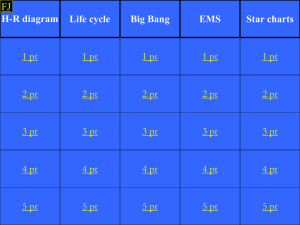
Main Sequence Stars
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
... Denmark, and Henry Norris Russell at Princeton University, around 1913. They plotted the locations of stars on a graph with the horizontal coordinate being spectral type (equivalent to temperature) and the vertical coordinate being absolute magnitude (equivalent to luminosity). The result, called th ...
Unit 12 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
... Classification • H-R diagram • Absolute magnitude vs. temperature • For most stars the brightness increases as surface temp increases • Main sequence stars are band in center ...
chap17_s05_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
chap17_f04_probs
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
... Given a star with an apparent magnitude of 10.0, and an absolute magnitude of 2.5, you are asked to find the distance to the star. ANSWER: Stars appear fainter if located further away, just like any luminous object. The magnitude of a star represents its brightness, either its perceived brightness, ...
Figure 10-6 The same star field shown in Figure
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
... Hipparchus misjudged the magnitudes of some of the brighter stars, however. When the magnitude scale was extended and expressed by a mathematical formula, it developed that the brighter stars are brighter than those of the first magnitude; indeed they are even brighter than those of zero magnitude. ...
Chapter 18 Study Guide
... 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
... 1. What is a star? 2. Describe the process of star formation in 5 steps. ...
Study Guide_galaxies, Tools, and Stars Test
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
... 6. Name and describe the 3 types of galaxies. 7. Where is our solar system located in the Milky Way galaxy? 8. What is a light year? 9. What contains all the matter and energy that exists? 10. Name two types of optical telescopes. 11. What do radio telescopes receive and where do they come from? 12. ...
The Hot-plate Model of a Star Model of Stars— 3 Oct
... How does the energy from the hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand an ...
... How does the energy from the hot-plate get to my hand? What are two ways to make a hot plate produce more energy per second? (The same question applies to a star: What are two ways to make a star brighter or more luminous?) What can I do to make the same hot-plate at the same setting burn my hand an ...
Unit 11 Guide: Concepts of Earth Science Stars, Galaxies, and the
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
... 1. What are the names and characteristics of the three types of galaxies? What type of galaxy is the Milky Way galaxy? 2. What evidence do scientists use to support the Big Bang Theory? Explain the sequence of events predicted by the Big Bang Theory. 3. Explain Hubble’s Law. 4. Compare and contrast ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
... The creator of the system for measuring the apparent brightness of stars is believed to be Hipparchus, who lived in Nicaea (Turkey) during the second century BCE. Hipparchus is believed by many to be the greatest of the ancient astronomers. The original scale of apparent magnitude gave the brightest ...
Astronomical distances and Stellar magnitudes
... Astronomical distances and stellar magnitudes 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate dis ...
... Astronomical distances and stellar magnitudes 1. What is meant by a light year? 2. What is meant by an astronomical unit (AU)? 3. What is meant by a parsec (pc)? 4. What is meant by a mega parsec (Mpc)? 5. What is meant by the apparent magnitude of an astronomical object? 6. Give the approximate dis ...
Blank Jeopardy
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
... A rainbow of colors is produced when white light passes through a prism because the light ___ ...
red shift blue shift
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
... The event horizon is the boundary that marks the “point of no return” for a black hole. Also thought of as the size of the black hole. There is a super-massive black hole at the center of the Milky Way. ...
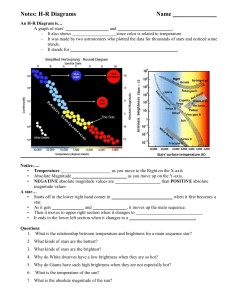
H-R Diagram Notes
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
... An H-R Diagram is… A graph of stars’ ___________________ and ________________________. – It also shows ___________________ since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. – It stands for _____________________ ...
Physical properties of stars
... Too little mass-failed star (Brown dwarf) Too much mass- Blue Giants that fuse their fuel at incredible rates and have short lived lives. Pg 460 diagram of stellar masses Chemical Composition: Primarily hydrogen and helium Trace amounts of other elements Nuclear fusion is the source of energy for a ...
... Too little mass-failed star (Brown dwarf) Too much mass- Blue Giants that fuse their fuel at incredible rates and have short lived lives. Pg 460 diagram of stellar masses Chemical Composition: Primarily hydrogen and helium Trace amounts of other elements Nuclear fusion is the source of energy for a ...
PH507 - University of Kent
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
... 1. Calculate the luminosity (in units of the solar luminosity) of a blackbody of Saturn’s radius that has a temperature of 1000 K? Explain the steps you take in the derivation. The surface temperature of the Sun is 5780 K. The radii of Saturn and the Sun are 6.00 x 107 m and 6.96 x 108 m, respective ...
One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
... One physical property of a star is apparent magnitude. Which of the following is used in determining the apparent magnitude of a star? A. the constellation the star is in B. the distance the star is from Earth C. the number of times the star rotates D. the number of prominences the star makes ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.