Lecture 7 (Jan 31): BRAIN DEVELOPMENT and EVOLUTION
... specific part of the Optic Tectum Evidence for Chemical Markers (in vitro experiments) TOPDV, high concentration in Dorsal Retina, low in Ventral Retina AND high in Ventral Tectum, low in Dorsal Tectum ….. forms a chemical gradient ...
... specific part of the Optic Tectum Evidence for Chemical Markers (in vitro experiments) TOPDV, high concentration in Dorsal Retina, low in Ventral Retina AND high in Ventral Tectum, low in Dorsal Tectum ….. forms a chemical gradient ...
1244509Health Nervous System 2012
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
... without oxygen. After that cells begin die. The slowest speed at which information travels between neurons is 260 mph!!! ...
Signature Research Areas
... • Global leadership in wind tunnel testing of some of the world’s most recognizable buildings, bridges and structures • Related work in hazard assessment, simulated structural testing and policy development to mitigate the effects of natural disasters Environmental Sustainability and Green Energy ...
... • Global leadership in wind tunnel testing of some of the world’s most recognizable buildings, bridges and structures • Related work in hazard assessment, simulated structural testing and policy development to mitigate the effects of natural disasters Environmental Sustainability and Green Energy ...
Nervous System
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...
... PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Messages about your environment travel through the nervous system called neurons. A neuron is a nerve cell that is specialized to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy. These electrical messages are called impulses. A neuron has a large region i ...
AI: Thinking rationally AI: Acting Rationally What is AI?
... “A field of study that seeks to explain and emulate intelligent behavior in terms of computation processes” Schalkoff, 1990 “The branch of computer science that is concerned with the automation of intelligent behavior” Luger and Stubblefield Rational behavior: doing the right thing q ...
... “A field of study that seeks to explain and emulate intelligent behavior in terms of computation processes” Schalkoff, 1990 “The branch of computer science that is concerned with the automation of intelligent behavior” Luger and Stubblefield Rational behavior: doing the right thing q ...
The Brain** in Brain Computer Interface - CBMSPC
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
... Why study the brain and nervous system ? • It’s the control center ! • There are many things even scientists still don’t know • Search for better understanding of brain function and brain repair • The answer to these problems will rely not only on the current generation of physicians and scientists ...
Brain Structure and Function
... brain contain dopamine. Role in ; - complex movement -cognition - motor control - emotional responses such as euphoria or pleasure. Newer antipsychotic medication focus on particular dopaminergic pathways in the brain. Lessening EPSE’s. ...
... brain contain dopamine. Role in ; - complex movement -cognition - motor control - emotional responses such as euphoria or pleasure. Newer antipsychotic medication focus on particular dopaminergic pathways in the brain. Lessening EPSE’s. ...
AP Psych Mid-Term Review
... organize, and interpret sensory information in order to recognize meaningful objects and events . • perception ...
... organize, and interpret sensory information in order to recognize meaningful objects and events . • perception ...
Elicited Behavior Chapter 2 pp. 32-53 and the internet if you can`t
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
... 3. What do reflexes have to do with elicited behavior? 4. What three neurons are involved in a simple reflex? 5. How can other neurons be involved in the production of a reflex? 6. What are modal action patterns and why are they called modal action patterns? 7. What is a releasing stimulus? 8. How a ...
Nervous System Chapter 14 – 18
... enclose) capillaries so that any substance that can diffuse through the capillary wall must also diffuse through the astrocyte to get the brain. ...
... enclose) capillaries so that any substance that can diffuse through the capillary wall must also diffuse through the astrocyte to get the brain. ...
BIOL 2402 Lecture Outline Chapter 5
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
... each full cycle lasts about 90 minutes, and in each successive cycle the amount of paradoxical/REM sleep increases paradoxical sleep involves low muscle tone, increased cortical activity, and dreaming switching between slow wave/NREM and paradoxical/REM is controlled by paradoxical/REM “sleep-on” ne ...
LAB 5 – CORONAL 1 (Jan 29)
... Column & Body of the Fornix Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The pa ...
... Column & Body of the Fornix Any structure resembling an arch, especially the archlike band of white fibres in the limbic system at the base of the brain, projecting from the hippocampus to the mammillary bodies , involved in memory and the control of eating. Also called the vault. Optic Tract The pa ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
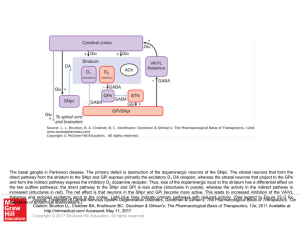
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
... direct pathway from the striatum to the SNpr and GPi express primarily the excitatory D1 DA receptor, whereas the striatal neurons that project to the GPe and form the indirect pathway express the inhibitory D2 dopamine receptor. Thus, loss of the dopaminergic input to the striatum has a differentia ...
Introduction to Psychology
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
Chapter 2 PPT Neuroscience and Behavior
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
... MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) a technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce computer – generated images that distinguish among different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain. ...
Reward system - Basic Knowledge 101
... the same. This is when Berridge came up with the incentive salience hypothesis to explain why the dopamine seems to only sometimes control pleasure when in fact that does not prove to be happening at all. This hypothesis dealt with the wanting aspect of rewards. Scientists can use this study done by ...
... the same. This is when Berridge came up with the incentive salience hypothesis to explain why the dopamine seems to only sometimes control pleasure when in fact that does not prove to be happening at all. This hypothesis dealt with the wanting aspect of rewards. Scientists can use this study done by ...
SM 11.04.12 - Premio principe asturias
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...
... for their significant neurobiological research into so-called «mirror neurons,» nerve cells found in the ventral premotor cortex of the brain which are activated not only when an individual performs a particular action, such as a hand movement, but also when the individual observes the same action b ...