* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Stars and their Properties
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
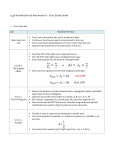
Daniel Fischbach Physics 202-004 – Astronomy 6/21/17 Created on: 3/9/05 Topic: Stars and their Properties We know the most about the Sun than any other star Closest stars (besides the Sun) are hundreds of thousands of times further away than the Sun Stars are so far away so it’s safe to look at them All stars are made up of 75% hydrogen and 25% helium Parallax – Apparent movement of an object based on your own movement You cannot see parallax with the naked eye LARGEST Parallax measurements are 1/3600th of a degree!! 1/60th of a degree = 1 arc minute (1’) 1/60th of an arc minute = 1 arc second (1’’) Nearest stars to the Earth are a couple hundred thousand time the distance between the Sun and the Earth There is a limit to how far out you can use Parallax (100 parsecs) Professional astronomers do not use light years to measure distance Parsec (pc) – Parallax arc second – A star is so far away so it’s parallax is one arc second o Parsec = 3.26 light years Nearest stars to Earth are actually a little bit more than one parsec Cosmological distance ladder – Distance indicators (methods) used to measure distances in space o Lower rungs on the ladder can effect the higher rungs on the ladder o Stellar Parallax and Proper Motion – Used to 100 parsecs – Lowest (smallest distance) Proper Motion is the measurement of a star’s physical motion Must be measured in parallel with Parallax o The Moving Cluster Method – Stars converge to a central point if you are moving backwards in space at very high speed – Used to 1,000 parsecs Sun is not in a star cluster Convergent Point – Point at which the cluster of stars are converging (coming together) Convergent point can be outside the star cluster Taurus has two clusters – Pleiades and Hyades (closest to Earth) Cosmic horizon – Edge of the Observable Universe Age of the Universe is determined by the size of the Observable Universe (right now it’s between 14 and 15 billion years old) Astrometry – Measuring the distance of stars and how they move around Solar Neighborhood – Closest stars to the Sun If you know the distance to a star, you can find out the luminosity, and a lot more about a star Intensity = (luminosity (aka power output)) / (4r2) (r = distance) Apparent magnitude (aka intensity) – Stars are grouped depending on how bright it is (The lower the number, the brighter the star) (you see this when you look at stars in the sky) o Apparent magnitude can change because of where the Earth is in space (ie, if you are closer to a star, it is brighter) The Absolute magnitude (aka luminosity) is how bright a star really is 874005148 Instructor: Libarid A. Maljian Page 1 of 2 Daniel Fischbach Physics 202-004 – Astronomy 6/21/17 Luminosity (proportional to) (4r2) (r = radius of the star) Luminosity is also (proportional to) (surface temperature)4 We need to find the star’s temperature to find out the luminosity and size of the star How to find a star’s temperature (aka spectral type) o Blue magnitude (B) = Blue filter o Visual magnitude (V) = Green filter o Red magnitude (R) = Red filter B–V V–R + (More Blue than Green) + (More Green than Red) Fin. Color: Blue Temp: Hot – (More Green than Blue) – (More Red than Green) Fin. Color: Red Temp: Cool – (More Green than Blue) + (More Green than Red) Fin. Color: Green Temp: Medium o Old star temperature classification: O (hottest, Blue), B, A (White), F, G (Sun is G2), K, M (coolest, Red)) Each letter can range from 0 to 9 (ie, O0 is the hottest, while O9 is the coolest O star) Oh Be A Fine Gal Kiss Me 874005148 Instructor: Libarid A. Maljian Page 2 of 2