1to7
... It didn’t explain such things as why elements give off light of specific colors when heated: Example: fireworks, iron ...
... It didn’t explain such things as why elements give off light of specific colors when heated: Example: fireworks, iron ...
1-7-
... It didn’t explain such things as why elements give off light of specific colors when heated: Example: fireworks, iron ...
... It didn’t explain such things as why elements give off light of specific colors when heated: Example: fireworks, iron ...
Chem 400 Chem 150 REVIEW SHEET Amanda R
... Draw a Lewis structure for any molecule and find bond order ...
... Draw a Lewis structure for any molecule and find bond order ...
Chem 121 QU 78 Due in lecture
... 5. Solve the following problems from the text pages 353-357: →_________________________________________________________________ 10 What is Coulomb’s law↑? →_________________________________________________________________ 18 What are valence electrons?↑ →_____________________________________________ ...
... 5. Solve the following problems from the text pages 353-357: →_________________________________________________________________ 10 What is Coulomb’s law↑? →_________________________________________________________________ 18 What are valence electrons?↑ →_____________________________________________ ...
Notes-15 - KSU Physics
... where the first integral is the classical expression for the interaction energy between two electron clouds represented by the modulus square of each wavefunction. The second term has no classical analog-- it is the exchange interaction. The latter is a consequence of quantum effect, due to that the ...
... where the first integral is the classical expression for the interaction energy between two electron clouds represented by the modulus square of each wavefunction. The second term has no classical analog-- it is the exchange interaction. The latter is a consequence of quantum effect, due to that the ...
Chem 101A Exam 4 Concepts Chapter 7 – Modern Atomic Theory
... Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum Numbers (n,l,ml,ms), when they are allowed, how they describ ...
... Use formulas that relate energy of photon, frequency, wavelength, speed of light, and the Rydberg Equation Notable scientists and their contributions: Rutherford, Bohr, Planc, de Broglie, Heisenberg, Schrödinger. The four Quantum Numbers (n,l,ml,ms), when they are allowed, how they describ ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... of the orbital depends only on principle quantum number For atoms with more than 2 electrons, the energy depends on l & n ...
... of the orbital depends only on principle quantum number For atoms with more than 2 electrons, the energy depends on l & n ...
This `practice exam`
... a) no two electrons in an atom can have the same spin. b) electrons can have either ±½ spins. c) electrons with opposing spins are attracted to each other. d) no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers. e) atoms with no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic. 35. Which element ha ...
... a) no two electrons in an atom can have the same spin. b) electrons can have either ±½ spins. c) electrons with opposing spins are attracted to each other. d) no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers. e) atoms with no unpaired electrons are diamagnetic. 35. Which element ha ...
Quiz 8
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
... 3. (15 points) For each of the four quantum numbers: (1) give the name of the quantum number, (2) give the abbreviation of the quantum number, (3) give a short explanation of the physical attributes of the quantum number (energy, shape , etc.), and (4) tell the range in values for this quantum numb ...
The Modern Nuclear Atom
... • Proposed a Hydrogen-atom model in 1913 • Electrons circle the nucleus in a specific orbit ...
... • Proposed a Hydrogen-atom model in 1913 • Electrons circle the nucleus in a specific orbit ...
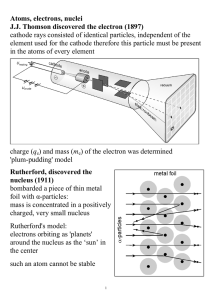
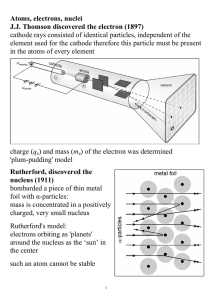
Atoms, electrons, nuclei J.J. Thomson discovered the electron (1897
... where λ is the wavelength of the matter wave corresponding to the electron, and h is the Planck constant. Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a gen ...
... where λ is the wavelength of the matter wave corresponding to the electron, and h is the Planck constant. Davisson and Germer (1927) used electron beams to induce diffraction through a thin metal foil: interference interference phenomena have been shown with various other particles: duality is a gen ...
Chapter 5 Electrons In Atoms 5.1 Models of the Atom The
... moving around the nucleus is similar to the motion of a rotating propeller blade. Atomic Orbitals An _______________________ orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. The energy levels of _____________________________ in the quantum ...
... moving around the nucleus is similar to the motion of a rotating propeller blade. Atomic Orbitals An _______________________ orbital is often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron. The energy levels of _____________________________ in the quantum ...
Exam #2
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
... (a) Electron affinities decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (b) Ionization energies decrease going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (c) Chemical reactivity decreases going down the group (from smaller to larger elements). (d) The second ionization energy ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.