homework assignment 1
... 3. Compare the size of an electron to the size of the universe. By what factor is the universe bigger? Approximately how many orders of magnitude is this? ...
... 3. Compare the size of an electron to the size of the universe. By what factor is the universe bigger? Approximately how many orders of magnitude is this? ...
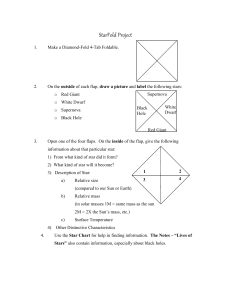
Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
... Properties of Main Sequence Stars 10 points Extra Credit. Due next class. ...
Stars - cmamath
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
... Describe the life cycle of stars and be able to diagram it. Make and use an H-R diagram. Define luminosity and magnitude. ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Apparent Magnitude The measurement of brightness is assigned a number on a scale – Brightest stars have lowest numbers – Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
... Apparent Magnitude The measurement of brightness is assigned a number on a scale – Brightest stars have lowest numbers – Dimmest stars have highest numbers ...
Name
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
... The Apparent Magnitude Scale The apparent magnitude of stars was first recorded by the Greek astronomer Hipparchus about 160 B.C. Hipparchus grouped stars according to their brightness or magnitude. He called the twenty brightest stars first magnitude stars. Stars half that bright were second magnit ...
chapter 18
... uranium to form lead, Pb. b) helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
... uranium to form lead, Pb. b) helium nuclei to form carbon nuclei. c) hydrogen nuclei to form helium nuclei. d) carbon nuclei to form magnesium nuclei. ...
CONSTELLATION CANES VENATICI the two hunting dogs Canes
... known as a brache, which is the same word as brace, meaning pair, and embrace). Here the leash is held by Bootes, the Herdsman or Bear Driver as they together pursue the Great Bear, Ursa Major, as it circles the Pole. The Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius formed this constellation in 1687 from a s ...
... known as a brache, which is the same word as brace, meaning pair, and embrace). Here the leash is held by Bootes, the Herdsman or Bear Driver as they together pursue the Great Bear, Ursa Major, as it circles the Pole. The Polish astronomer Johannes Hevelius formed this constellation in 1687 from a s ...
Ginger Dublin 6th Grade Science
... causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
... causing its core to collapse. • So dense that even light can’t escape its gravity. ...
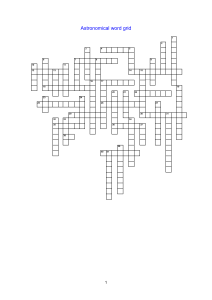
Astronomy word grid
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
... 18. The apparent backwards movement of the planets in the sky 22. A type of variable star used to measure distance 25. The name used to describe the brightness of a star 26. The name given to a very large but cool star 29. He discovered the moons of Jupiter 30. A type of telescope using lenses 35. A ...
Ch 28 Fact Sheet
... Name _______________________________________________________ Date ____________ Per ______ Ch 28 Fact Sheet ________________ 1. The two lenses of a refracting telescope. ________________ ________________ 2. Type of constellation Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Draco & Cepheus are because they go counter cloc ...
... Name _______________________________________________________ Date ____________ Per ______ Ch 28 Fact Sheet ________________ 1. The two lenses of a refracting telescope. ________________ ________________ 2. Type of constellation Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Draco & Cepheus are because they go counter cloc ...
Stellar Evolution and the HR Diagram Study Guide
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
... Which star will appear brighter in the night sky, a star with an apparent magnitude of 0 or a star with an apparent magnitude of +1? Star with apparent magnitude of 0 ...
Astronomy
... Argued that if the Earth orbited the sun, then stars should appear to move over a period of 6 months. Called this the stellar parallax (the shift of an object against a background caused by a change in observer position; hard to see) Kepler was his apprentice ...
... Argued that if the Earth orbited the sun, then stars should appear to move over a period of 6 months. Called this the stellar parallax (the shift of an object against a background caused by a change in observer position; hard to see) Kepler was his apprentice ...
Study Guide
... What does each color represent? Blue: . ______________________________ White: . ______________________________ Yellow: . ______________________________ Red: . ______________________________ ...
... What does each color represent? Blue: . ______________________________ White: . ______________________________ Yellow: . ______________________________ Red: . ______________________________ ...
Chapter 28 Notes
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
... A group of stars that appear to form a pattern in the sky How many constellations can be seen from the northern and southern hemispheres? ...
Magnitude Scale
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
... Absolute Magnitude • Measure of the brightness of a star if observed from 10 parsecs away (equivalent of luminosity) • Denoted by M or MV • Absolute magnitude and apparent magnitude are the same at a distance of 10 parsecs. ...
The Life Cycle of Stars Webquest
... http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. Stars begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called_____________. 2. What is a protostar? ...
... http://www.seasky.org/cosmic/sky7a01.html and answer the following questions: 1. Stars begin their lives as clouds of dust and gas called_____________. 2. What is a protostar? ...
The Stellar Luminosity Function
... Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 light year radius that are in trinsically brighter than the sun. They are Sirius A (1.45), ...
... Th e absolute magnitudes were then rounded to the nearest whole magnitude and then plotted. (See fig.1 .) The sun's absolute magnitude is 4.8. It can be seen readily that there are only 3 stars within the 16 light year radius that are in trinsically brighter than the sun. They are Sirius A (1.45), ...
homework assignment 3
... nearby star will appear… (You are welcome to formulate your own sentence, but it should convey what parallax is without resorting to diagrams.) ...
... nearby star will appear… (You are welcome to formulate your own sentence, but it should convey what parallax is without resorting to diagrams.) ...
Chapter 27 Stars and Galaxies
... Absolute Magnitude Brightness from 32.6 ly Ex: If the sun was 32.6 ly away, it would be a fifth magnitude star. Its absolute magnitude = +5 Most stars are between a -5 and +15 ...
... Absolute Magnitude Brightness from 32.6 ly Ex: If the sun was 32.6 ly away, it would be a fifth magnitude star. Its absolute magnitude = +5 Most stars are between a -5 and +15 ...
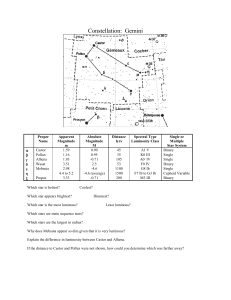
Gemini
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
... corresponds to a linear diameter of about 24 light years; its central density is about 6.21 stars per cubic parsec. Some authors have estimated a larger diameter of up to 46' (H. Shapley in 1930). With about 100 million years (WEBDA gives a value 95, the Sky Catalogue 2000.0 of 110 million years), i ...
Surface Environments of the Planets o+ our Solar System
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
... In this exercise, you will also become more familiar with the various naming systems for stars. Remember, only the brightest stars which form our constellations have been given proper names. There are thousands of stars that have either Bayer Greek letter names, and even more that have Flamsteed num ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.