Chapter 4 Test Question Topics
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
... 1- Know the definitions of the ground state and the excited states of an atom. 2- What must occur for an atom to move from the ground to the excited state or from the excited to the ground state? 3- Know the definitions of an electron cloud and an atomic nucleus. 4- What determines the size and shap ...
Trends in the periodic table - Brigham Young University
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
... • Shielding effect of core electrons (S) • Nuclear effective charge, Zeff • Zeff = Z – S – What is Z? What is S? ...
Atomic Radius and Ionization Energy
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
... • The pattern of properties within a period repeats as you move across a period from left to right… When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, there is a periodic repetition of their physical and chemical properties ...
Chemistry I Unit Review: The Atom Text Chapters 2 and 7 1. The
... Determine the number of valence electrons and draw the dot diagram for the following atoms: ...
... Determine the number of valence electrons and draw the dot diagram for the following atoms: ...
Chem 1st Sem Rev Ch2
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
... c. father of the modern atomic theory, everything made of atoms d. planetary model of the atom, electrons move around the nucleus like planets around sun. e. plum pudding model of the atom: atom looks like chocolate chip cookie f. gold foil experiment – atoms have a dense core called nucleus g. he g ...
Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry Name Period ___ Date ___/___/___
... Write the equation for the first ionization energy of Be. What is the phase of Be? ____ (g)/(l)/(s) ...
... Write the equation for the first ionization energy of Be. What is the phase of Be? ____ (g)/(l)/(s) ...
Science Olympiad
... ______ 5. In the lanthanide elements, which orbitals are only partially filled? (A) 5s and 4d (B) 5d and 4f (C) 6s and 5d (D) 6p and 5f (E) 4f only ______ 6. Ions with the electronic structure 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 would not be present in which aqueous solution? (A) NaF(aq) (B) NaCl(aq) (C) KBr(aq) ( ...
... ______ 5. In the lanthanide elements, which orbitals are only partially filled? (A) 5s and 4d (B) 5d and 4f (C) 6s and 5d (D) 6p and 5f (E) 4f only ______ 6. Ions with the electronic structure 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 would not be present in which aqueous solution? (A) NaF(aq) (B) NaCl(aq) (C) KBr(aq) ( ...
Unit 2 Intro Worksheet - Coral Gables Senior High
... ____ 7. discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy ____ 8. energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another ____ 9. number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time ____ 10. distance between wave crests ____ 11. separation of light into different wavelengths ____ 12. frequenci ...
... ____ 7. discrete bundle of electromagnetic energy ____ 8. energy needed to move an electron from one energy level to another ____ 9. number of wave cycles passing a point per unit of time ____ 10. distance between wave crests ____ 11. separation of light into different wavelengths ____ 12. frequenci ...
Chem 1151
... The electron configuration [Kr] describes the electron configuration for all of the following except A. **B. C. D. ...
... The electron configuration [Kr] describes the electron configuration for all of the following except A. **B. C. D. ...
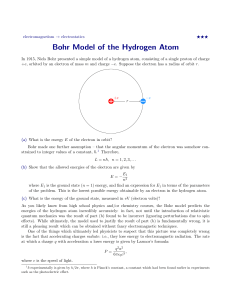
Modern Physics
... Calculate the location at which the radial probability density is a maximum for the 2-s state of the hydrogen atom. Then calculate the expectation value of the radial coordinate in this state. Which answer if either is consistent with the Bohr model ...
... Calculate the location at which the radial probability density is a maximum for the 2-s state of the hydrogen atom. Then calculate the expectation value of the radial coordinate in this state. Which answer if either is consistent with the Bohr model ...
Unit 2: Atoms and their Electrons
... energy level first and then up, Pauli Exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have all four quantum numbers the same, Hund’s rule states that electrons do not pair up to fill an orbital in a sublevel until all orbitals in the same sublevel are half filled. 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 ...
... energy level first and then up, Pauli Exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have all four quantum numbers the same, Hund’s rule states that electrons do not pair up to fill an orbital in a sublevel until all orbitals in the same sublevel are half filled. 1s22s22p63s23p64s2 ...
Electron spin and the periodic table
... mystery until 1926. We can now see that successively heavier elements are obtained by adding one positive charge to the nucleus and one electron to neutralize it. With the Pauli exclusion principle and the enumeration of the states using the quantum numbers n,l,m, and Sz, we can easily understand th ...
... mystery until 1926. We can now see that successively heavier elements are obtained by adding one positive charge to the nucleus and one electron to neutralize it. With the Pauli exclusion principle and the enumeration of the states using the quantum numbers n,l,m, and Sz, we can easily understand th ...
AP Chemistry Study Guide – Chapter 7, Atomic Structure
... 6) Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference betwe ...
... 6) Account for each of the following in terms of principles of atomic structure, including the number, properties, and arrangements of subatomic particles. (a) The second ionization energy of sodium is about three times greater than the second ionization energy of magnesium. (b) The difference betwe ...
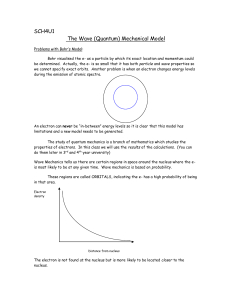
3.4oquantum.4u
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
... Problems with Bohr’s Model: Bohr visualised the e- as a particle by which its exact location and momentum could be determined. Actually, the e- is so small that it has both particle and wave properties so we cannot specify exact orbits. Another problem is when an electron changes energy levels durin ...
Atomic Structure Practice Answers
... 28. Which of the following does not have the same level of shielding as the others? A. Na B. F C. O D. N E. C 29. Which orbital type shields higher energy orbitals the most? A. s B. p C. d D. f E. All are the same 30. Which type of orbital has the greatest penetration? A. s B. p C. d D. f E. All are ...
... 28. Which of the following does not have the same level of shielding as the others? A. Na B. F C. O D. N E. C 29. Which orbital type shields higher energy orbitals the most? A. s B. p C. d D. f E. All are the same 30. Which type of orbital has the greatest penetration? A. s B. p C. d D. f E. All are ...
Ionization

Ionization is the process by which an atom or a molecule acquires a negative or positive charge by gaining or losing electrons to form ions, often in conjunction with other chemical changes. Ionization can result from the loss of an electron after collisions with sub atomic particles, collisions with other atoms, molecules and ions, or through the interaction with light. Heterolytic bond cleavage and heterolytic substitution reactions can result in the formation of ion pairs. Ionization can occur through radioactive decay by the internal conversion process, in which an excited nucleus transfers its energy to one of the inner-shell electrons causing it to be ejected.