166 - UCSF Physiology - University of California, San Francisco
... in long-term potentiation (LTP). Deletion of 1 integrin at a later postnatal stage also impaired LTP but not synaptic responses to HFS. Thus, the 1-class integrins appear to play distinct roles at different stages of synaptic development, critical for the proper maturation of readily releasable po ...
... in long-term potentiation (LTP). Deletion of 1 integrin at a later postnatal stage also impaired LTP but not synaptic responses to HFS. Thus, the 1-class integrins appear to play distinct roles at different stages of synaptic development, critical for the proper maturation of readily releasable po ...
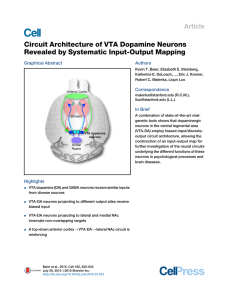
Circuit Architecture of VTA Dopamine Neurons Revealed by
... neurons, we used DAT-Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression pattern of the plasma membrane dopamine transporter (Bäckman et al., 2006; Lammel et al., 2015), and GAD2Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase-2 (Taniguchi et al., 2011), an enzyme that coverts g ...
... neurons, we used DAT-Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression pattern of the plasma membrane dopamine transporter (Bäckman et al., 2006; Lammel et al., 2015), and GAD2Cre mice, in which Cre mimics the expression of glutamic acid decarboxylase-2 (Taniguchi et al., 2011), an enzyme that coverts g ...
- AVMA Journals Online
... particular, the ruminant brainstem manifests the prion disease bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Recently, Miyashita et al25 showed, by means of immunohistochemistry, a reduction of synaptophysin staining in the RN of cattle with bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Our preliminary results have shown t ...
... particular, the ruminant brainstem manifests the prion disease bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Recently, Miyashita et al25 showed, by means of immunohistochemistry, a reduction of synaptophysin staining in the RN of cattle with bovine spongiform encephalopathy. Our preliminary results have shown t ...
Brief neonatal maternal separation alters extinction of conditioned
... with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Bloomington Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. ...
... with the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Bloomington Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. ...
completion
... The _________________ controls such basic drives as sexual activity. a. hypothalamus b. medial forebrain bundle c. blood-brain barrier d. amygdala ANS: A ...
... The _________________ controls such basic drives as sexual activity. a. hypothalamus b. medial forebrain bundle c. blood-brain barrier d. amygdala ANS: A ...
Maruska & Tricas 2011
... 2009). In fishes and other vertebrates, the terminal nerve GnRH system also modulates processing of visual and olfactory information at the periphery (i.e., retina and olfactory epithelium) (Eisthen et al., 2000; Kawai et al., 2009; Park and Eisthen, 2003; Stell et al., 1987; Zhang and Delay, 2007). ...
... 2009). In fishes and other vertebrates, the terminal nerve GnRH system also modulates processing of visual and olfactory information at the periphery (i.e., retina and olfactory epithelium) (Eisthen et al., 2000; Kawai et al., 2009; Park and Eisthen, 2003; Stell et al., 1987; Zhang and Delay, 2007). ...
reciprocal inhibition in the motor nervous system of the nematode
... The VI neurons also have commissures; however, their output regions lie in the ventral cord where they synapse onto the ventral musculature; VI dendrites are in the dorsal cord where they receive anatomically defined synaptic input from all three types of DE neurons (J. E. Donmoyer, P. A. Desnoyers, ...
... The VI neurons also have commissures; however, their output regions lie in the ventral cord where they synapse onto the ventral musculature; VI dendrites are in the dorsal cord where they receive anatomically defined synaptic input from all three types of DE neurons (J. E. Donmoyer, P. A. Desnoyers, ...
Identification of the Amino Terminus of Neuronal Ca2
... saline (as above plus 1.8 mM C aC l2 ) supplemented with 100 mg /ml penicillin, 100 I U/ml streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), and 2.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Whole-cell recordings from oocytes were made in the two-electrode voltage-clamp configuration with a chloride-free solution conta ...
... saline (as above plus 1.8 mM C aC l2 ) supplemented with 100 mg /ml penicillin, 100 I U/ml streptomycin (Life Technologies, Gaithersburg, MD), and 2.5 mM sodium pyruvate. Whole-cell recordings from oocytes were made in the two-electrode voltage-clamp configuration with a chloride-free solution conta ...
hanPNAS11
... potential relevance to TBR1 transcriptional activity in the neocortex, we cross-analyzed our mRNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq data. We selected the loci of significantly differentially expressed genes based on mRNA-Seq data to which a significant enrichment of TBR1 ChIP-Seq reads mapped proximally. Analysis of t ...
... potential relevance to TBR1 transcriptional activity in the neocortex, we cross-analyzed our mRNA-Seq and ChIP-Seq data. We selected the loci of significantly differentially expressed genes based on mRNA-Seq data to which a significant enrichment of TBR1 ChIP-Seq reads mapped proximally. Analysis of t ...
stereological estimates of dopaminergic, gabaergic and
... Total estimates of the number of GABAergic and dopaminergic neurons were obtained from four brains processed for GAD in situ hybridization and TH immunohistochemistry. Estimates of glutamatergic neurons were obtained from a further four brains processed for VGluT2 in situ hybridization and TH immuno ...
... Total estimates of the number of GABAergic and dopaminergic neurons were obtained from four brains processed for GAD in situ hybridization and TH immunohistochemistry. Estimates of glutamatergic neurons were obtained from a further four brains processed for VGluT2 in situ hybridization and TH immuno ...
Joseph and Heberlein 1 Tissue-specific Activation of a
... between repulsive positional and attractive egg-laying responses towards the bittertasting compound lobeline. Surprisingly, we found that neurons expressing Gr66a, a gustatory receptor normally involved in avoidance behaviors, receive input for both attractive and aversive preferences. We hypothesiz ...
... between repulsive positional and attractive egg-laying responses towards the bittertasting compound lobeline. Surprisingly, we found that neurons expressing Gr66a, a gustatory receptor normally involved in avoidance behaviors, receive input for both attractive and aversive preferences. We hypothesiz ...
Noradrenergic Suppression of Synaptic Transmission May Influence Cortical Signal-to-Noise Ratio
... 4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)] and slow time courses [Nmethyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)]. Each feed-forward interneuron connects to 10 pyramidal cells. These synapses elicit synaptic potentials with both fast (20%) and slow (80%) time courses representing GABAA and GABAB receptors. Both time courses hav ...
... 4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA)] and slow time courses [Nmethyl-D-aspartate (NMDA)]. Each feed-forward interneuron connects to 10 pyramidal cells. These synapses elicit synaptic potentials with both fast (20%) and slow (80%) time courses representing GABAA and GABAB receptors. Both time courses hav ...
Experimental heart failure causes depression
... 2001) and in humans (Almeida et al., 2012). However, the mechanisms and potential systemic consequences, as well as structural or molecular changes in the brain due to CHF are unknown. Moreover, no studies in mice were conducted so far and studies in mice would allow a more feasible genetic manipula ...
... 2001) and in humans (Almeida et al., 2012). However, the mechanisms and potential systemic consequences, as well as structural or molecular changes in the brain due to CHF are unknown. Moreover, no studies in mice were conducted so far and studies in mice would allow a more feasible genetic manipula ...
Spontaneous firing patterns of identified spiny neurons in the rat
... or never exhibit antidromic responses to stimulation of substantia nigra21. Pure excitatory orthodromic responses are, on the other hand, more commonly reported for otherwise silent neurons, and these may also respond antidromically, to nigral stimulation21,27. Findings of this type have led some in ...
... or never exhibit antidromic responses to stimulation of substantia nigra21. Pure excitatory orthodromic responses are, on the other hand, more commonly reported for otherwise silent neurons, and these may also respond antidromically, to nigral stimulation21,27. Findings of this type have led some in ...
Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Mediates Activity
... Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes postnatal maturation of GABAergic inhibition in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices, and its expression and release are enhanced by neuronal activity, suggesting that it acts in a feedback manner to maintain a balance between excitation and inhibiti ...
... Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) promotes postnatal maturation of GABAergic inhibition in the cerebral and cerebellar cortices, and its expression and release are enhanced by neuronal activity, suggesting that it acts in a feedback manner to maintain a balance between excitation and inhibiti ...
Heterogeneity of the Population of Command Neurons in the Lamprey
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
... The influences could be seen in the ventral root branches both ipsilateral and contralateral to an RS neuron. The amplitude of the response, that is, a deviation of the summated M N activity from the level observed before the arrival of the RS spike, and the response duration varied considerably. Fo ...
Virtual Fly Brain – under the hood.
... the partonomy is complicated – parts of neurons are part of various structures. Where are the synapses, what is their direction ? What is the lineage of the neurons? What neurotransmitters do they release ? What functions are they implicated in ? ...
... the partonomy is complicated – parts of neurons are part of various structures. Where are the synapses, what is their direction ? What is the lineage of the neurons? What neurotransmitters do they release ? What functions are they implicated in ? ...
Lemniscal recurrent and transcortical influences on
... applied to the ML should induce a double discharge in the DCN, the first being produced through recurrent collaterals of activated lemniscal axons and the second by the activation of the thalamo-corticoDCN loop. This would imply that the corticofugal discharges excite lemniscal neurons,1., 15., 24., ...
... applied to the ML should induce a double discharge in the DCN, the first being produced through recurrent collaterals of activated lemniscal axons and the second by the activation of the thalamo-corticoDCN loop. This would imply that the corticofugal discharges excite lemniscal neurons,1., 15., 24., ...
leptin
... regulation or resistance to the action of leptin. Reduced leptin production or fewer receptors may also account for those who are overweight but not obese (5). Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in which glucose is under-utilized, producing hyperglycaemia. It i ...
... regulation or resistance to the action of leptin. Reduced leptin production or fewer receptors may also account for those who are overweight but not obese (5). Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of disorders of carbohydrate metabolism in which glucose is under-utilized, producing hyperglycaemia. It i ...
Glycemic State Regulates Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor
... system (CNS) (43; 115) and particular peripheral tissues including muscles (128), adipose (197), and liver (38). As a result, both proteins are widely distributed throughout the nervous system(43; 217) while, at the cellular level, BDNF and its receptors, TrkB and p75, can be located in both the axo ...
... system (CNS) (43; 115) and particular peripheral tissues including muscles (128), adipose (197), and liver (38). As a result, both proteins are widely distributed throughout the nervous system(43; 217) while, at the cellular level, BDNF and its receptors, TrkB and p75, can be located in both the axo ...
Synapse
... Cocaethylene is a neuroactive metabolite derived from the concurrent consumption of cocaine and ethanol. The effects of cocaethylene on locomotor activity, stereotypy, and rearing in Long-Evans and Sprague-Dawley rats were compared. A single cocaine injection (molar equivalent of 60 µmol/kg cocaethy ...
... Cocaethylene is a neuroactive metabolite derived from the concurrent consumption of cocaine and ethanol. The effects of cocaethylene on locomotor activity, stereotypy, and rearing in Long-Evans and Sprague-Dawley rats were compared. A single cocaine injection (molar equivalent of 60 µmol/kg cocaethy ...
The Emerging Roles of Oxytocin in Rhythmic Prolactin Release
... return when the OT antagonist leaves the system. That is, OT at the lactotroph is required for the expression of the rhythm, but not for triggering the rhythm. Time (days) As predicted, the prolactin rhythm comes back once the antagonist clears the system (day 2 – no rhythm; day 3 – rhythm present) ...
... return when the OT antagonist leaves the system. That is, OT at the lactotroph is required for the expression of the rhythm, but not for triggering the rhythm. Time (days) As predicted, the prolactin rhythm comes back once the antagonist clears the system (day 2 – no rhythm; day 3 – rhythm present) ...
Hepatotoxicity Induced by Arsenic Trioxide in Adult Mice and Their
... solution and centrifuged at 2500 g for 10 min. One milliliter of a solution containing 0.67 % thiobarbituric acid (TBA) and 0.5 ml of supernatant were incubated for 15 min at 90◦C and cooled. Absorbance of TBA-MDA complex was determined at 532 nm using a spectrophotometer. Lipid peroxidation was exp ...
... solution and centrifuged at 2500 g for 10 min. One milliliter of a solution containing 0.67 % thiobarbituric acid (TBA) and 0.5 ml of supernatant were incubated for 15 min at 90◦C and cooled. Absorbance of TBA-MDA complex was determined at 532 nm using a spectrophotometer. Lipid peroxidation was exp ...
Regulation of Elovl and fatty acid metabolism
... long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), a process that is initiated by the rate-limiting condensation reaction. To date, six mammalian enzymes responsible for this reaction, ELOVL1-6 (Elongation of very long chain fatty acid), have been characterized. All of them exert substrate specificity and tissue-speci ...
... long chain fatty acids (VLCFA), a process that is initiated by the rate-limiting condensation reaction. To date, six mammalian enzymes responsible for this reaction, ELOVL1-6 (Elongation of very long chain fatty acid), have been characterized. All of them exert substrate specificity and tissue-speci ...