June 2016 night sky chart
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
... The star chart shows the stars and constellations visible in the night sky for Sydney, Melbourne, Canberra, Hobart and Adelaide for June 2016 at about 7:30 pm (local standard time). For Darwin and similar locations the chart will still apply, but some stars will be lost off the southern edge while e ...
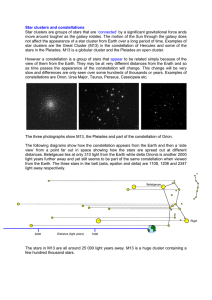
Star clusters and constellations
... star clusters are the Great Cluster (M13) in the constellation of Hercules and some of the stars in the Pleiades. M13 is a globular cluster and the Pleiades an open cluster. However a constellation is a group of stars that appear to be related simply because of the view of them from the Earth. They ...
... star clusters are the Great Cluster (M13) in the constellation of Hercules and some of the stars in the Pleiades. M13 is a globular cluster and the Pleiades an open cluster. However a constellation is a group of stars that appear to be related simply because of the view of them from the Earth. They ...
Monday, October 27
... position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
... position 10 pc away – If a star is actually closer than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a bigger number, i.e. it is intrinsically dimmer than it appears – If a star is farther than 10pc, its absolute magnitude will be a smaller number, i.e. it is intrinsically brighter than it appears ...
Slide 1 - Henrico
... Which energy wave is NOT given off by our sun? seismic, infrared, gamma, or micro ...
... Which energy wave is NOT given off by our sun? seismic, infrared, gamma, or micro ...
INV 12B MOTION WITH CHANGING SPEED DRY LAB DATA
... 2. What relationship do you see between star color and star temperature? (Hint: Cooler stars are…, hotter stars are…) ...
... 2. What relationship do you see between star color and star temperature? (Hint: Cooler stars are…, hotter stars are…) ...
Astronomy Lecture Notes: Stellar Nomenclature I Introduction
... 1. If one star is 1 magnitude brighter than another then that star is actually about 2.5 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 2. If one star is 5 magnitudes brighter than another then that star is actually exactly 100 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 3. Exam ...
... 1. If one star is 1 magnitude brighter than another then that star is actually about 2.5 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 2. If one star is 5 magnitudes brighter than another then that star is actually exactly 100 times brighter as measured in Watts/m2 by a photometer. 3. Exam ...
Stellar Magnitude, Distance, and Motion
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
... Actual star brightness The apparent magnitude that a star would have if it were (in our imagination) placed at a distance of 10 parsecs (which is 32.6 light years) from the Earth Used to describe luminosity - The amount of energy a star gives off each second The 20 Brightest Stars in the Sky C ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. Its center then contracts, and the temperature and pressure at t ...
... hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. Its center then contracts, and the temperature and pressure at t ...
3.6 spectral classes
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
... • Absorption spectra are used to classify stars into nine principal types, called spectral classes. • Hydrogen lines are much stronger in the spectra of some stars than in the Sun’s spectrum. • Astronomers once mistakenly thought that these stars had more hydrogen than other stars. • They classified ...
The Brightness of Stars
... The surface area of a star is another factor in the brightness of a star Two stars of the same temperature will have different magnitudes, depending on their size A red supergiant can emit vastly more light than a red dwarf ...
... The surface area of a star is another factor in the brightness of a star Two stars of the same temperature will have different magnitudes, depending on their size A red supergiant can emit vastly more light than a red dwarf ...
LT 5: I can describe how astronomers determine the composition
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
... All stars have dark-line spectra Because different elements absorb different wavelengths of light, scientists can determine the elements that make up a star by studying its spectrum ...
STARS and GALAXIES
... heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
... heat and light. • Some stars are very old and the size of planets or moons, and some no longer ...
Solar System Project
... citing your sources, and an oral presentation. You are to include the following in your model of the Life Cycle of a Star: a) Life cycle- stages, colors, temperatures (3-D model) b) Technology used to research Stars c) Choose a specific Star to research and include to following in your essay: What t ...
... citing your sources, and an oral presentation. You are to include the following in your model of the Life Cycle of a Star: a) Life cycle- stages, colors, temperatures (3-D model) b) Technology used to research Stars c) Choose a specific Star to research and include to following in your essay: What t ...
Astronomy Learning Objectives and Study Questions for Chapter 12
... 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star bri ...
... 5. At the end of its main-sequence life, H-fusion in a medium mass star like Sol will shift to a shell outside the core and the star will become a _____. A. red dwarf B. red giant C. white dwarf D. blue-white supergiant E. supernova 6. The period during which an RR Lyrae or Cepheid variable star bri ...
It is evident from our observations of impact craters on planets and
... A handout was given that showed the effect of motion on spectra. Much useful information can be determined by studying binary stars. Masses of stars can be determined through such studies using the same equation from Lab # 4—Moons of Jupiter. The Doppler effect is apparent in such orbiting binary sy ...
... A handout was given that showed the effect of motion on spectra. Much useful information can be determined by studying binary stars. Masses of stars can be determined through such studies using the same equation from Lab # 4—Moons of Jupiter. The Doppler effect is apparent in such orbiting binary sy ...
Stars - etpt2020s11
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
... The Sun Located in the center of our solar system is the brightest of all the stars, the sun. The sun is the closest star to the Earth. Due to the spatial arrangement of the Earth and the Sun, it sun is visible to us and responsible for most of the Earth’s energy. ...
Magnitude scale theory
... The magnitudes of stars - theory How bright a star looks is given by its apparent magnitude. This is different from its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude of a star is defined as the apparent magnitude that it would have if placed at a distance of 10 parsecs from the Earth. Consider two star ...
... The magnitudes of stars - theory How bright a star looks is given by its apparent magnitude. This is different from its absolute magnitude. The absolute magnitude of a star is defined as the apparent magnitude that it would have if placed at a distance of 10 parsecs from the Earth. Consider two star ...
A Brief History of Planetary Science
... numerals (e.g. Ca II, calcium with 2 electrons missing) ...
... numerals (e.g. Ca II, calcium with 2 electrons missing) ...
Boötes

Boötes /boʊˈoʊtiːz/ is a constellation in the northern sky, located between 0° and +60° declination, and 13 and 16 hours of right ascension on the celestial sphere. The name comes from the Greek Βοώτης, Boōtēs, meaning herdsman or plowman (literally, ox-driver; from βοῦς bous “cow”). The ""ö"" in the name is a diaeresis, not an umlaut, meaning that each 'o' is to be pronounced separately.One of the 48 constellations described by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, Boötes is now one of the 88 modern constellations. It contains the fourth brightest star in the night sky, the orange-hued Arcturus. Boötes is home to many other bright stars, including eight above the fourth magnitude and an additional 21 above the fifth magnitude, making a total of 29 stars easily visible to the naked eye.