* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars - Quia
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
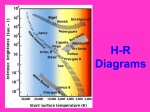
What is a star? - body of gasses that give off “tons of” energy (light & heat) - clusters = those little specks in the sky that we see may really be more than one star…. PHYSICAL PROPERTIES OF STARS -1. Differ in SIZE 2. Differ in COLOR 3. Differ in D I S T A N C E from us 4. Differ in COMPOSITION 5. Differ in BRIGHTNESS Our Sun in considered an average-sized star! The diameter of our sun is about 109 times the diameter of the Earth! X 109 = It has been burning for about 5 billion years. It is only middle-aged. It will burn for about 5 billion more years!! How Are Star Sizes Like Celebrities? • Sometimes the larger the star, the shorter the life span. • This is like the bigger the celebrity (more famous), the shorter their life span! Ex. James Dean, Chris Farley BRIGHTNESS Function of how LARGE the star is, how OLD it is, and how FAR AWAY. APPARENT MAGNITUDE - IS HOW BRIGHT THE STAR IS TO OBSERVERS ON EARTH APPARENT Magnitude: - the brightness how WE see it - the brightest star in a constellation is called the ‘alpha’, then ‘beta’, etc… Size and closeness can effect apparent magnitude - Distance to Stars Our Sun is the closest star at 93 million miles distance. Next is Alpha Centauri at a distance of 4.27 light years. A light year is 5.88 trillion miles. Stellar Parallax Parallax = shift in angle that occurs when a nearby object is seen against a distant backdrop from two different perspectives is a star’s apparent brightness if we could position the star 32.6 light-years away (the distance that is the furthest star we can see from Earth) THERE ARE DIFFERENT WAYS TO MEASURE STAR BRIGHTNESS : SIZE -depends on and TEMPERATURE COLOR Yes, stars have different colors! The temperature of the star determines its color. Star Color - if you look close enough…you’ll see colors…. - blue = HOT = 17,000o - red = not so hot = 1,700o Our sun = orange ~ 10,000o What are the Star Colors? Blue White Yellow Orange Red Hottest Coolest Star patterns : - 1000’s of years of observations - want to organize what they saw -constellations = they are named after animals, greek gods and legendary heroes - there are 88 named constellations What should be the brightest star for us? - THE SUN! - it’s the closest - so it should appear the brightest - BUT - it’s just average in reality - ABSOLUTE magnitude = real brightness - H e r t z s p r u n g R U S S E L L D I A G R A M A. 70% HYDROGEN B. 28 % HELIUM C. 1-2% heavy elements like IRON, TITANIUM, CALCIUM & SODIUM D. 2 % other heavy elements •Every element has its own characteristic color when made to emit light. •The light from glowing elements can be analyzed with a Spectroscope Spectrum Viewed from these two different locations, a nearby star would appear to shift position with respect to more distant stars The bigger the shift, the closer the start is to earth