HR-diagram - Bakersfield College
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
... • two stars with the same absolute magnitude would not be the same apparent magnitude WHY? • To compare absolute brightness • use a standard distance of 32.6 light-years away from earth ...
SNC1PL Celestial Objects and Constellations
... Meteoroid: A lump of rock or metal smaller than an asteroid travelling through space Meteor: A meteoroid that has become trapped in Earth’s gravity. Friction from Earth’s atmosphere causes the meteor to glow. Meteorite: A meteor that has enough mass to strike the surface of Earth before burning up ...
... Meteoroid: A lump of rock or metal smaller than an asteroid travelling through space Meteor: A meteoroid that has become trapped in Earth’s gravity. Friction from Earth’s atmosphere causes the meteor to glow. Meteorite: A meteor that has enough mass to strike the surface of Earth before burning up ...
File
... Absolute magnitude is the brightness of the star compared to other stars at the same distance. Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears from Earth. ...
... Absolute magnitude is the brightness of the star compared to other stars at the same distance. Apparent magnitude is how bright it appears from Earth. ...
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
... 4. How many kilometers are in three light-years? (You won’t find this answer word for word in the book. You have to think about it after reading the book example). ...
Astronomy Objectives
... Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know ...
... Doppler effect and measuring motion of stars with their absorption spectra: Red-shift → going away from us; blue-shift → coming toward us The Hubble Law; state it and describe the evidence that supports it Big Bang Theory: be able to explain how the universe was formed according to this theory; know ...
Northern Hemisphere – December 2012
... month and about 02:30 at the end. Its brightness rises from +0.7 to +0.6 during December, while its angular diameter increases from 15.7 to 16.1". Its rings now cover around twice that diameter as they have now opened out to around 18-19 degrees from the line of sight, the greatest angle for six yea ...
... month and about 02:30 at the end. Its brightness rises from +0.7 to +0.6 during December, while its angular diameter increases from 15.7 to 16.1". Its rings now cover around twice that diameter as they have now opened out to around 18-19 degrees from the line of sight, the greatest angle for six yea ...
Stellar Brightness Apparent magnitude
... same distance away to do a fair test for their brightness? This is what astronomers do with the Absolute Magnitude scale They ‘pretend’ to line up the stars exactly 10 parsecs (32.6 l.y.)away and figure out how bright each start would look ...
... same distance away to do a fair test for their brightness? This is what astronomers do with the Absolute Magnitude scale They ‘pretend’ to line up the stars exactly 10 parsecs (32.6 l.y.)away and figure out how bright each start would look ...
F03HW09
... Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparent motions. Therefore, we are limited to the only the nearest stars. If E ...
... Parallax measurements are limited because we measure the motion of a star due to the motion of Earth around the sun. Earth’s orbit is so small compared to the distance to stars that even the nearest stars show very small apparent motions. Therefore, we are limited to the only the nearest stars. If E ...
How Do Astronomers Measure the Brightness of a Star?
... Apparent magnitude- brightness of a star as viewed from Earth A difference of 1 magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 in brightness The smaller (more negative) the #, the brighter the star ...
... Apparent magnitude- brightness of a star as viewed from Earth A difference of 1 magnitude corresponds to a factor of 2.5 in brightness The smaller (more negative) the #, the brighter the star ...
Vocabulary Review
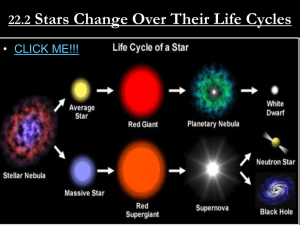
... gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form neutrons ...
... gravity to the point that the electrons and protons have smashed together to form neutrons ...
Slide 1 - Fort Bend ISD
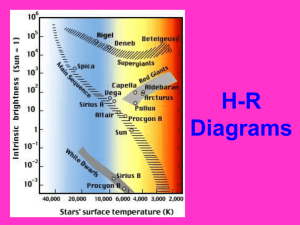
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
... • Betelgeuse fairly cool, but big. Shines brightly • Rigel is a lot smaller than Betelgeuse, but it’s hot, so it also shines brightly ...
name - New York Science Teacher
... Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on the sheet of paper provided to be turned in. 1. Name the brightest star in the known universe. _____________________________ 2. What is its magnitude? ______________ ...
... Use the Stars: Lights in the Sky (www.seasky.org/celestial-objects/stars.html) and write out the answers to the following questions on the sheet of paper provided to be turned in. 1. Name the brightest star in the known universe. _____________________________ 2. What is its magnitude? ______________ ...
H-R Diagrams
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
... – It also shows color since color is related to temperature – It was made by two astronomers who plotted the data for thousands of stars and noticed some trends. ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.