9 Functions of the Middle Prefrontal Cortex
... Attuned Communication is the ability to feel another ones feelings. Feeling felt. Children need attunement to feel secure and to develop well. Through out our life we need attunement to feel close and connected. ...
... Attuned Communication is the ability to feel another ones feelings. Feeling felt. Children need attunement to feel secure and to develop well. Through out our life we need attunement to feel close and connected. ...
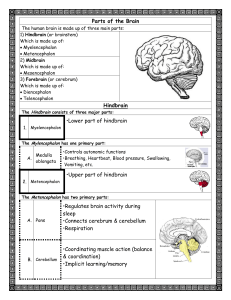
Parts of the Brain Hindbrain •Lower part of hindbrain •Upper part of
... Cerebrum: usually categorized as the lobes, and the interior parts of the forebrain The four lobes and each one’s function are: ...
... Cerebrum: usually categorized as the lobes, and the interior parts of the forebrain The four lobes and each one’s function are: ...
File
... take a little longer time to exert their effects, but they can affect cells and organs distant from the source of the hormone’s production. Some neurotransmitters also function as neurohormones. Examples: Dopamine is released both by the axons and the hypothalamus. Norepinepherine is released both b ...
... take a little longer time to exert their effects, but they can affect cells and organs distant from the source of the hormone’s production. Some neurotransmitters also function as neurohormones. Examples: Dopamine is released both by the axons and the hypothalamus. Norepinepherine is released both b ...
Myers AP - Unit 3B
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
... Figure 3B.14 New technology shows the brain in action This fMRI (functional MRI) scan shows the visual cortex in the occipital lobes activated (color representation of increased bloodflow) as a research participant looks at a photo. When the person stops looking, the region instantly calms down. ...
Chapter Two
... fMRI imaging takes a series of images of the brain in quick succession and then statistically analyzes the images for differences among them Brain areas with more blood flow have been shown to have better visibility on fMRI images BOLD Better visibility is correlated with brain activation ...
... fMRI imaging takes a series of images of the brain in quick succession and then statistically analyzes the images for differences among them Brain areas with more blood flow have been shown to have better visibility on fMRI images BOLD Better visibility is correlated with brain activation ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
... • A synaptic potential can be excitatory (they depolarize) or inhibitory (they polarize). Some neurotransmitters depolarize and others polarize. • There are more than 50 different neurotransmitters. • In the brain and spinal cord, hundreds of excitatory potentials may be needed before a postsynaptic ...
Axia College Material Appendix B Structures of the Nervous System
... This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this document to write a description for t ...
... This activity will increase your understanding of the different structures of the nervous system and brain. During the Web activity, you will view a variety of structures of the brain and nervous system and label each with the appropriate term. You will use this document to write a description for t ...
The SIX Grand Theories of Psychology (Psyc 20)
... -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of their current way of thinking) 2. Accommodation refers to changes in existing ways of thinking in response to encounter with new stimuli or ...
... -Human thinking is arranged into schemes or organized mental patterns 2 big Ideas: 1. Assimilation (process by which people understand or experience in terms of their current way of thinking) 2. Accommodation refers to changes in existing ways of thinking in response to encounter with new stimuli or ...
Behavior The way an organism responds to stimuli in its
... Behavioral Rhythms - periodic cycles of behavior Circadian - behaviors repeated with about a 24 hour cycle Circannual - behaviors repeated on an annual cycle Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior m ...
... Behavioral Rhythms - periodic cycles of behavior Circadian - behaviors repeated with about a 24 hour cycle Circannual - behaviors repeated on an annual cycle Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior m ...
Behavior The way an organism responds to stimuli in its
... Behavioral Rhythms - periodic cycles of behavior Circadian - behaviors repeated with about a 24 hour cycle Circannual - behaviors repeated on an annual cycle Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior ...
... Behavioral Rhythms - periodic cycles of behavior Circadian - behaviors repeated with about a 24 hour cycle Circannual - behaviors repeated on an annual cycle Other behaviors keyed to tidal, lunar, and other external cycles Biological Clock - an internal time-keeper that governs cycling of behavior ...
Dr. Doug Leonard PowerPoint Presentation regarding the Teenage
... understood, organ. Hundreds of billions of cells bathe one another in chemical messengers that influence moment to moment changes in brain function, behavior, and experience. • Some chemical messengers can also trigger changes in gene expression in other cells, leading to long-term changes in how th ...
... understood, organ. Hundreds of billions of cells bathe one another in chemical messengers that influence moment to moment changes in brain function, behavior, and experience. • Some chemical messengers can also trigger changes in gene expression in other cells, leading to long-term changes in how th ...
Social Brains: EEG Hyperconnectivity between operetor pairs whilst actively performing demanding interdependent goal-oriented tasks
... Functional neuroimaging has been a major tool for cognitive neuroscience, experimental psychology, and psychiatry. Noninvasive high-resolution imaging would provide tremendous benefits to better understanding of the brain mechanisms behind mental processes, such as perception, attention, learning, e ...
... Functional neuroimaging has been a major tool for cognitive neuroscience, experimental psychology, and psychiatry. Noninvasive high-resolution imaging would provide tremendous benefits to better understanding of the brain mechanisms behind mental processes, such as perception, attention, learning, e ...
ANIMAL BEHAVIORS
... – Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward, and avoid those that end in punishment – “trial-and-error” learning – This learning begins with “random behavior” – Many animals use this type of learning to identify sources of food ...
... – Animal learns to repeat behaviors that result in reward, and avoid those that end in punishment – “trial-and-error” learning – This learning begins with “random behavior” – Many animals use this type of learning to identify sources of food ...
Abnormal Psych (Ch 2..
... The diagram here shows the structure of the neuron and the mode of transmission of neural impulses between neurons. Neurons transmit messages, or neural impulses, across synapses, which consist of the axon terminal of the transmitting neuron, the gap or synapse between the neurons, and the dendrite ...
... The diagram here shows the structure of the neuron and the mode of transmission of neural impulses between neurons. Neurons transmit messages, or neural impulses, across synapses, which consist of the axon terminal of the transmitting neuron, the gap or synapse between the neurons, and the dendrite ...
The Impact of Ecstasy on the Brain
... Paranoia and hallucinations Irrational behavior (even violence) Convulsions, heart attack, or death ...
... Paranoia and hallucinations Irrational behavior (even violence) Convulsions, heart attack, or death ...
answers - UCSD Cognitive Science
... Define the following: 1. Ipsilateral: refers to structures on the same side of the body 2. Contralateral: refers to structures on opposite sides of the body 3. Lateral: toward the side 4. Medial: toward the midline Hemispheric Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the function ...
... Define the following: 1. Ipsilateral: refers to structures on the same side of the body 2. Contralateral: refers to structures on opposite sides of the body 3. Lateral: toward the side 4. Medial: toward the midline Hemispheric Specialization (in general, what are the differences between the function ...
Breakdown of the Nervous System
... c) association areas i) prefrontal cortex (a) found in anterior portions of frontal lobe (b) involved with intellect, complex learning, and personality ii) gnostic area (a) found in undefined areas of parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (b) only one per hemisphere (c) receives input from all se ...
... c) association areas i) prefrontal cortex (a) found in anterior portions of frontal lobe (b) involved with intellect, complex learning, and personality ii) gnostic area (a) found in undefined areas of parietal, temporal, and occipital lobes (b) only one per hemisphere (c) receives input from all se ...
Central Nervous System
... b) association fibers – transmit within a hemisphere c) projection fibers – run to and from lower brain areas F) basal nuclei 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine ...
... b) association fibers – transmit within a hemisphere c) projection fibers – run to and from lower brain areas F) basal nuclei 1) bundles of subcortical gray matter deep within white matter 2) control large automatic skeletal muscle contractions and produce dopamine ...
Ch. 11: Machine Learning: Connectionist
... How do neurons change • There are changes to neurons that are presumed to reflect or enable learning: The synaptic connections exhibit plasticity. In other words, the degree to which a neuron will react to a stimulus across a particular synapse is subject to longterm change over time (long-term p ...
... How do neurons change • There are changes to neurons that are presumed to reflect or enable learning: The synaptic connections exhibit plasticity. In other words, the degree to which a neuron will react to a stimulus across a particular synapse is subject to longterm change over time (long-term p ...
Contemporary Perspectives on Abnormal Behavior
... ►Developed due to: ►A. Not reinforced for adaptive behaviors ►B. Punished for behaviors that later would be considered adaptive ►C. Were reinforced for maladaptive behaviors ►D. Were reinforced under inappropriate circumstances for what would otherwise be ...
... ►Developed due to: ►A. Not reinforced for adaptive behaviors ►B. Punished for behaviors that later would be considered adaptive ►C. Were reinforced for maladaptive behaviors ►D. Were reinforced under inappropriate circumstances for what would otherwise be ...
Parts of a Neuron
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate ...
... Adrenal glands consist of the adrenal medulla and the cortex. The medulla secretes hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) during stressful and emotional situations, while the adrenal cortex regulates salt and carbohydrate ...