Stars Part 2 - westscidept
... if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 light years away. There are thousands of closer stars in the sky that we do not see because they are too dim. ...
... if it is close. At the same time, we may barely be able to see a very bright star if it is too far away. • Betelgeuse which is one of the brightest stars in the sky is 310 light years away. There are thousands of closer stars in the sky that we do not see because they are too dim. ...
Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... 3) Which property of a star can be determined by its color? Temperature 4) About how many stars are estimated to occur in pairs or multiples? 50% ...
... 3) Which property of a star can be determined by its color? Temperature 4) About how many stars are estimated to occur in pairs or multiples? 50% ...
stars and constellations
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
... the axis will only point at Polaris for a few hundred years, then, another star will be “North”. The ancient Egyptians could not have used Polaris as a compass. Why stars “move” ...
HR DIAGRAM REPORT FORM
... 2. In Table 10.1, the brightest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnitude (M) not higher. If double both must be considered. # brighter than the sun: ________ In Table 10.2, the closest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnit ...
... 2. In Table 10.1, the brightest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnitude (M) not higher. If double both must be considered. # brighter than the sun: ________ In Table 10.2, the closest stars, how many stars are brighter than the sun? Brighter means lower magnit ...
Document
... • Mass, diameter and luminosity (energy output of the star per second) are the basic properties of a star • Magnitude: how bright the star appears; +1 was the brightest star, +2 was the next brightest star, +3 was the third brightest star ...
... • Mass, diameter and luminosity (energy output of the star per second) are the basic properties of a star • Magnitude: how bright the star appears; +1 was the brightest star, +2 was the next brightest star, +3 was the third brightest star ...
What Can We See in the Night Sky?
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies ...
... Star Clusters • Groups of stars that are close together and travel together are known as star clusters • Star clusters are part of galaxies ...
KOI-54 Claude Plymate There is a star system about 45 light years
... pulsation modes are synced to their orbital period! The strongest pulsation modes turn out to be 90 and 91 times their orbital period. Apparently, these modes are natural resonance periods for the two stars. The stars are nearly but not exactly identical with slightly different resonance periods. Ev ...
... pulsation modes are synced to their orbital period! The strongest pulsation modes turn out to be 90 and 91 times their orbital period. Apparently, these modes are natural resonance periods for the two stars. The stars are nearly but not exactly identical with slightly different resonance periods. Ev ...
a geolocation. Obtain the information related to certain star.
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
... An amateur astronomer is searching for a star in the field. She forgot her star charts or they don't have the exact information she is looking for.... ...
Stars
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
... A ‘Star’ is a large celestial body composed of gravitationally contained hot gases emitting electromagnetic radiation, especially light, as a result of nuclear reactions inside the star. The sun is a star. With the exception of the sun, stars appear to be fixed, maintaining the same pattern in the s ...
Sun, Earth and Moon Model
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
... is a planet orbiting a distant star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But de ...
Understanding Stars
... – Absolute magnitude – how bright the star would be at 10 parsecs. • Measure of how bright it really is – Reminder: small magnitudes are bright • A parsec is 3.26 light years Luminosity • Luminosity: how much energy the star puts out. – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • ...
... – Absolute magnitude – how bright the star would be at 10 parsecs. • Measure of how bright it really is – Reminder: small magnitudes are bright • A parsec is 3.26 light years Luminosity • Luminosity: how much energy the star puts out. – luminosity is a measure of the energy in the form of photons • ...
Study Guide for Stars and the Universe Test
... The source of energy that generates light How astronomers determine the distance to stars How a star’s color relates to temperature The order of the spectral classes of stars (O, B, etc.) What determines the brightness (magnitude) of a star. The difference between absolute magnitude, and apparent ma ...
... The source of energy that generates light How astronomers determine the distance to stars How a star’s color relates to temperature The order of the spectral classes of stars (O, B, etc.) What determines the brightness (magnitude) of a star. The difference between absolute magnitude, and apparent ma ...
Quiz #4 – The Electromagnetic Spectrum and Stars
... On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by ___________________and ___________________. ...
... On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by On an H-R Diagram, stars are classified by ___________________and ___________________. ...
The Planet with Three Suns
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
... star.) The strange new world was discovered orbiting a star in a triple star system. That means its parent star orbits alongside two other stars. This makes sunrises and sunsets something special — sometimes one sun rises in the sky, sometimes it’s two or three! But despite this, this planet is not ...
Astronomy Snakes and Ladders Earth, third planet in Solar System
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
... consist of dust and gas. Usually seen when it is close to the Sun ...
Allison McGraw - WordPress.com
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
... Orionis (β Ori, β Orionis), is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the seventh brightest star in the night sky, with visual magnitude 0.13. The star as seen from Earth is actually a triple star system, with the primary star (Rigel A) a bluewhite supergiant of absolute magnitude −7.84 a ...
07-01TheColsmologicalDistanceLadder
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
... Cepheid Variables: How to measure the distance to a galaxy using Cepheid variable stars: 1. Find the Cepheid, measure its spectrum 2. Measure a couple periods, and its apparent magnitude m 3. Look up its absolute magnitude 4. Use M = m - 5 log10(d/10) to find d ...
File
... color index for each star. • In 1913 Henry Norris Russell (U.S.) plotted the absolute magnitude versus the spectral type. • The results were the same, the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
... color index for each star. • In 1913 Henry Norris Russell (U.S.) plotted the absolute magnitude versus the spectral type. • The results were the same, the HertzsprungRussell diagram. ...
Problem Sheet for Introduction to Astrophysics
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
... a) If you could stand on the event horizon of a one-solar-mass black hole (M=1.991030 kg), what is the tidal force acting on you? (Assume your weight is 70kg and your height is 2 m) b) If you could stand on the event horizon of a 109 solar mass black hole, what is the tidal force acting on you (the ...
a star.
... • Hottest, most massive stars • Shortest lives: just millions of years • Use hydrogen quickly ...
... • Hottest, most massive stars • Shortest lives: just millions of years • Use hydrogen quickly ...
Planetarium Activity 1 Learning to measure brightness and Limiting
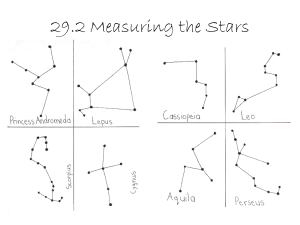
... 1. You will be shown five popular constellations (Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Leo, Ursa Minor and Orion) fix their position in the sky when the lights are off so that its approximated location can be found as the lights brighten. Use dots to Sketch the constellations on your worksheet and connect the st ...
... 1. You will be shown five popular constellations (Ursa Major, Cassiopeia, Leo, Ursa Minor and Orion) fix their position in the sky when the lights are off so that its approximated location can be found as the lights brighten. Use dots to Sketch the constellations on your worksheet and connect the st ...
PISGAH Text by Dr. Bob Hayward ASTRONOMICAL Astronomer
... describes the timing of the five visible or “classical” planets in early June. The giant Jupiter leads the way and is high in the south at sunset. Lying just under the hind legs of the celestial king of the beasts, Leo the lion, Jupiter, the king of the planets, is the brightest object in the sky. I ...
... describes the timing of the five visible or “classical” planets in early June. The giant Jupiter leads the way and is high in the south at sunset. Lying just under the hind legs of the celestial king of the beasts, Leo the lion, Jupiter, the king of the planets, is the brightest object in the sky. I ...
KMS Universe Test Study Guide
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
... 6) Why does the sun have such a great apparent magnitude, when it has only an average absolute magnitude? The Sun is very close to us, so it appears to be brighter than it is compared to other stars in the Universe. 7) Why are red giant stars so bright, when they are among the coolest of stars? Beca ...
Answers Universe Cornell Notes Chapter 8, Sec 2
... how bright it appears to be from Earth, not how bright it actually is. Absolute magnitude is how bright the star is at a standard distance from Earth. It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main ...
... how bright it appears to be from Earth, not how bright it actually is. Absolute magnitude is how bright the star is at a standard distance from Earth. It is a diagram or graph that compares the relationship between a star’s temperature and its brightness (magnitude). 90% of all stars are in the main ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.