1 - Optus
... Discuss the advantages of using superconductors and identify limitations to their use. Below critical temperature, cooper pairs stay together. Because resistance is effectively zero, very narrow wires can carry very large currents. The lower the temperature, the higher that current can be. That curr ...
... Discuss the advantages of using superconductors and identify limitations to their use. Below critical temperature, cooper pairs stay together. Because resistance is effectively zero, very narrow wires can carry very large currents. The lower the temperature, the higher that current can be. That curr ...
Lect1.LawsofThr
... Thermodynamic coordinates (T, P, ) define macroscopic state of equilibrium. Microscopic state is defined by atomic positions, and momenta - many microscopic states are consistent with a macroscopic state Statistical mechanics connects microscopic description and detail with macroscopic state ...
... Thermodynamic coordinates (T, P, ) define macroscopic state of equilibrium. Microscopic state is defined by atomic positions, and momenta - many microscopic states are consistent with a macroscopic state Statistical mechanics connects microscopic description and detail with macroscopic state ...
Energy: Conservation and Interconversion Demonstration:
... and work are processes or interactions between the system and the surroundings. Heat and work depend on the way the process is carried out. They “depend on the path”. Note that positive heat absorbed by the system results in an increase in the internal energy of the system. Similarly, the surroundin ...
... and work are processes or interactions between the system and the surroundings. Heat and work depend on the way the process is carried out. They “depend on the path”. Note that positive heat absorbed by the system results in an increase in the internal energy of the system. Similarly, the surroundin ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... • A: Electrons have lots of their own energy. E=hf due to their position around the nucleus. Electrons are constantly moving, very fast. • This kinetic energy overcomes the positive attraction of the nucleus. ...
... • A: Electrons have lots of their own energy. E=hf due to their position around the nucleus. Electrons are constantly moving, very fast. • This kinetic energy overcomes the positive attraction of the nucleus. ...
Chapter Summary
... Essential Idea: Heat can be used to do work. In this chapter we looked at the connection between heat, work, and the change in internal energy, and we saw how the laws of thermodynamics can be applied to understand the basic operation of practical devices such as engines, refrigerators, and air cond ...
... Essential Idea: Heat can be used to do work. In this chapter we looked at the connection between heat, work, and the change in internal energy, and we saw how the laws of thermodynamics can be applied to understand the basic operation of practical devices such as engines, refrigerators, and air cond ...
Pyroelectric Effect. Primary Pyroelectricity. Secondary Pyroelectricity
... Independent of geometry, manufacture etc. Only a function of materials and temperature. ...
... Independent of geometry, manufacture etc. Only a function of materials and temperature. ...
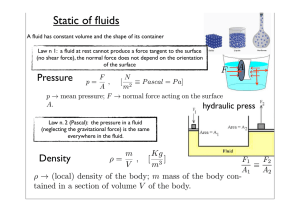
Static of fluids
... Equipartition of energy In the motion of molecules in a gas at a given temperature, to every independent component of the motion (degree of freedom) corresponds the same kinetic energy ...
... Equipartition of energy In the motion of molecules in a gas at a given temperature, to every independent component of the motion (degree of freedom) corresponds the same kinetic energy ...
Atoms, Elements, Compounds, and Periodic Table Directions
... 11. How does the potential energy of an object change as you move farther away from sea level? ________________________________________________ Part VI: Newton’s Laws of Motion and Rate 1. Newton’s laws describe motion and force Define force: ...
... 11. How does the potential energy of an object change as you move farther away from sea level? ________________________________________________ Part VI: Newton’s Laws of Motion and Rate 1. Newton’s laws describe motion and force Define force: ...
Physical Science – Ch. 5 – Energy Study Guide ANSWERS
... GPE = 9.8mh mgh PE = weight x height 5. Describe how energy can be transformed from one form to another. ...
... GPE = 9.8mh mgh PE = weight x height 5. Describe how energy can be transformed from one form to another. ...
Solutions - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... the potential energy of this spring when it compressed by 3.50cm? First we need to find the spring constant k. We use the force formula Fspring=kx 120N = (k)(0.0225m) → k = 5333 N/m Now we can find the potential energy: Uelastic = ½ kx2 Uelastic = ½(5333 N/m)(0.035m)2 Uelastic = 3.27 J 6) A 100kg cr ...
... the potential energy of this spring when it compressed by 3.50cm? First we need to find the spring constant k. We use the force formula Fspring=kx 120N = (k)(0.0225m) → k = 5333 N/m Now we can find the potential energy: Uelastic = ½ kx2 Uelastic = ½(5333 N/m)(0.035m)2 Uelastic = 3.27 J 6) A 100kg cr ...
Atomic Radii Answers File
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
... A.R. increases going down a group. An extra shell is being added in successive elements and the electrons in the outer shell are “shielded” from the nucleus by the inner shells. There is a decreasing attractive pull on them from the nucleus. ...
Photosynthesis Stores Energy in Organic Compounds
... electron-carrying molecules electron transport system (chain) • With each transfer, a small amount of energy is released ...
... electron-carrying molecules electron transport system (chain) • With each transfer, a small amount of energy is released ...
Heat transfer physics

Heat transfer physics describes the kinetics of energy storage, transport, and transformation by principal energy carriers: phonons (lattice vibration waves), electrons, fluid particles, and photons. Heat is energy stored in temperature-dependent motion of particles including electrons, atomic nuclei, individual atoms, and molecules. Heat is transferred to and from matter by the principal energy carriers. The state of energy stored within matter, or transported by the carriers, is described by a combination of classical and quantum statistical mechanics. The energy is also transformed (converted) among various carriers.The heat transfer processes (or kinetics) are governed by the rates at which various related physical phenomena occur, such as (for example) the rate of particle collisions in classical mechanics. These various states and kinetics determine the heat transfer, i.e., the net rate of energy storage or transport. Governing these process from the atomic level (atom or molecule length scale) to macroscale are the laws of thermodynamics, including conservation of energy.