labex7
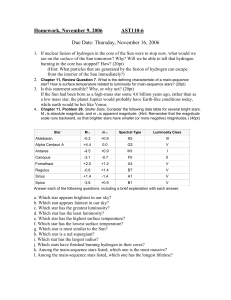
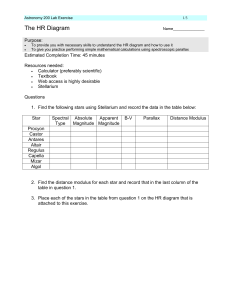
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) ...
... online notes Chp 8.5) Record this in the table shown above. Also estimate the radius for each star from the HR diagram and where you placed these stars. 6. Use the distance modulus found earlier to compute the distance to these stars. (See Chp 8.1) ...
Astronomy Toolkit
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
... appears in the sky – Some faint stars are intrinsically bright, but are very distant – Some bright stars are very faint but happen to lie close to us ...
ASTR2050 Spring 2005 • In this class we will ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
... Two stars in orbit about their common center of mass Various types of binary stars. Doppler shifts give velocity Orbital mechanics give the masses of the two stars Eclipses allow determination of individual stellar radii See Studio Laboratory this Friday ...
Homework, August 29, 2002 AST110-6
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
... e. Which star has the highest surface temperature? f. Which star has the lowest surface temperature? g. Which star is most similar to the Sun? h. Which star is a red supergiant? i. Which star has the largest radius? j. Which stars have finished burning hydrogen in their cores? k. Among the main-sequ ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
... What is the name of our galaxy ? ____MILKY WAY______ The planets that are closer to the sun have a ...
Earth Science
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
... Apparent change in position of an object resulting from a change in the angle or in the position from which it is ...
Slide 1
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
... • Size can be small, medium or massive • Binary Stars: when two stars orbit around each other • Stars of equal mass have their center of mass in the middle ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... Absolute Magnitude • The brightness the star would have if it were at a standard distance from Earth. • Astronomers must find out the star’s apparent magnitude and its distance from Earth then calculate its absolute magnitude. ...
... Absolute Magnitude • The brightness the star would have if it were at a standard distance from Earth. • Astronomers must find out the star’s apparent magnitude and its distance from Earth then calculate its absolute magnitude. ...
Name Date Period ______ 30.1 Characteristics of Stars Definitions
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
... 19. What are circumpolar stars? What is one example? ...
The magnitudes of stars
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
... However this does not give a true impression of the actual brightness of a star. A nearby faint star may well look brighter than another star that is actually brighter but more distant. (A good example of this is shown by Rigel and Sirius in the following table. Sirius looks brighter than Rigel when ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
... Brightness of Stars • Absolute magnitude – measure of the amount of light given off by a star • Apparent magnitude – a measure of the amount of light received on Earth (a dim star can appear bright if its close to Earth; a bright star can appear dim if its far away) ...
Star
... Size & Mass: -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is m ...
... Size & Mass: -Some dwarf stars are as small as the Earth. -Our sun is a medium size star (1,390,000 km). -Some stars are 1,000 times larger than our sun. -Density affects mass…no relationship between size and mass. Example: a star can be smaller than our sun, but have a greater mass…meaning it is m ...
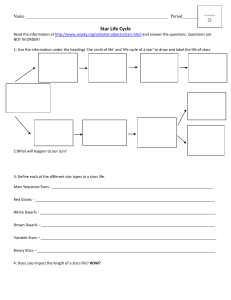
Life Cycle of Star Flipbook
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
... 6. What is going to happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its next stage? 7. What is the final stage of our Sun’s life? 8. What will happen to our Sun’s magnitude and temperature when it goes to its final stage? 9. What determines which star will go supernova? 10. What two fo ...
9 spectroscopic parallax
... The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26. What might its absolute magnitude be? A. –26 B. –23 C. 4.85 D. –33 E. Cannot determine ...
... The Sun has an apparent magnitude of –26. What might its absolute magnitude be? A. –26 B. –23 C. 4.85 D. –33 E. Cannot determine ...
18.3 NOTES What is magnitude? Objective: Compare apparent
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
... Without a telescope, you can see about 2000 stars in the night sky. Some appear brighter than others. One way to measure a star’s brightness is by magnitude. The brightness of a star depends on its temperature, size, and distance from Earth. A hot star is usually brighter than a cool star. A large s ...
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
... 10: Our solar system formed from a ____________________________________________________generation nebula. 11. What two pieces of information classify stars? ...
Characteristics of Stars
... It is a cluster of stars (hundreds of billions of stars) Our solar system is located in the Milky ...
... It is a cluster of stars (hundreds of billions of stars) Our solar system is located in the Milky ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
... Approximately 90% of the visible universe’s mass is composed of ___hydrogen___ In the H-R diagram, stars are classified on the basis of ...
How Bright is that Star?
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
... A 1st magnitude star is 100x brighter than a “6th ” Each order of magnitude is therefore 2.15 times brighter than the one below it. Magnitude is now given in decimal form. Deneb now rates a 1.26, and Betelgeuse rates .87. Hipparchus underestimated how bright the brightest were, so now we even use ne ...
REVIEW: STAR`S TEST
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
... What looks like a potato, orbits the sun between Mars and Jupiter, and is made of rock ? _________________________ A rock that hits the Earth’s surface is called a _______________________. A rock that is flying through space is called a _____________________________. A rock that burns up in our atmo ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.