* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars - BrainBytes
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Hayashi track wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
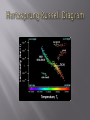
Stars are born from great clouds of gas and dust They mature, grow old, and die The more massive a star is, the shorter its life A star is a sphere of super-hot gases – mostly hydrogen and helium Vary greatly in their masses, size and density The range of colors a star emits depends on its surface temperature. Cool stars redder in color Stars 3900-7000 degrees C yellow Stars 7000-9500 degree C white Stars 9500+ degrees C blue Diagram that pictures the life of a star Classifies stars based on temperature and luminosity Majority of stars (about 90%) fall in this category Runs from upper left (high luminosity, high surface temperature ) to lower right (low luminosity, low surface temperature) Life span: 1 million – 1 billion yrs Actively fuse hydrogen and helium Example: our Sun Closest star to Earth Middle aged star predicted to keep shining for 5 billion more years Diameter: 870,000 miles wide If the sun were hollowed, you could fit 330,000 Earths inside Core Temperature: 27 million degrees Fahrenheit Made out of mostly hydrogen Most stars are red dwarfs Stars with less than 50% the mass of the sun 1/10,000th the energy of the sun It is estimated there are between 200-400 billion stars in our galaxy The closest star to Earth, besides the sun is Proxima Centauri – located 4.2 light years away On the fastest spacecraft, it would still take 70,000 yrs to get there Greater luminosity than main sequence stars Star is moving toward end of life Helium sinks to the center of the core Raises star’s temp. Outer shell begins to swell Beginning of star shedding its outer layer Becomes a small, dense body Cools for billions of years and eventually becomes dark and produces no energy A few stars do not follow the evolutionary path and go out with a bang Violent explosion that leaves behind a small core known as a neutron star If the remnant is large enough = black hole