Examination questions Division of Condensed Matter Physics
... 18. Quantum dots, quantum wires, quantum wells: fabrication, electronic states in low dimensional systems. 19. Carbon nanostructures: fullerenes, nanotubes, graphen… 20. Classical and quantum Hall effect. ...
... 18. Quantum dots, quantum wires, quantum wells: fabrication, electronic states in low dimensional systems. 19. Carbon nanostructures: fullerenes, nanotubes, graphen… 20. Classical and quantum Hall effect. ...
Test #3 Review
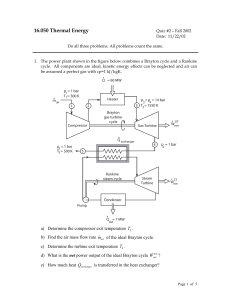
... Open Systems In open systems, matter may flow in and out of the system boundaries. The first law of thermodynamics for open systems states: the increase in the internal energy of a system is equal to the amount of energy added to the system by matter flowing in and by heating, minus the amount lost ...
... Open Systems In open systems, matter may flow in and out of the system boundaries. The first law of thermodynamics for open systems states: the increase in the internal energy of a system is equal to the amount of energy added to the system by matter flowing in and by heating, minus the amount lost ...
Problem 1. An unstable Pu-‐240 nucleus (mass
... 1. The potential energy of the system decreases as the planet moves from r1 to r2. 2. The potential energy of the system increases as the planet moves from r1 to r2. 3. When the separation b ...
... 1. The potential energy of the system decreases as the planet moves from r1 to r2. 2. The potential energy of the system increases as the planet moves from r1 to r2. 3. When the separation b ...
chapter 2 - Extras Springer
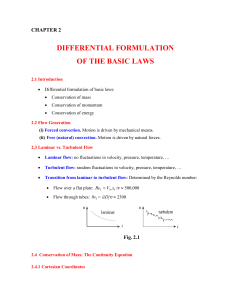
... Unknown variables are: u, v, w, p and T . These variables depend on the four independent variables. In addition various quantities affect the solutions. They ...
... Unknown variables are: u, v, w, p and T . These variables depend on the four independent variables. In addition various quantities affect the solutions. They ...
DES601-Module13
... • velocity head is v2/2g where g = gravitational acceleration. • Total energy (head) = h + p/g + v2/2g ...
... • velocity head is v2/2g where g = gravitational acceleration. • Total energy (head) = h + p/g + v2/2g ...
Physics 334 Modern Physics
... heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape. Secondary emission: The electron gains enough energy by transfer from another high-speed particle that strikes the material from outside. Field emission: A strong external electric field pulls the electron out of the material. Photoelectric effe ...
... heat allows electrons to gain enough energy to escape. Secondary emission: The electron gains enough energy by transfer from another high-speed particle that strikes the material from outside. Field emission: A strong external electric field pulls the electron out of the material. Photoelectric effe ...
Neutron stars and white dwarfs
... small enough that the tidal effects of the gravitational field are small across its volume, the electrons fill up all the available levels to the Fermi energy. ...
... small enough that the tidal effects of the gravitational field are small across its volume, the electrons fill up all the available levels to the Fermi energy. ...
Ch 14, 15, 16
... • An iron spoon and a silver spoon have the same mass. Which becomes hotter when both are left in ...
... • An iron spoon and a silver spoon have the same mass. Which becomes hotter when both are left in ...
CHAPTER 8
... freezing, condensation, sublimation, deposition, phase diagrams, crystalline solids. 2. Quantum mechanics: electromagnetic radiation, quantum mechanics, quantum numbers, shape and energy of orbitals, Pauli Exclusion Principle, multi-electron atoms, Aufbau method, valence bond theory, hybridization, ...
... freezing, condensation, sublimation, deposition, phase diagrams, crystalline solids. 2. Quantum mechanics: electromagnetic radiation, quantum mechanics, quantum numbers, shape and energy of orbitals, Pauli Exclusion Principle, multi-electron atoms, Aufbau method, valence bond theory, hybridization, ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.