun. Only discovered in 1992 Pluto is the largest known member of the Kuiper Belt This discovery is what helped Pluto ...
At the Heart of the Matter: The Blue White Dwarf in M 57. Paul Temple
... elements may be observed in smaller amounts. DB This class may be regarded as an extension of the DO group into lower temperature regions (below around 30,000K). The cooler temperatures are insufficient to ionise helium, and so the spectrum is dominated by He I, with only trace amounts of H (only 1/ ...
... elements may be observed in smaller amounts. DB This class may be regarded as an extension of the DO group into lower temperature regions (below around 30,000K). The cooler temperatures are insufficient to ionise helium, and so the spectrum is dominated by He I, with only trace amounts of H (only 1/ ...
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...
... Along the main sequence, stars of greater magnitude are hotter (have more energy) c. How is a star’s luminosity related to its energy? For main-sequence stars, the luminosity increases with temperature. For the giants and super-giants, large (high magnitude) and luminous stars are actually quite coo ...
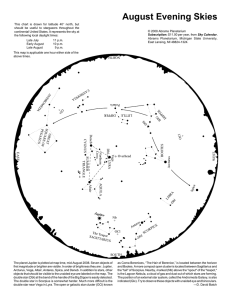
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2008. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2008. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
February - Bristol Astronomical Society
... Laelaps, Acteon's hound; the hound of Procris, Diana's nymph; or the one given by Aurora to Cephalus, so famed for its speed that Zeus elevated it to the sky. It is however most commonly known as, the largest of Orion's hunting dogs. Canis Minor represents a second smaller dog. ...
... Laelaps, Acteon's hound; the hound of Procris, Diana's nymph; or the one given by Aurora to Cephalus, so famed for its speed that Zeus elevated it to the sky. It is however most commonly known as, the largest of Orion's hunting dogs. Canis Minor represents a second smaller dog. ...
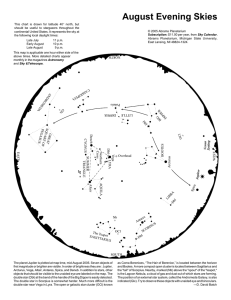
August Evening Skies
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
... The planet Jupiter is plotted at map time, mid-August 2005. Seven objects of first magnitude or brighter are visible. In order of brightness they are: Jupiter, Arcturus, Vega, Altair, Antares, Spica, and Deneb. In addition to stars, other objects that should be visible to the unaided eye are labeled ...
Word
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
HOMEWORK #1
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
... Just as brightness is related to apparent magnitude, luminosity is related to a term called “absolute magnitude.” Astronomers refer to a star’s “absolute magnitude (M)” as the apparent magnitude it would have at an arbitrary standardized distance of 10 parsecs (i.e., 32.6 light-years). #2. Combine ...
Star Classification
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
... The first people to combine a camera with a spectroscope were the father and son team of John and Henry Draper in the 1870s. Their work was carried on by Edward C. Pickering who, by 1918, had listed the spectra of over 200000 stars. Using details about luminosity and composition, stars are classifie ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... 34. What is a parallax? What is it used to measure in space? 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 39. How are main sequence stars represented on a HR Diagram? 40. W ...
... 34. What is a parallax? What is it used to measure in space? 35. What is a Hertzsprung Russell Diagram? 36. What is on the X axis of a HR Diagram? 37. What is on the Y axis of the HR Diagram? 38. What is used to determine luminosity? 39. How are main sequence stars represented on a HR Diagram? 40. W ...
Stars and Galaxies - Earth Science: Astronomy
... Section 4 Galaxies and the Universe A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from ...
... Section 4 Galaxies and the Universe A. Galaxy—gravity holds together a large collection of stars, gas, and dust 1. Earth’s galaxy is Milky Way which is part of a galaxy cluster named the Local Group 2. Spiral galaxies—spiral arms wind out from ...
CONSTELLATION CASSIOPEIA named after the
... It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper. In northern locations it is visible year-round and it can be seen even in low southern ...
... It is easily recognizable due to its distinctive 'W' shape formed by five bright stars. It is bordered by Andromeda to the south, Perseus to the southeast, and Cepheus to the north. It is opposite the Big Dipper. In northern locations it is visible year-round and it can be seen even in low southern ...
ORIGIN OF THE UNIVERSE
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
... - When all of the helium fuel of the Red Giant has been used. The outer layers explode off into space just leaving the white hot core (very small nearing the end of life) ...
Types of Stars - WordPress.com
... luminosity and distance from Earth. • Hertzsprung and Russell independently discovered that each type of star has specific properties. They organized their findings into what is now called a Hertzsprung and Russell ( H-R) diagram ...
... luminosity and distance from Earth. • Hertzsprung and Russell independently discovered that each type of star has specific properties. They organized their findings into what is now called a Hertzsprung and Russell ( H-R) diagram ...
An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
... An Introduction to the Night Sky Stars and Constellations 1. What is the Latin root word of star? 2. Why do stars “twinkle”? 3. Why do planets “shine”? ...
a geolocation. Obtain the information related to certain star.
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
The Lives of Stars
... 200 billion years • medium-mass stars like the sun live for about 10 billion years • astronomers think the sun is about 4.6 billion years old, so it is almost halfway through its lifetime ...
... 200 billion years • medium-mass stars like the sun live for about 10 billion years • astronomers think the sun is about 4.6 billion years old, so it is almost halfway through its lifetime ...
stars concept review
... b. Carbon fuses into hydrogen. c. Helium fuses into hydrogen. d. Carbon fuses into oxygen. _____ 8. How long would a star with the sun’s mass stay on the main sequence? a. a million years c. 10 trillion years b. a billion years d. 10 billion years _____ 9. After a protostar’s temperature rises to 10 ...
... b. Carbon fuses into hydrogen. c. Helium fuses into hydrogen. d. Carbon fuses into oxygen. _____ 8. How long would a star with the sun’s mass stay on the main sequence? a. a million years c. 10 trillion years b. a billion years d. 10 billion years _____ 9. After a protostar’s temperature rises to 10 ...
Measuring the Stars pages 813-820
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
... the constellation that is just starting to become apparent, over the horizon, when the sun disappears, and darkness closes on the Earth. ...
Discussion Activity #10
... 1. Suppose two stars are identical except that one is twice as far away from us as the other. Which statement is true? A. Both stars have the same luminosity, but the apparent brightness of the closer star is four times as great as that of the more distant star. B. Both stars have the same apparent ...
... 1. Suppose two stars are identical except that one is twice as far away from us as the other. Which statement is true? A. Both stars have the same luminosity, but the apparent brightness of the closer star is four times as great as that of the more distant star. B. Both stars have the same apparent ...
Document
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
... Most of the stars on the HR Diagram are classified as which type of star? ___________________________________________ ...
Characteristics of stars powerpoint
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
... • The distance that light travels in one year • It travels about 9.5 million million km • Travels at a speed of 300,000 km per second ...
Stars - Quia
... we could position the star 32.6 light-years away (the distance that is the furthest star we can see from Earth) ...
... we could position the star 32.6 light-years away (the distance that is the furthest star we can see from Earth) ...
Auriga (constellation)

Auriga is one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Located north of the celestial equator, its name is the Latin word for ""charioteer"", associating it with various mythological charioteers, including Erichthonius and Myrtilus. Auriga is most prominent during winter evenings in the Northern Hemisphere, along with the five other constellations that have stars in the Winter Hexagon asterism. Because of its northern declination, Auriga is only visible in its entirety as far as 34° south; for observers farther south it lies partially or fully below the horizon. A large constellation, with an area of 657 square degrees, it is half the size of the largest constellation, Hydra.Its brightest star, Capella, is an unusual multiple star system among the brightest stars in the night sky. Beta Aurigae is an interesting variable star in the constellation; Epsilon Aurigae, a nearby eclipsing binary with an unusually long period, has been studied intensively. Because of its position near the winter Milky Way, Auriga has many bright open clusters in its borders, including M36, M37, and M38, popular targets for amateur astronomers. In addition, it has one prominent nebula, the Flaming Star Nebula, associated with the variable star AE Aurigae.In Chinese mythology, Auriga's stars were incorporated into several constellations, including the celestial emperors' chariots, made up of the modern constellation's brightest stars. Auriga is home to the radiant for the Aurigids, Zeta Aurigids, Delta Aurigids, and the hypothesized Iota Aurigids.